- Table of Contents
-
- 27-WLAN Configuration Guide (AC)
- 00-Preface
- 01-Compatibility of hardware and AC functionality
- 02-AP management configuration
- 03-Radio management configuration
- 04-WLAN access configuration
- 05-WLAN security configuration
- 06-WIPS configuration
- 07-WLAN QoS configuration
- 08-WLAN roaming configuration
- 09-WLAN load balancing configuration
- 10-WLAN radio resource measurement configuration
- 11-Channel scanning configuration
- 12-Band navigation configuration
- 13-WLAN high availability configuration
- 14-Wireless location configuration
- 15-WLAN multicast optimization configuration
- 16-User isolation configuration
- 17-WLAN probe configuration
- 18-Spectrum management configuration
- 19-WLAN optimization configuration
- 20-WLAN RRM configuration
- 21-WLAN IP snooping configuration
- 22-WLAN radio load balancing configuration
- 23-Client roaming center configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 07-WLAN QoS configuration | 275.57 KB |
Restrictions and guidelines: WLAN QoS configuration
Setting EDCA parameters of AC-BE or AC-BK queues for clients
Setting EDCA parameters of AC-VI or AC-VO queues for clients
Configuring a port to trust packet priority for priority mapping
Configuring bandwidth guaranteeing
Configuring client rate limiting
Configuring service-template-based client rate limiting
Configuring radio-based client rate limiting
Configuring client-type-based client rate limiting
WLAN QoS configuration examples
Example: Configuring basic WMM
Example: Configuring SVP mapping
Example: Configuring traffic differentiation
Example: Configuring service-template-based client rate limiting
Configuring WLAN QoS
About WLAN QoS
An 802.11 network provides contention-based wireless access. To provide applications with QoS services, IEEE developed 802.11e for 802.11-based WLANs.
WLAN QoS features include WMM, SVP, bandwidth guaranteeing, and client rate limiting.
WMM protocol
About WMM
Wi-Fi Alliance defined the Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) standard to allow QoS provision devices of different vendors to interoperate. WMM enables a WLAN to provide QoS services, so that audio and video applications can have better performance in WLANs.
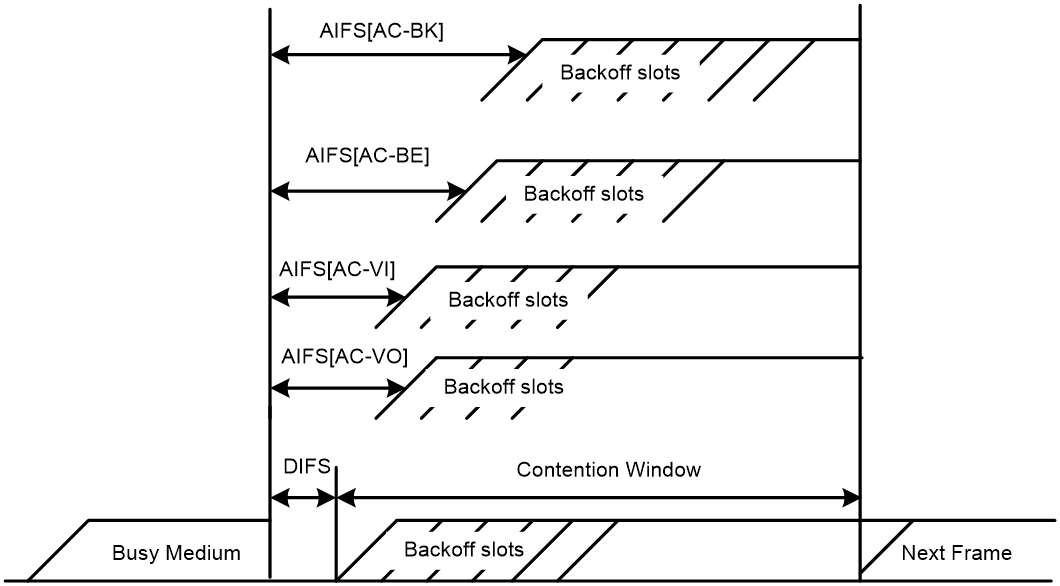
The Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) in 802.11 requires APs and clients to use the carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) access mechanism. APs or clients listen to the channel before they hold the channel for data transmission. When the specified idle duration of the channel times out, APs or clients randomly select a backoff slot within the contention window to perform backoff. The device that finishes backoff first gets the channel. With 802.11, all devices have the same idle duration and contention window. Therefore, they are equal when contending for a channel.
To provide QoS services, WMM divides data traffic into four ACs that have different priorities. Traffic in an AC with a high priority has a better chance to use the channel.
Terminology
· Enhanced distributed channel access—EDCA is a channel contention mechanism defined by WMM to preferentially transmit packets with high priority and allocate more bandwidth to such packets.
· Access category—WMM defines the following ACs: AC-VO for voice traffic, AC-VI for video traffic, AC-BE for best effort traffic, and AC-BK for background traffic. The priorities of the four ACs are in descending order.
· Connect Admission Control—CAC limits the number of clients that can use high-priority ACs (AC-VO and AC-VI) to guarantee enough bandwidth for these clients.
· Unscheduled automatic power save delivery—U-APSD is a power saving method defined by WMM to save client power.
EDCA parameters
· Arbitration inter-frame spacing number—In 802.11-based WLAN, each client has the same idle duration (DIFS), but WMM defines an idle duration for each AC. The idle duration increases as the AIFSN increases.
· Exponent form of CWmin/Exponent form of CWmax—ECWmin/ECWmax determines the backoff slots, which increase as the two values increase.
· Transmission opportunity limit—TXOP limit specifies the maximum time that a client can hold the channel after a successful contention. A larger value represents a longer time. If the value is 0, a client can send only one packet each time it holds the channel.
CAC admission policies
CAC requires a client to obtain permission from an AP before it can use a high-priority AC for transmission. This guarantees bandwidth for the clients that have gained access. CAC controls real time traffic (AC-VO and AC-VI traffic) but not common data traffic (AC-BE and AC-BK traffic).
If a client wants to use a high-priority AC (AC-VO or AC-VI), it must send a request to the AP. The AP returns a positive or negative response based on either of the following admission control policies:
· Channel usage-based admission policy—The AP calculates the channel occupation time of the existing high-priority AC queues and the requested AC queues within a time period, respectively. If the sum of the two values is smaller than or equal to the maximum hold time of the channel, the client can use the requested AC queue. If it is not, the request is rejected.
· Client-based admission policy—If the number of clients using high-priority AC queues is smaller than the maximum number of high-priority AC clients, the request is accepted. If it is not, the request is rejected. During calculation, a client is counted as one client if it is using both the AC-VO and AC-VI queues.
If the request is rejected because of lack of media resources, the AP assigns AC-BE to the client. Clients that already use high-priority AC queues will not be affected.
When calculating media resources, the AP takes requests before CAC is enabled into account. Whether subsequent requests for high-priority AC queues will be accepted is greatly restricted by the resource usage.
U-APSD power-save mechanism
U-APSD enables clients in sleep mode to wake up and receive the specified number of packets only after receiving a trigger packet. U-APSD improves the 802.11 APSD power saving mechanism.
U-APSD is automatically enabled after you enable WMM.
ACK policy
WMM defines the following ACK policies:
· Normal ACK—The recipient acknowledges each received unicast packet.
· No ACK—The recipient does not acknowledge received packets during wireless packet exchange. This policy improves the transmission efficiency in an environment where communication quality is strong and interference is weak. If communication quality deteriorates, this policy might increase the packet loss rate. For A-MPDU packets sent by 802.11n clients, the No ACK policy does not take effect.
SVP
SpectraLink Voice Priority (SVP) is developed by SpectraLink to provide QoS services for voice traffic.
Client rate limiting
This feature prevents aggressive use of bandwidth by one client and ensures fair use of bandwidth among clients associated with the same AP.
You can configure either of the following modes for client rate limiting:
· Dynamic mode—Sets the total bandwidth shared by all clients. The rate limit for each client is the total rate divided by the number of online clients. For example, if the total rate is 10 Mbps and five clients are online, the rate limit for each client is 2 Mbps.
· Static mode—Sets the bandwidth that can be used by each client. When the rate limit multiplied by the number of associated clients exceeds the available bandwidth provided by the AP, the clients might not get the set bandwidth.
·
Protocols and standards
· 802.11e-2005, Amendment 8: Medium Access Control (MAC) Quality of Service Enhancements, IEEE Computer Society, 2005
Wi-Fi, WMM Specification version 1.1, Wi-Fi Alliance, 2005
Restrictions and guidelines: WLAN QoS configuration
You can configure APs by using the following methods:
· Configure APs one by one in AP view.
· Assign APs to an AP group and configure the AP group in AP group view.
· Configure all APs in global configuration view.
For an AP, the settings made in these views for the same parameter take effect in descending order of AP view, AP group view, and global configuration view.
Configuring WMM
WMM tasks at a glance
To configure WMM, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling WMM
2. (Optional.) Setting EDCA parameters
3. (Optional.) Setting EDCA parameters of AC-VI or AC-VO queues for clients
4. (Optional.) Configuring a port to trust packet priority for priority mapping
Enabling WMM
About this task
All 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax clients must support WMM. For 802.11n, 802.11ac, or 802.11ax clients to communicate with the associated AP, enable WMM when the radio operates in 802.11an, 802.11gn, 802.11ac, or 802.11ax mode.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Enable WMM.
wmm enable
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, WMM is enabled.
Setting EDCA parameters
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set EDCA parameters.
edca radio { ac-be | ac-bk | ac-vi | ac-vo } { ack-policy { noack | normalack } | aifsn aifsn-value | ecw ecwmin ecwmin-value ecwmax ecwmax-value | txoplimit txoplimit-value } *
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the values for EDCA parameters are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Default EDCA parameter values
|
AC |
AIFSN |
ECWmin |
ECWmax |
TXOP Limit |
|
AC-BK |
7 |
4 |
10 |
0 |
|
AC-BE |
3 |
4 |
6 |
0 |
|
AC-VI |
1 |
3 |
4 |
94 |
|
AC-VO |
1 |
2 |
3 |
47 |
Setting EDCA parameters of AC-BE or AC-BK queues for clients
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set EDCA parameters of AC-BE or AC-BK queues for clients.
edca client { ac-be | ac-bk } { aifsn aifsn-value | ecw ecwmin ecwmin-value ecwmax ecwmax-value | txoplimit txoplimit-value } *
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the values for EDCA parameters of AC-BE or AC-BK queues are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Default EDCA parameter values of AC-BE or AC-BK queues for clients
|
AC |
AIFSN |
ECWmin |
ECWmax |
TXOP Limit |
|
AC-BK |
7 |
4 |
10 |
0 |
|
AC-BE |
3 |
4 |
10 |
0 |
Setting EDCA parameters of AC-VI or AC-VO queues for clients
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Set EDCA parameters of AC-VI or AC-VO queues for clients.
edca client { ac-vi | ac-vo } { aifsn aifsn-value | cac { disable | enable } | ecw ecwmin ecwmin-value ecwmax ecwmax-value | txoplimit txoplimit-value } *
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the values for EDCA parameters of AC-VI or AC-VO queues are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Default EDCA parameter values of AC-VI or AC-VO queues for clients
|
AC |
AIFSN |
ECWmin |
ECWmax |
TXOP Limit |
|
AC-VI |
2 |
3 |
4 |
94 |
|
AC-VO |
2 |
2 |
3 |
47 |
5. (Optional.) Configure the CAC policy.
cac policy { channelutilization [ channelutilization-value ] | client [ client-number ] }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, the client-based admission policy is used, and the maximum number of admitted clients is 20.
Configuring a port to trust packet priority for priority mapping
About this task
When the packet trust mode is disabled, an AP assigns the port priority to all packets for the service template.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature takes effect only on uplink packets.
The port priority setting does not take effect if the trusted packet priority type is configured.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Configure the trusted packet priority type.
qos trust { dot11e | dscp }
By default, the port priority is trusted.
4. Set the port priority.
qos priority priority
By default, the port priority is 0.
Configuring SVP mapping
About this task
This feature assigns packets that have the protocol ID 119 in the IP header to the AC-VI or AC-VO queue to provide SVP packets with the specified priority. SVP does not require random backoff for SVP packets. Therefore, you can set both ECWmin and ECWmax to 0 when there are only SVP packets in the AC-VI or AC-VO queue.
When SVP mapping is disabled, SVP packets are assigned to the AC-BE queue.
Restrictions and guidelines
SVP mapping takes effect only on non-WMM clients.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Enable SVP mapping.
svp map-ac { ac-vi | ac-vo }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, SVP mapping is disabled.
To disable SVP mapping, use the svp map-ac disable command.
Configuring bandwidth guaranteeing
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum bandwidth for the specified radio mode.
wlan max-bandwidth { dot11a | dot11ac | dot11an | dot11b | dot11g | dot11gac | dot11gn | dot11ax | dot11gax } bandwidth
The following default settings apply:
¡ 30000 Kbps for dot11a and dot11g.
¡ 250000 Kbps for dot11an, dot11gn, dot11gac, and dot11gax.
¡ 500000 Kbps for dot11ac.
¡ 7000 Kbps for dot11b.
¡ 700000 Kbps for dot11ax.
3. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
4. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
5. Configure bandwidth guaranteeing.
bandwidth-guarantee { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, if the service template setting in AP group view is used, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view. If a service template is manually bound to the radio, bandwidth guaranteeing is disabled.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, bandwidth guaranteeing is disabled.
6. Set a guaranteed bandwidth percentage for the specified service template.
bandwidth-guarantee service-template service-template-name percent percent
By default:
¡ In radio view, if the service template setting in AP group view is used, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view. If a service template is manually bound to the radio, no guaranteed bandwidth percentage is set for the service template.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, no guaranteed bandwidth percentage is set for a service template.
Configuring client rate limiting
About client rate limiting
By rate limit method, you can configure service-template-based, radio-based, or client-type-based client rate limiting. By rate limit mode, you can configure the dynamic or static mode for client rate limiting.
If more than one method and mode are configured, all settings take effect. The rate for a client will be limited to the minimum value among all the client rate limiting settings.
Restrictions and guidelines
Service-template-based client rate limiting takes effect on all clients associated with the same service template.
Radio-based client rate limiting takes effect on all clients associated with the same radio.
Client-type-based client rate limiting takes effect on all clients of the specified protocol.
Configuring service-template-based client rate limiting
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Configure service-template-based client rate limiting.
client-rate-limit { inbound | outbound } mode { dynamic cir cir [ min min-cir ] [ max max-cir ] | static cir cir } [ cbs cbs ]
By default, service-template-based client rate limiting is not configured.
Configuring radio-based client rate limiting
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or an AP group's AP model view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's AP model view:
wlan ap-group group-name
ap-model ap-model
3. Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
4. Enable radio-based client rate limiting.
client-rate-limit { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, radio-based client rate limiting is disabled.
5. Configure radio-based client rate limiting.
client-rate-limit { inbound | outbound } mode { dynamic cir cir [ min min-cir ] [ max max-cir ] | static cir cir }
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in an AP group's radio view.
¡ In an AP group's radio view, radio-based client rate limiting is not configured.
Configuring client-type-based client rate limiting
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure client-type-based client rate limiting.
wlan client-rate-limit { dot11a | dot11ac | dot11an | dot11b | dot11g | dot11gac | dot11gn } { inbound | outbound } cir cir [ cbs cbs ]
By default, client-type-based client rate limiting is not configured.
Verifying and maintaining WMM
Displaying WMM statistics
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display WMM statistics for clients.
display wlan wmm client [ ap ap-name | mac-address mac-address ]
· Display WMM statistics for radios.
display wlan wmm radio [ ap ap-name ]
Clearing WMM statistics
Perform clear tasks in user view.
· Clear WMM statistics for clients.
reset wlan wmm client [ ap ap-name | mac-address mac-address ]
· Clear WMM statistics for radios.
reset wlan wmm radio [ ap ap-name ]
WLAN QoS configuration examples
Example: Configuring basic WMM
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, enable WMM on the AC so that the AP and the client can prioritize the traffic.
Procedure
# Create a service template named market, set the SSID to market, and enable the service template.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan service-template market
[AC-wlan-st-market] ssid market
[AC-wlan-st-market] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-market] quit
# Create a manual AP named ap1, and specify the AP model and serial ID.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
# Enable WMM, bind service template market to radio 1, and enable radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] wmm enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template market
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display WMM statistics for radios.
[AC] display wlan wmm radio
AP ID : 1 AP Name : ap1
Radio : 1
Client EDCA updates : 0
QoS mode : WMM
WMM status : Enabled
Radio max AIFSN : 15 Radio max ECWmin : 10
Radio max TXOPLimit : 32767 Radio max ECWmax : 10
CAC information
Clients accepted : 0
Voice : 0
Video : 0
Total request medium time(μs) : 0
Voice(μs) : 0
Video(μs) : 0
Calls rejected due to insufficient resources : 0
Calls rejected due to invalid parameters : 0
Calls rejected due to invalid medium time : 0
Calls rejected due to invalid delay bound : 0
Radio : 2
Client EDCA updates : 0
QoS mode : WMM
WMM status : Enabled
Radio max AIFSN : 15 Radio max ECWmin : 10
Radio max TXOPLimit : 32767 Radio max ECWmax : 10
CAC information
Clients accepted : 0
Voice : 0
Video : 0
Total request medium time(μs) : 0
Voice(μs) : 0
Video(μs) : 0
Calls rejected due to insufficient resources : 0
Calls rejected due to invalid parameters : 0
Calls rejected due to invalid medium time : 0
Calls rejected due to invalid delay bound : 0
Example: Configuring CAC
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, configure CAC to allow a maximum of 10 clients to use the AC-VO and AC-VI queues.
Procedure
1. Create a service template named market, set the SSID to market, and enable the service template.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan service-template market
[AC-wlan-st-market] ssid market
[AC-wlan-st-market] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-market] quit
2. Create a manual AP named ap1, and specify the AP model and serial ID.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
3. Configure WMM:
# Bind service template market to radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template market
# Enable WMM for AC-VO and AC-VI queues, and configure a CAC policy to limit the number of clients to 10.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] wmm enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] edca client ac-vo cac enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] edca client ac-vi cac enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] cac policy client 10
# Enable radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
Verifying the configuration
# Assume that a client requests to use a high-priority AC queue (AC-VO or AC-VI). Verify the following information:
· If the number of clients using high-priority AC queues is smaller than the maximum number of high-priority AC clients (10 in this example), the request is accepted.
· If the number of clients using high-priority AC queues is equal to the maximum number of high-priority AC clients (10 in this example), the request is rejected. The AP decreases the priority of packets from the client.
Example: Configuring SVP mapping
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4, configure SVP mapping on the AC to assign SVP packets to the AC-VO queue. Set ECWmin and ECWmax to 0 for the AC-VO queue of the AP.
Procedure
1. Create a service template named market, set the SSID to market, and enable the service template.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan service-template market
[AC-wlan-st-market] ssid market
[AC-wlan-st-market] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-market] quit
2. Create a manual AP named ap1, and specify the AP model and serial ID.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
3. Configure SVP mapping:
# Enable WMM.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] wmm enable
# Assign SVP packets to the AC-VO queue, and set EDCA parameters of AC-VO queues for clients.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] svp map-ac ac-vo
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] edca client ac-vo ecw ecwmin 0 ecwmax 0
# Bind service template market to radio 1, and enable the radio.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template market
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the AC assigns SVP packets to the AC-VO queue if a non-WMM client comes online and sends SVP packets to the AC.
Example: Configuring traffic differentiation
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, configure priority mapping on the AC to add 802.11 packets from the client to the AC-VO queue.
Procedure
# Create a service template named market, and set the SSID to market.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan service-template market
[AC-wlan-st-market] ssid market
# Configure priority mapping, and enable the service template.
[AC-wlan-st-market] qos priority 7
[AC-wlan-st-market] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-market] quit
# Create a manual AP named ap1, and specify the AP model and serial ID.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
# Enable WMM.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] wmm enable
# Bind service template market to radio 1, and enable radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template market
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Perform the following tasks on the AC:
· Execute the terminal monitor command to enable monitoring of logs on the current terminal.
· Execute the terminal debugging command to enable display of debugging information on the current terminal.
· Execute the debugging wlan wmm all command to enable all the WMM debugging features.
# Ping the client and the switch on the AP to verify that the network connections are correct.
# Verify that the priority of packets from the client to the AP is changed to 7 and the priority of packets from the AP to the client is not changed.
Example: Configuring service-template-based client rate limiting
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 6, the AC is in the same network as the AP. Perform the following tasks on the AC:
· Configure static mode client rate limiting to limit the rate of incoming client traffic.
· Configure dynamic mode client rate limiting to limit the rate of outgoing client traffic.
Procedure
# Create a service template named service, and set its SSID to service.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan service-template service
[AC-wlan-st-service] ssid service
# Limit the rate of incoming traffic to 8000 Kbps in static mode, and limit the rate of outgoing traffic to 8000 Kbps in dynamic mode.
[AC-wlan-st-service] client-rate-limit inbound mode static cir 8000
[AC-wlan-st-service] client-rate-limit outbound mode dynamic cir 8000
[AC-wlan-st-service] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-service] quit
# Create a manual AP named ap1, and specify the AP model and serial ID.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
# Bind service template service to radio 1, and enable radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template service
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] return