- Table of Contents
-
- 27-WLAN Configuration Guide (AC)
- 00-Preface
- 01-Compatibility of hardware and AC functionality
- 02-AP management configuration
- 03-Radio management configuration
- 04-WLAN access configuration
- 05-WLAN security configuration
- 06-WIPS configuration
- 07-WLAN QoS configuration
- 08-WLAN roaming configuration
- 09-WLAN load balancing configuration
- 10-WLAN radio resource measurement configuration
- 11-Channel scanning configuration
- 12-Band navigation configuration
- 13-WLAN high availability configuration
- 14-Wireless location configuration
- 15-WLAN multicast optimization configuration
- 16-User isolation configuration
- 17-WLAN probe configuration
- 18-Spectrum management configuration
- 19-WLAN optimization configuration
- 20-WLAN RRM configuration
- 21-WLAN IP snooping configuration
- 22-WLAN radio load balancing configuration
- 23-Client roaming center configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 23-Client roaming center configuration | 156.76 KB |
Contents
Configuring the client roaming center
About the client roaming center
Client roaming center tasks at a glance
Enabling the client roaming center
Specifying an IP address and port number of the WLAN roaming center
Setting the response timeout timer for packets to the WLAN roaming center
Setting the maximum number of transmission attempts for packets to the WLAN roaming center
Setting the aging timer for address security entries
Enabling WLAN address security
Client roaming center configuration examples
Example: Configuring the client roaming center
Configuring the client roaming center
About the client roaming center
In a roaming center network, client roaming centers work with the WLAN roaming center to perform client address security check, preventing MAC or IP address spoofing attackers from coming online. This enhances WLAN security.
Network structure
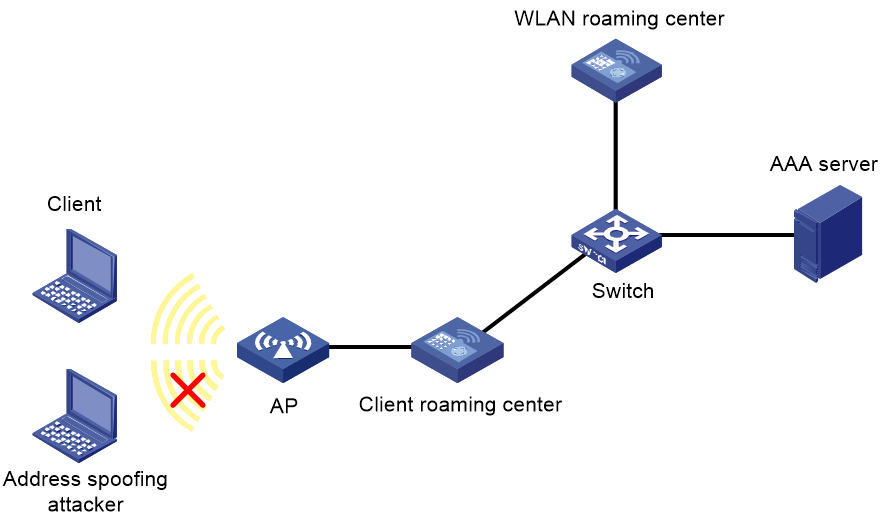
As shown in Figure 1, address security requires the following devices:
· Client roaming center—An AC that identifies and collects user information, and verifies the validity of client MAC addresses and IP addresses.
· WLAN roaming center—An AC that maintains MAC address entries and IP address entries for clients based on information reported by client roaming centers for address conflict query.
For more information about the WLAN roaming center, see "Configuring the WLAN roaming center."
Operating mechanism
With address security configured, a client roaming center examines the local MAC and IP address entries for matches every time a client attempts to come online or the IP address of a client changes.
· If no match is found, the client roaming center sends a conflict query request to the WLAN roaming center. Then, the WLAN roaming center examines its MAC and IP address entries for conflicts.
¡ If no conflict is detected, the WLAN roaming center notifies the client roaming center of the address check result, and generates a MAC address entry and an IP address entry for the client. Then, the system starts accounting on the client.
¡ If any address conflict is detected, the WLAN roaming center checks the spoofing attack blacklist, and notifies the client roaming center to updates its local blacklist.
- If the address spoofing attacker, the spoofed client, or both exist in the blacklist, the WLAN roaming center does not update its blacklist.
- If neither the address spoofing attacker nor the spoofed client exists in the blacklist, the WLAN roaming center adds both the attacker and spoofed client to the blacklist.
Clients in the blacklist are not allowed to come online.
· If an IP address match is found, the client roaming center compares the username of the new client and the username of the online client.
¡ If the usernames are the same, the client roaming center logs off the online client. Then, it updates its local MAC and IP address entries, notifies the WLAN roaming center to update the address entry, and add the old client to the blacklist.
¡ If the usernames are different, the client roaming center logs off the online client, adds both clients to the blacklist, and forbids both clients to come online within the entry aging period.
· If a MAC address match is found, the client roaming center requests the WLAN roaming center to check the manually configured spoofing attack blacklist, and logs off the client in the blacklist. Then, the client roaming center adds the client to the local blacklist and forbids the client to come online within the entry aging period.
Client roaming center tasks at a glance
To configure a client roaming center, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling the client roaming center
2. Specifying an IP address and port number of the WLAN roaming center
3. (Optional.) Setting the response timeout timer for packets to the WLAN roaming center
4. (Optional.) Setting the maximum number of transmission attempts for packets to the WLAN roaming center
5. (Optional.) Setting the aging timer for address security entries
6. Enabling WLAN address security
Enabling the client roaming center
About this task
This feature enables the AC to act as a client roaming center to synchronize information about associated clients to the WLAN roaming center. This allows the WLAN roaming center to monitor client MAC address and IP address spoofing globally.
Restrictions and guidelines
For the client roaming center to take effect, you must also configure address security. For more information about address security, see "Configuring the WLAN roaming center."
With address security configured, disabling the client roaming center disables new clients from coming online even if the clients pass 802.1X authentication. Online clients are not affected.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a client roaming center and enter its view.
client roaming-center
3. Enable the client roaming center.
roaming-center enable
By default, the client roaming center is disabled.
Specifying an IP address and port number of the WLAN roaming center
About this task
Perform this task to specify an IP address and UDP port number of the WLAN roaming center for the client roaming center to communicate with the WLAN roaming center.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can specify only one IP address of the WLAN roaming center for a client roaming center. The address can be any IP address used by the WLAN roaming center. If you perform this task multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
As a best practice to ensure data consistency, do not change the specified IP address or port number of the WLAN roaming center when online clients are present.
Make sure the specified UDP port number is the same as the UDP port number configured in WLAN roaming center view.
As a best practice to avoid data residuals, disable the WLAN roaming center before you change the UDP port number.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter client roaming center view.
client roaming-center
3. Specify an IP address of the WLAN roaming center.
wlan-roaming-center ip ip-address
By default, the IP address of the WLAN roaming center is not specified.
4. Specify the UDP port number of the WLAN roaming center.
wlan-roaming-center port port-number
By default, the UDP port number of the WLAN roaming center is 1088.
Setting the response timeout timer for packets to the WLAN roaming center
About this task
The client roaming center sends client data synchronization and echo packets to the WLAN roaming center periodically. If it fails to receive a response before the response timeout timer expires, it retransmits the packets.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter client roaming center view.
client roaming-center
3. Set the response timeout timer for packets to the WLAN roaming center.
response-timeout timeout
By default, the response timeout timer is 3 seconds.
Setting the maximum number of transmission attempts for packets to the WLAN roaming center
About this task
The client roaming center sends client data synchronization and echo packets to the WLAN roaming center periodically. If it fails to receive a response before the response timeout timer expires, it retransmits the packets. If the client roaming center fails to receive any response after the last transmission attempt, it determines that the synchronization has failed.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter client roaming center view.
client roaming-center
3. Set the maximum number of transmission attempts for packets to the WLAN roaming center.
retry retries
By default, the maximum number of transmission attempts is 5.
Setting the aging timer for address security entries
About this task
The client roaming center generates address security entries at client associations to record client MAC address, IP address, and username information. When the aging timer of an entry expires, the client roaming center deletes the entry.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice, set an aging timer not larger than the lease of the IP addresses assigned to clients by the DHCP server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter client roaming center view.
client roaming-center
3. Set the aging timer for address security entries.
address-security cache { ipv4-aging-time aging-time | ipv6-aging-time aging-time }
By default, the aging timer is 14400 seconds for IPv4 entries and 604800 seconds for IPv6 entries.
Enabling WLAN address security
About this task
This feature enables the WLAN roaming center to check clients coming online from the specified service template for MAC address or IP address spoofing attacks. If a MAC or IP address spoofing attack is detected, the AC adds the attacker to the blacklist, and logs off both the attacker and the client whose address is spoofed.
Restrictions and guidelines
For WLAN address security to take effect, configure 802.1X authentication.
WLAN address security takes effect only on clients that come online afterwards.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Enable address security.
address-security enable
By default, address security is disabled.
Client roaming center configuration examples
Example: Configuring the client roaming center
Network configuration
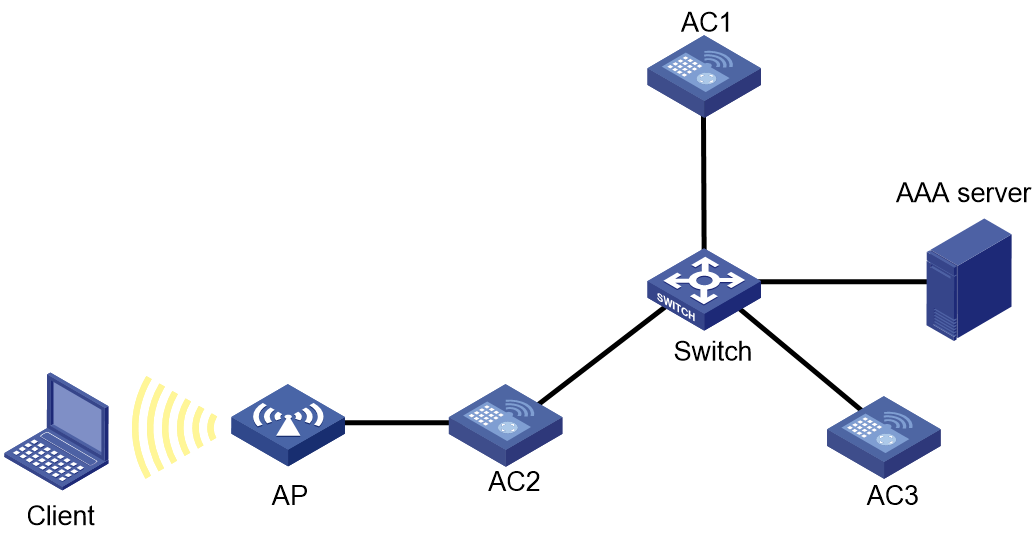
As shown in Figure 2, AC 1 acts as the WLAN roaming center, and AC 2 and AC 3 act as client roaming centers. Configure 802.1X authentication and address security for AC 2 and AC 3 to perform address security check every time a client attempts to come online.
Configuring AC 1
# Create the WLAN roaming center and enter its view.
<AC1> system-view
[AC1] wlan roaming-center
# Enable the WLAN roaming center.
[AC1-wlan-roaming-center] roaming-center enable
[AC1-wlan-roaming-center] quit
Configuring AC 2
1. Configure IP addresses for AC interfaces. Make ensure the AC and the AAA server can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure a RADIUS scheme:
# Create a RADIUS scheme named rs1.
<AC2> system-view
[AC2] radius scheme rs1
# Specify the primary authentication and account servers and specify the authentication key and account key.
[AC2-radius-rs1] primary authentication 192.168.0.112
[AC2-radius-rs1] primary accounting 192.168.0.112
[AC2-radius-rs1] key authentication simple radius
[AC2-radius-rs1] key accounting simple radius
# Configure the AC to remove the domain name from the usernames sent to the RADIUS servers.
[AC2-radius-rs1] user-name-format without-domain
[AC2-radius-rs1] quit
3. Configure an ISP domain:
# Create an ISP domain named dm1.
[AC2] domain dm1
# Specify the authentication, authorization, and accounting methods for LAN users.
[AC2-isp-dm1] authentication lan-access radius-scheme rs1
[AC2-isp-dm1] authorization lan-access radius-scheme rs1
[AC2-isp-dm1] accounting lan-access radius-scheme rs1
[AC2-isp-dm1] quit
4. Configure 802.1X authentication.
# Specify the authentication method as EAP.
[AC2] dot1x authentication-method eap
# Create AP ap2, and specify the AP model and serial ID.
[AC2] wlan ap ap2 model WA6320
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap2] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap2] quit
# Create service template newst and specify the SSID as AddrSec.
[AC2] wlan service-template newst
[AC2–wlan-st-newst] ssid AddrSec
# Configure RSN+802.1X authentication for the service template.
[AC2–wlan-st-newst] client-security authentication-mode dot1x
[AC2–wlan-st-newst] akm mode dot1x
[AC2–wlan-st-newst] cipher-suite ccmp
[AC2–wlan-st-newst] security-ie rsn
[AC2–wlan-st-newst] dot1x domain dm1
# Enable address security.
[AC2–wlan-st-newst] address-security enable
# Enable the service template.
[AC2–wlan-st-newst] service-template enable
[AC2–wlan-st-newst] quit
# Set the working channel to channel 11 for radio 2.
[AC2] wlan ap ap2
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap2] radio 2
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-2] channel 11
# Bind service template newst to radio 2.
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-2] radio enable
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-2] service-template newst
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap2-radio-2] quit
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap2] quit
5. Configure client roaming center settings:
# Create a client roaming center and enter its view.
[AC2] client roaming-center
# Specify the IP address of the WLAN roaming center.
[AC2-client-roaming-center] wlan-roaming-center ip 192.168.1.1
# Enable the client roaming center feature.
[AC2-client-roaming-center] roaming-center enable
[AC2-client-roaming-center] quit
Configuring AC 3
Configure AC 3 in the same way AC 2 is configured.
Configuring the AAA server
Configure the RADIUS server to provide authentication and accounting services. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Make the client pass 802.1X authentication and come online.
# Display client information on AC 2.
<AC2> display dot1x connection
Total connections: 1
User MAC address : 9cd3-6d9e-6742
AP name : ap1
Radio ID : 1
SSID : roam-relay
BSSID : 487a-da52-d321
Username : rsn4x
Authentication domain : imc
IPv4 address : 126.0.0.12
IPv6 address : 2000:1000:1020::2
Authentication method : EAP
Initial VLAN : 1
Authorization VLAN : 1
Authorization ACL number : N/A
Authorization user profile : N/A
Authorization CAR : N/A
Authorization URL : http://oauth.h3c.com
Termination action : N/A
Session timeout last from : N/A
Session timeout period : N/A
Online from : 2020/06/06 13:23:31
Online duration : 0h 0m 20s
# Display the local MAC address entries on AC 2.
[AC2] probe
[AC2-probe] display system internal wlan address-security local-cache mac
Total number of MACs: 1
MAC address User name Duration
9cd3-6d9e-6742 rsn4x 0days 0hours 0minutes 42seconds
# Display the local IP address entries on AC 2.
[AC2-probe] display system internal wlan address-security local-cache ip
Total number of IPs: 2
IP address User name MAC address
126.0.0.12 rsn4x 9cd3-6d9e-6742
2000:1000:1020::2 rsn4x 9cd3-6d9e-6742
# Display the MAC address entries obtained from the WLAN roaming center on AC 1.
[AC1] probe
[AC1-probe] display system internal wlan address-security cache mac
Total number of MACs: 1
MAC address User name Duration
9cd3-6d9e-6742 rsn4x 0days 0hours 1minutes 7seconds
# Display the IP address entries obtained from the WLAN roaming center on AC 1.
[AC1] probe
[AC1-probe] display system internal wlan address-security cache ip
Total number of IPs: 2
IP address User name MAC address
126.0.0.12 rsn4x 9cd3-6d9e-6742
2000:1000:1020::2 rsn4x 9cd3-6d9e-6742