- Table of Contents
-
- 27-WLAN Configuration Guide (AC)
- 00-Preface
- 01-Compatibility of hardware and AC functionality
- 02-AP management configuration
- 03-Radio management configuration
- 04-WLAN access configuration
- 05-WLAN security configuration
- 06-WIPS configuration
- 07-WLAN QoS configuration
- 08-WLAN roaming configuration
- 09-WLAN load balancing configuration
- 10-WLAN radio resource measurement configuration
- 11-Channel scanning configuration
- 12-Band navigation configuration
- 13-WLAN high availability configuration
- 14-Wireless location configuration
- 15-WLAN multicast optimization configuration
- 16-User isolation configuration
- 17-WLAN probe configuration
- 18-Spectrum management configuration
- 19-WLAN optimization configuration
- 20-WLAN RRM configuration
- 21-WLAN IP snooping configuration
- 22-WLAN radio load balancing configuration
- 23-Client roaming center configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-WIPS configuration | 489.80 KB |
Broadcast disassociation/deauthentication attack detection
Detection on clients with the 40 MHz bandwidth mode disabled
AP impersonation attack detection
Association/reassociation DoS attack detection
Signature-based attack detection
Configuring an attack detection policy
Applying an attack detection policy
Configuring signature-based attack detection
Configuring a signature policy
Configuring device classification
Configuring an automatic device classification policy
Configuring a manual AP classification policy
Applying a classification policy
Configuring a countermeasure policy
Applying a countermeasure policy
Configuring the countermeasure packet sending interval
Enabling the enhanced countermeasure mode
Detecting clients with NAT configured
Configuring the alarm-ignoring feature
Configuring APs to perform WIPS scanning while providing access services
Enabling fast learning of client association entries
Verifying and maintaining WIPS
Example: Configuring device classification and countermeasures
Example: Configuring malformed packet and flood attack detection
Example: Configuring signature-based attack detection
WIPS overview
About WIPS
Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS) helps you monitor your WLAN, detect attacks and rogue devices, and take countermeasures. WIPS provides a complete solution for WLAN security.
WIPS components
WIPS contains the network management module, ACs, and sensors (APs enabled with WIPS).
· The sensors monitor the WLAN, collect channel information, and report the information to the AC for further analysis.
· The AC determines attacks and rogue devices, takes countermeasures, and triggers alarms.
· The network management module allows you to configure WIPS in the Web interface. It provides configuration management, report generation, and alarm management functions.
WIPS features
WIPS provides the following features:
· Attack detection—WIPS detects attacks by listening for 802.11 frames and triggers alarms to notify the administrator.
· Signature-based attack detection—WIPS provides signature-based attack detection. A signature contains a packet identification method and actions to take on the matching packets.
· Device classification—WIPS identifies wireless devices by listening for 802.11 frames and classifies the devices based on the classification rules.
· Countermeasures—WIPS enables you to take countermeasures against rogue devices.
Attack detection
Flood attack detection
An AP might be facing a flood attack if it receives a large number of same-type frames within a short period of time. To prevent the AP from being overwhelmed, WIPS periodically examines incoming packet statistics, and triggers an alarm when it detects a suspicious flood attack. WIPS can detect the following flood attacks:
· Authentication request flood attack—Floods the association table of an AP by imitating many clients sending authentication requests to the AP.
· Probe request/association request/reassociation request flood attack—Floods the association table of an AP by imitating many clients sending probe requests/association requests/reassociation requests to the AP.
· EAPOL-start flood attack—Exhausts the AP's resources by imitating many clients sending EAPOL-start frames defined in IEEE 802.1X to the AP.
· Broadcast/unicast deauthentication flood attack—Spoofs deauthentication frames from the AP to the associated clients to disassociate the clients from the AP. This attack can rapidly terminate wireless services to multiple clients.
· Broadcast/unicast disassociation flood attack—Spoofs disassociation frames from the AP to the associated clients to disassociate the clients from the AP. This attack can rapidly terminate wireless services to multiple clients.
· RTS/CTS flood attack—Floods RTS/CTS frames to reserve the RF medium and force other wireless devices sharing the RF medium to hold back their transmissions. This attack takes advantage of vulnerabilities of the virtual carrier mechanism.
· Block Ack flood attack—Floods Block Ack frames to the AP to interrupt the operation of the Block Ack mechanism.
· Null data flood attack—Spoofs null data frames with a power management bit of 1 from a client to the AP. The AP determines that the client is in power save mode and buffers frames for the client. When the aging time of the buffered frames expires, the AP discards the frames. This interrupts the client's communication with the AP.
· Beacon flood attack—Floods beacon frames imitating a large number of fake APs to interrupt client association.
· EAPOL-logoff flood attack—The IEEE 802.1X standard defines the authentication protocol using Extensible Authentication Protocol over LANs (EAPOL). A client needs to send an EAPOL-logoff frame to terminate the session with an AP. The EAPOL-logoff frames are not authenticated, and an attacker can spoof EAPOL-logoff frames to disassociate a client.
· EAP-success/failure flood attack—In a WLAN using 802.1X authentication, an AP sends an EAP-success or EAP-failure frame to a client to inform the client of authentication success or failure. An attacker can spoof the MAC address of an AP to send EAP-success or EAP-failure frames to a client to disrupt the authentication process.
Malformed packet detection
WIPS determines that a frame is malformed if the frame matches the criteria shown in Table 1, and it then triggers alarms and logs.
Table 1 Malformed frame match criteria
|
Detection type |
Applicable frames |
Match criteria |
|
Invalid IE length detection |
All management frames |
The IE length does not conform to the 802.11 protocol. The remaining length of the IE is not zero after the packet is resolved. |
|
Duplicate IE detection |
All management frames |
Duplicate IE. This type of detection is not applicable to vendor-defined IEs. |
|
Redundant IE detection |
All management frames |
The IE is not a necessary IE to the frame and is not a reserved IE. |
|
Invalid packet length detection |
All management frames |
The remaining length of the IE is not zero after the packet payload is resolved. |
|
Abnormal IBSS and ESS setting detection |
· Beacon frames · Probe response frames |
Both IBSS and ESS are set to 1. |
|
Malformed authentication request frame detection |
Authentication request frames |
· The authentication algorithm number does not conform to the 802.11 protocol and is larger than 3. · The authentication transaction sequence number is 0. · The authentication transaction sequence number is 1 and the status code is not 0. · The authentication transaction sequence number is larger than 4. |
|
Malformed association request frame detection |
Association request frames |
The frame length is 0. |
|
Malformed HT IE detection |
· Beacon frames · Probe responses · Association responses · Reassociation requests |
· The SM power save value for the HT capabilities IE is 2. · The secondary channel offset value for the HT operation IE is 2. |
|
Oversized duration detection |
· Unicast management frames · Unicast data frames · RTS, CTS, and ACK frames |
The packet duration value is larger than the specified threshold. |
|
Malformed probe response frame detection |
Probe response frames |
The frame is not a mesh frame and its SSID length is 0. |
|
Invalid deauthentication code detection |
Deauthentication frames |
The reason code is 0 or is in the range of 67 to 65535. |
|
Invalid disassociation code detection |
Disassociation frames |
The reason code is 0 or is in the range of 67 to 65535. |
|
Oversized SSID detection |
· Beacon frames · Probe requests · Probe responses · Association request frames |
The SSID length is larger than 32. |
|
FATA-Jack detection |
Authentication frames |
The value of the authentication algorithm number is 2. |
|
Invalid source address detection |
All management frames |
· The TO DS is 1, indicating that the frame is sent to the AP by a client. · The source MAC address of the frame is a multicast or broadcast address. |
|
Oversized EAPOL key detection |
EAPOL-Key frames |
The TO DS is 1 and the length of the key is larger than 0. |
Spoofing attack detection
In a spoofing attack, the attacker sends frames on behalf of another device to threaten the network. WIPS supports detection of the following spoofing attacks:
· Frame spoofing—A fake AP spoofs an authorized AP to send beacon or probe response frames to induce clients to associate with it.
· AP MAC address spoofing—A client spoofs an authorized AP to send deauthentication or disassociation frames to other clients. This can cause the clients to go offline and affect the correct operation of the WLAN.
· Client MAC address spoofing—A fake AP spoofs an authorized client to associate with an authorized AP.
Frame spoofing attack detection
WIPS calculates the startup time of an AP by using the frame receiving time and timestamp. If the calculated startup time of the AP is not the same as the startup time recorded in WIPS, WIPS determines that this is a spoofing attack.
AP MAC address spoofing attack detection
WIPS examines the MAC address of the sender. If the MAC address of the sender already exists in the AP MAC address table, WIPS determines that this is a spoofing attack.
Client MAC address spoofing attack detection
WIPS examines the MAC address of the sender. If the MAC address of the sender already exists in the client MAC address table, WIPS determines that this is a spoofing attack.
Weak IV detection
When the RC4 encryption algorithm, used by the WEP security protocol, uses an insecure IV, the WEP key is more likely to be cracked. An IV is a weak IV if its first byte is smaller than 16 (decimal) and its second byte is FF. WIPS prevents this kind of attack by detecting the IV in each WEP packet.
Omerta attack detection
Omerta is a DoS attack tool based on the 802.11 protocol. It sends disassociation frames with the reason code 0x01 to disassociate clients. Reason code 0x01 indicates an unknown disassociation reason. WIPS detects Omerta attacks by detecting the reason code of each disassociation frame.
Broadcast disassociation/deauthentication attack detection
An attacker spoofs a legitimate AP to send a broadcast disassociation or deauthentication frame to log off all clients associated with the AP.
Detection on clients with the 40 MHz bandwidth mode disabled
802.11n devices support both the 20 MHz and 40 MHz bandwidth modes. If the 40 MHz bandwidth mode is disabled on a client, the use of network for other clients associated with the same AP as the client will be affected. Thus the network throughput and efficiency will be affected.
WIPS detects such clients by detecting probe request frames sent by the clients.
Power save attack detection
An attacker spoofs the MAC address of a client to send power save on frames to an AP. The AP caches the frames for the client. The attacked client cannot receive data frames because the AP determines that the client is still in power save mode. When the aging time of the cached frames expires, the AP discards the frames. WIPS detects power save attacks by determining the ratio of power save on frames to power save off frames.
Prohibited channel detection
After you configure a permitted channel list and enable prohibited channel detection, WIPS determines that channels that are not in the permitted channel list are prohibited channels.
Soft AP detection
A soft AP refers to a client that acts as an AP and provides wireless services. An attacker can access the internal network through a soft AP and then initiate further attacks. WIPS detects soft APs by detecting the interval at which a device switches its roles between client and AP. WIPS does not perform soft AP detection on unassociated clients.
Windows bridge detection
When a wireless client connected to a wired network establishes a Windows bridge through the wired NIC, the client can bridge an external AP with the internal network. This might bring security problems to the internal network. WIPS detects Windows bridges by analyzing data frames sent by associated clients.
Unencrypted device detection
An authorized AP or client that is transmitting unencrypted frames might bring security problems to the network. WIPS detects unencrypted devices by analyzing the frames sent the by authorized APs or clients.
Hotspot attack detection
An attacker sets up a rogue AP with the same SSID as a hotspot to lure the clients to associate with it. After the clients associate with the malicious AP, the attacker initiates further attacks to obtain client information.
You can configure a hotspot information to enable WIPS to detect hotspot attacks.
AP impersonation attack detection
In an AP impersonation attack, a malicious AP that has the same BSSID and ESSID as a legitimate AP lures the clients to associate with it. Then this impersonating AP initiates hotspot attacks or fools the detection system.
WIPS detects AP impersonation attacks by detecting the interval at which an AP sends beacon frames.
HT-greenfield AP detection
An AP operating in HT-greenfield mode might cause collisions, errors, and retransmissions because it cannot communicate with 802.11a/b/g devices. WIPS detects HT-greenfield APs by analyzing the beacon frames or probe response frames sent by APs.
Honeypot AP detection
In a honeypot AP attack, the attacker sets up a malicious AP to lure clients to associate with it. The SSID of the malicious AP is similar to the SSID of a legitimate AP. After a client associates with a honeypot AP, the honeypot AP initiates further attacks such as port scanning or fake authentication to obtain client information.
WIPS detects honeypot APs by detecting SSIDs of external APs. If the similarity between the SSID of an external AP and the SSID of a legitimate AP reaches the specified threshold, WIPS generates an alarm.
MITM attack detection
In an MITM attack, the attacker sets up a rogue AP and lures a client to associate with it. Then the rogue AP spoofs the MAC address of the client to associate with the authorized AP. When the client and the authorized AP communicate, the rogue AP captures packets from both the client and the authorized AP. The rogue AP might modify the frames and obtain the frame information. WIPS detects MITM attacks by detecting clients that are disassociated from an authorized AP and associated with a honeypot AP. WIPS can detect MITM attacks only when you enable both honeypot AP detection and MITM attack detection.
Wireless bridge detection
An attacker might intrude on the internal networks through a wireless bridge. When detecting a wireless bridge, WIPS generates an alarm. If the wireless bridge is in a mesh network, WIPS records the mesh link.
Association/reassociation DoS attack detection
An association/reassociation DoS attack floods the association table of an AP by imitating many clients sending association requests to the AP. When the number of entries in the table reaches the upper limit, the AP cannot process requests from legitimate clients.
AP flood attack detection
WIPS detects the number of APs in the WLAN and triggers an alarm for an AP flood attack when the number of APs exceeds the specified threshold.
Device entry attack detection
Attackers can send invalid packets to WIPS to increase processing costs. WIPS periodically examines the learned device entries to determine whether to rate limit device entry learning. If the number of AP or client entries learned within the specified interval exceeds the threshold, WIPS triggers an alarm and stops learning new entries.
You can set an inactivity timer and aging timer for device entries. If a wireless device does not receive or send packets before the inactivity timer expires, the device enters inactive status. If a wireless device does not receive or send packets before the aging timer expires, the device entry is deleted.
Signature-based attack detection
WIPS provides signature-based attack detection. A signature contains a packet identification method and actions to take on the matching packets. The sensor matches the detected packets against the signature, and takes actions defined in the signature if a packet matches the signature.
A signature can contain a maximum of six subsignatures, which can be defined based on the frame type, MAC address, serial ID, SSID length, SSID, and frame pattern. A packet matches a signature only when it matches all the subsignatures in the signature.
Device classification
AP classification
AP categories
As shown in Table 2, WIPS classifies detected APs according to the predefined classification rules.
|
Category |
Description |
Classification rule |
|
Authorized AP |
An AP that is permitted in the WLAN. |
· Has been connected to the AC and not in the prohibited device list. · Configured as an authorized AP. · In the permitted device list. · Classified as an authorized AP by a user-defined AP classification rule. |
|
Rogue AP |
An AP that cannot be used in the WLAN. |
· In the prohibited device list. · Not in the OUI configuration file. · Configured as a rogue AP. · Classified as a rogue AP by a user-defined AP classification rule. If the wired port on an AP has been connected to the network and the AP is not connected to the AC, the AP might be a rogue AP. |
|
Misconfigured AP |
An AP that can be used in the WLAN but has incorrect configuration. |
· Configured as a misconfigured AP. · Classified as a misconfigured AP by a user-defined AP classification rule. |
|
External AP |
An AP that is in an adjacent WLAN. |
· Configured as an external AP. · Classified as an external AP by a user-defined AP classification rule. |
|
Ad hoc |
An AP operating in Ad hoc mode. WIPS detects Ad hoc APs by listening to beacon frames. |
N/A |
|
Mesh AP |
An AP in a WLAN mesh network. |
WIPS identifies mesh APs through beacon frames. |
|
Potential-authorized AP |
An AP that is possibly authorized. |
An AP is a potential-authorized AP if it meets all the following conditions: · Not in the permitted device list. · Not in the prohibited device list. · Not in the trusted SSID list. · Not in the trusted OUI list. · Has been connected to the AC. · Not manually classified. · Does not match any user-defined AP classification rules. |
|
Potential-rogue AP |
An AP that is possibly a rogue AP. |
Has incorrect wireless configuration and is not in any one of the following lists: · Permitted device list. · Prohibited device list. · Trusted OUI list. If the wired port on an AP has been connected to the network, the AP is a rogue AP. |
|
Potential-external AP |
An AP that is possibly an external AP. |
· Has incorrect wireless service configuration. · The wired port has not been connected to the network. · Not in any one of the following lists: ¡ Permitted device list. ¡ Prohibited device list. ¡ Trusted OUI list. |
|
Uncategorized AP |
An AP whose category cannot be determined. |
N/A |
AP classification flow
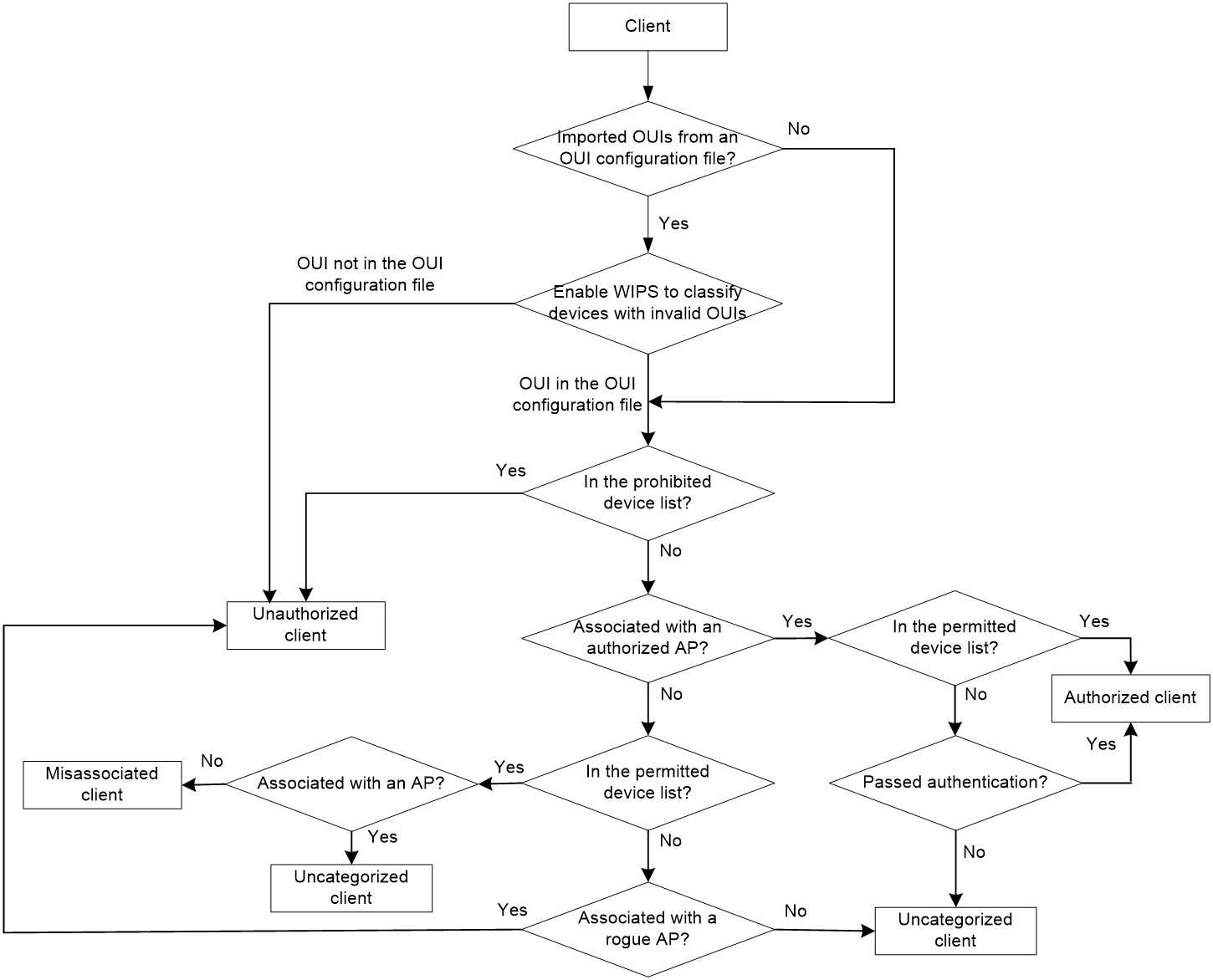
WIPS classifies detected APs by following the process shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 AP classification flow
|
|
NOTE: In the AP classification flow, only H3C devices support the wired network connection detection. |
Client classification
As shown in Table 3, WIPS classifies detected clients based on the predefined classification rules.
Client categories
|
Category |
Description |
Classification rule |
|
Authorized client |
A client that is permitted in the WLAN. |
· In the prohibited device list and associated with an authorized AP. · Has passed authentication and is associated with an authorized AP. |
|
Unauthorized client |
A client that cannot be used in the WLAN. |
· In the prohibited device list. · Associated with a rogue AP. · Not in the OUI configuration file. |
|
Misassociated client |
A client that is associated with an unauthorized AP. |
In the permitted device list but associated with an unauthorized AP. A misassociated client might introduce security threats to the network. |
|
Uncategorized client |
A client whose category cannot be determined. |
N/A |
Client classification flow
WIPS classifies detected clients by following the process shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Client classification flow
Countermeasures
Rogue devices are susceptible to attacks and might bring security problems to the WLAN. WIPS enables you to take countermeasures against rogue devices.
Configuring WIPS
WIPS tasks at a glance
To configure WIPS, perform the following tasks:
2. Configuring attack detection
a. Configuring an attack detection policy
b. Applying an attack detection policy
3. Configuring signature-based attack detection
b. Configuring a signature policy
c. Applying a signature policy
4. Configuring device classification
a. Configuring an automatic device classification policy
b. Configuring a manual AP classification policy
c. Applying a classification policy
5. Configuring countermeasures
a. Configuring a countermeasure policy
b. Applying a countermeasure policy
c. Configuring the countermeasure packet sending interval
d. Enabling the enhanced countermeasure mode
6. Configuring advanced WIPS features
¡ Detecting clients with NAT configured
¡ Configuring the alarm-ignoring feature
¡ Configuring APs to perform WIPS scanning while providing access services
¡ Enabling fast learning of client association entries
Enabling WIPS
About this task
You can divide a wireless network into multiple virtual security domains (VSDs) and apply different policies to these VSDs.
Before configuring WIPS for a radio of an AP, you must add the AP to a VSD.
Restricitons and guidelines
For WIPS to take effect correctly, WIPS cannot be enabled together with RRM and mesh.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or AP group view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Enter AP group view.
wlan ap-group group-name
3. Add the AP or AP group to a VSD.
wips virtual-security-domain vsd-name
By default:
¡ In AP view, an AP uses the configuration in AP group view.
¡ In AP group view, an AP group is not added to any VSDs.
4. Enter radio view or an AP group's radio view.
¡ Enter radio view.
radio radio-id
¡ Execute the following commands in sequence to enter an AP group's radio view:
ap-model ap-model
radio radio-id
5. Enable WIPS.
wips enable
By default:
¡ In radio view, a radio uses the configuration in AP group radio view.
¡ In AP group radio view, WIPS is disabled.
Configuring attack detection
Configuring an attack detection policy
Configuring flood attack detection
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Create an attack detection policy and enter its view.
detect policy policy-name
4. Configure flood attack detection.
¡ Configure association request flood attack detection.
flood association-request [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, association request flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure authentication request flood attack detection.
flood authentication [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, authentication request flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure beacon flood attack detection.
flood beacon [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, beacon flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure Block Ack flood attack detection.
flood block-ack [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, Block Ack flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure RTS flood attack detection.
flood rts [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, RTS flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure CTS flood attack detection.
flood cts [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, CTS flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure deauthentication flood attack detection.
flood deauthentication [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, deauthentication flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure disassociation flood attack detection.
flood disassociation [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, disassociation flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure EAPOL-start flood attack detection.
flood eapol-start [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, EAPOL-start flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure null data flood attack detection.
flood null data [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, null data flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure probe request flood attack detection.
flood probe-request [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, probe request flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure reassociation request flood attack detection.
flood reassociation-request [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, reassociation request flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure EAPOL-logoff flood attack detection.
flood eapol-logoff [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ]*
By default, EAPOL-logoff flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure EAP-failure flood attack detection.
flood eap-failure [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, EAP-failure flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure EAP-success flood attack detection.
flood eap-success [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, EAP-success flood attack detection is disabled.
Configuring malformed packet detection
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Create an attack detection policy and enter its view.
detect policy policy-name
4. Configure malformed packet detection.
¡ Configure duplicated IE detection.
malformed duplicated-ie [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, duplicated IE detection is disabled.
¡ Configure FATA-Jack detection.
malformed fata-jack [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, FATA-Jack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure abnormal IBSS or ESS setting detection.
malformed illegal-ibss-ess [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, abnormal IBSS or ESS setting detection is disabled.
¡ Configure invalid source address detection.
malformed invalid-address-combination [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, invalid source address detection is disabled.
¡ Configure malformed association request frame detection.
malformed invalid-assoc-req [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, malformed association request frame detection is disabled.
¡ Configure malformed authentication request frame detection.
malformed invalid-auth [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, malformed authentication request frame detection is disabled.
¡ Configure invalid deauthentication code detection.
malformed invalid-deauth-code [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, invalid deauthentication code detection is disabled.
¡ Configure invalid disassociation code detection.
malformed invalid-disassoc-code [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, invalid disassociation code detection is disabled.
¡ Configure invalid IE length detection.
malformed invalid-ie-length [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, invalid IE length detection is disabled.
¡ Configure malformed HT IE detection.
malformed invalid-ht-ie [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, malformed HT IE detection is disabled.
¡ Configure invalid packet length detection.
malformed invalid-pkt-length [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, invalid packet length detection is disabled.
¡ Configure oversized duration detection.
malformed large-duration [ quiet quiet-value | threshold value ]
By default, oversized duration detection is disabled.
¡ Configure malformed probe response frame detection.
malformed null-probe-resp [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, malformed probe response frame detection is disabled.
¡ Configure oversized EAPOL key detection.
malformed overflow-eapol-key [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, oversized EAPOL key detection is disabled.
¡ Configure oversized SSID detection.
malformed overflow-ssid [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, oversized SSID detection is disabled.
¡ Configure redundant IE detection.
malformed redundant-ie [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, redundant IE detection is disabled.
Configuring detection of other types of attacks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter attack detection policy view.
detect policy policy-name
4. Configure other attack detection.
¡ Configure client MAC address spoofing attack detection.
client-spoofing [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, client MAC address spoofing attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure AP MAC address spoofing attack detection.
ap-spoofing [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, AP MAC address spoofing attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure weak IV detection.
weak-iv [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, weak IV detection is disabled.
¡ Configure Omerta attack detection.
omerta [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, Omerta attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure broadcast disassociation attack detection.
disassociation-broadcast [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, broadcast disassociation attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure spoof deauthentication frame detection.
deauth-spoofing [ quiet quiet ]
By default, spoof deauthentication frame detection is disabled.
¡ Configure broadcast deauthentication attack detection.
deauthentication-broadcast [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, broadcast deauthentication attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure detection on clients with the 40 MHz bandwidth mode disabled.
ht-40mhz-intolerance [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, detection on clients with the 40 MHz bandwidth mode disabled is disabled.
¡ Configure power saving attack detection.
power-save [ interval interval-value | minoffpacket packet-value | onoffpercent percent-value | quiet quiet-value ] *
By default, power saving attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure Windows bridge detection.
windows-bridge [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, Windows bridge detection is disabled.
¡ Configure unencrypted authorized AP detection.
unencrypted-authorized-ap [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, unencrypted authorized AP detection is disabled.
¡ Configure unencrypted authorized client detection.
unencrypted-trust-client [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, unencrypted authorized client detection is disabled.
¡ Configure soft AP detection.
soft-ap [ convert-time time-value ]
By default, soft AP detection is disabled.
¡ Configure AP impersonation attack detection.
ap-impersonation [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, AP impersonation attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure HT-greenfield AP detection.
ht-greenfield [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, HT-greenfield AP detection is disabled.
¡ Configure association/reassociation DoS attack detection.
association-table-overflow [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, association/reassociation DoS attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure wireless bridge detection.
wireless-bridge [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, wireless bridge detection is disabled.
¡ Configure AP flood attack detection.
ap-flood [ apnum apnum-value | exceed exceed-value | quiet quiet-value ] *
By default, AP flood attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure honeypot AP detection.
honeypot-ap [ similarity similarity-value | quiet quiet-value ] *
By default, honeypot AP detection is disabled.
¡ Configure MITM attack detection.
man-in-the-middle [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, MITM attack detection is disabled.
¡ Configure channel change detection.
ap-channel-change [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, channel change detection is disabled.
¡ Configure WIPS to not trigger alarms for Apple terminals that use a random MAC address.
random-mac-scan enable
By default, WIPS triggers alarms for Apple terminals that use a random MAC address.
Configuring prohibited channel detection
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Create an attack detection policy and enter its view.
detect policy policy-name
4. Configure the permitted channel list.
permit-channel channel-id-list
By default, no channel is added to the permitted channel list.
5. Configure prohibited channel detection.
prohibited-channel [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, prohibited channel detection is disabled.
Configuring hotspot attack detection
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Configure hotspot information.
¡ Import hotspot information from a configuration file.
import hotspot file-name
By default, a device has built-in hotspot SSIDs and no configuration file containing hotspot information exists.
¡ Specify an SSID as a hotspot SSID.
hotspot ssid ssid-name
By default, a device has built-in hotspot SSIDs and no hotspot SSIDs are configured.
4. Enter attack detection policy view.
detect policy policy-name
5. Configure hotspot attack detection.
hotspot-attack [ quiet quiet-value ]
By default, hotspot attack detection is disabled.
Configuring device entry attack detection
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter attack detection policy view.
detect policy policy-name
4. Configure the client entry attack detection parameters.
¡ Rate limit client entry learning.
client-rate-limit [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, the statistics collection interval is 60 seconds, the quiet time is 1200 seconds, and the client entry threshold is 1024.
¡ Set a client entry timer.
client-timer inactive inactive-value aging aging-value
By default, the inactive time is 300 seconds, and the aging time is 600 seconds.
5. Configure the AP entry attack detection parameters.
¡ Rate limit AP entry learning.
ap-rate-limit [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, the statistics collection interval is 60 seconds, the quiet time is 1200 seconds, and the AP entry threshold is 512.
¡ Set an AP entry timer.
ap-timer inactive inactive-value aging aging-value
By default, the inactive time for APs is 300 seconds, and the aging time is 600 seconds.
Configuring RSSI-based wireless device detection
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter attack detection policy view.
detect policy policy-name
4. Set the RSSI threshold for clients or APs.
rssi-threshold { ap ap-rssi-value | client client-rssi-value }
By default, no RSSI threshold is set for clients or APs.
5. Set the RSSI difference threshold for wireless device detection.
rssi-change-threshold threshold-value
By default, the RSSI difference threshold is not configured.
Enabling WIPS to detect unassociated clients
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter attack detection policy view.
detect policy policy-name
4. Enable WIPS to detect unassociated clients.
detect dissociate-client enable
By default, WIPS does not detect unassociated clients.
Setting the wireless device information report interval
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter attack detection policy view.
detect policy policy-name
4. Set the interval at which APs report information about detected devices.
report-interval interval
By default, APs report information about detected devices every 30000 milliseconds.
Applying an attack detection policy
About this task
Applying an attack detection policy to a VSD enables the attack detection policy to take effect on all radios in the VSD.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Create a VSD and enter its view.
virtual-security-domain vsd-name
4. Apply an attack detection policy to the VSD.
apply detect policy policy-name
By default, no attack detection policy is applied to a VSD.
Configuring signature-based attack detection
Configuring a signature
About this task
If you configure multiple signatures, WIPS matches detected packets against the configured signatures in ascending order of ID until a match is found.
You can configure one or multiple subsignatures for a signature.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure a maximum of six subsignatures for a signature to match different attributes of packets.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Create a signature and enter its view.
signature rule rule-id
4. Configure subsignatures for the signature.
¡ Configure a subsignature to match the frame type of a frame.
frame-type { control | data | management [ frame-subtype { association-request | association-response | authentication | beacon | deauthentication | disassociation | probe-request } ] }
By default, no subsignature is configured to match the frame type of a frame.
¡ Configure a subsignature to match the MAC address of a frame.
mac-address { bssid | destination | source } mac-address
By default, no subsignature is configured to match the MAC address of a frame.
¡ Configure a subsignature to match the sequence number of a frame.
seq-number seq-value1 [ to seq-value2 ]
By default, no subsignature is configured to match the sequence number of a frame.
¡ Configure a subsignature to match the SSID length of a frame.
ssid-length length-value1 [ to length-value2 ]
By default, no subsignature is configured to match the SSID length of a frame.
¡ Configure a subsignature to match the SSID of a frame.
ssid [ case-sensitive ] [ not ] { equal | include } string
By default, no subsignature is configured to match the SSID of a frame.
¡ Configure a subsignature to match the specified bits of a frame.
pattern pattern-number offset offset-value mask hex-value value1 [ to value2 ] [ from-payload ]
By default, no subsignature is configured to match the specified bits of a frame.
¡ Configure the subsignatures to be in logical AND relationship.
match all
By default, the subsignatures are in logical OR relationship. A packet matches a signature if it matches any of the subsignatures of the signature.
After you configure this command, a packet matches a signature only when it matches all the subsignatures of the signature.
Configuring a signature policy
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter signature policy view.
signature policy policy-name
4. Bind the specified signature to the signature policy.
apply signature rule rule-id
By default, no signature is bound to a signature policy.
5. Enable WIPS to detect packets that match the signature.
detect signature [ interval interval-value | quiet quiet-value | threshold threshold-value ] *
By default, detection on packets that match a signature is enabled.
The statistics collection interval is 60 seconds, the quiet interval is 600 seconds, and the alarm threshold is 50.
Applying a signature policy
About this task
Applying a signature policy to a VSD enables the signature policy to take effect on all radios in the VSD.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter VSD view.
virtual-security-domain vsd-name
4. Apply the specified signature policy to the VSD.
apply signature policy policy-name
By default, no signature policy is applied to a VSD.
Configuring device classification
About device classification
You can enable WIPS to classify devices by using the following methods:
· Automatic classification—WIPS automatically classifies devices by adding MAC addresses, OUIs, or SSIDs to the specified lists. WIPS also allows you to classify APs by using user-defined AP classification rules.
· Manual classification—You manually specify a category for a device. Manual classification is applicable only to APs.
If you configure both automatic classification and manual classification, manual classification takes effect.
Configuring an automatic device classification policy
Configuring an automatic device classification policy
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Create a classification policy and enter its view.
classification policy policy-name
4. Configure automatic device classification.
¡ Configure WIPS to classify devices with invalid OUIs as rogue devices.
invalid-oui-classify illegal
By default, WIPS does not classify devices with invalid OUIs as rogue devices.
¡ Add a MAC address to the permitted device list.
trust mac-address mac-address
By default, no MAC address exists in the permitted device list.
¡ Add an OUI to the trusted OUI list.
trust oui oui
By default, no OUIs exist in the trusted OUI list.
This command is applicable only to AP classification.
¡ Add an SSID to the trusted SSID list.
trust ssid ssid-name
By default, no SSIDs exist in the trusted SSID list.
¡ Add a MAC address to the static prohibited device list.
block mac-address mac-address
By default, no MAC addresses exist in to the static prohibited device list.
¡ Categorize devices based on the built-in OUIs in the WIPS OUI library.
embedded-oui-classify enable
By default, the built-in OUIs are not used for device categorization.
¡ Bind the specified AP classification rule to the classification policy.
apply ap-classification rule rule-id { authorized-ap | { { external-ap | misconfigured-ap | rogue-ap } [ severity-level level ] } }
By default, no AP classification rule is bound to a classification policy.
Configuring an AP classification rule
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Create an AP classification rule and enter its view.
ap-classification rule rule-id
4. Configure AP classification rule criteria.
¡ Configure the AP classification rule to match the RSSI of an AP.
rssi value1 [ to value2 ]
By default, an AP classification rule does not match the RSSI of an AP.
¡ Configure the AP classification rule to match the SSID of the wireless service for an AP.
ssid [ case-sensitive ] [ not ] { equal | include } ssid-string
By default, an AP classification rule does not match the SSID of the wireless service for an AP.
¡ Configure the AP classification rule to match the running time of an AP.
up-duration value1 [ to value2 ]
By default, an AP classification rule does not match the running time of an AP.
¡ Configure the AP classification rule to match the number of associated clients for an AP.
client-online value1 [ to value2 ]
By default, an AP classification rule does not match the number of associated clients for an AP.
¡ Configure the AP classification rule to match the number of sensors that detect an AP.
discovered-ap value1 [ to value2 ]
By default, an AP classification rule does not match the number of sensors that detect an AP.
¡ Configure the AP classification rule to match the security mode used by an AP.
security { equal | include } { clear | wep | wpa | wpa2 }
By default, an AP classification rule does not match the security mode used by an AP.
¡ Configure the AP classification rule to match the authentication mode used by an AP.
authentication { equal | include } { 802.1x | none | other | psk }
By default, an AP classification rule does not match the authentication mode used by an AP.
¡ Configure the AP classification rule to match the OUI information of an AP.
oui oui-info
By default, an AP classification rule does not match the OUI information of an AP.
¡ Configure the AP classification rule criteria to be in logical AND relationship.
match all
By default, the AP classification rule criteria are in logical OR relationship. An AP matches an AP classification rule if it matches any of the criteria of the AP classification rule.
After you configure this command, an AP matches an AP classification rule only when it matches all criteria of the AP classification rule.
Configuring a manual AP classification policy
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter classification policy view.
classification policy policy-name
4. Specify a category for the specified AP.
manual-classify mac-address mac-address { authorized-ap | external-ap | misconfigured-ap | rogue-ap }
By default, no category is specified for an AP.
Applying a classification policy
About this task
Applying a classification policy to a VSD enables the classification to take effect on all radios in the VSD.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter VSD view.
virtual-security-domain vsd-name
4. Apply a classification policy to the VSD.
apply classification policy policy-name
By default, no classification policy is applied to a VSD.
Configuring countermeasures
Configuring a countermeasure policy
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Create a countermeasure policy and enter its view.
countermeasure policy policy-name
4. Configure WIPS countermeasures against APs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against external APs.
countermeasure external-ap
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against external APs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against misconfigured APs.
countermeasure misconfigured-ap
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against misconfigured APs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against potential-authorized APs.
countermeasure potential-authorized-ap
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against potential-authorized APs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against potential-external APs.
countermeasure potential-external-ap
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against potential-external APs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against potential-rogue APs.
countermeasure potential-rogue-ap
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against potential-rogue APs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against rogue APs.
countermeasure rogue-ap
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against rogue APs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against uncategorized APs.
countermeasure uncategorized-ap
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against uncategorized APs.
5. Configure WIPS countermeasures against clients.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against misassociated clients.
countermeasure misassociation-client
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against misassociated clients.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against unauthorized clients.
countermeasure unauthorized-client
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against unauthorized clients.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against uncategorized clients.
countermeasure uncategorized-client
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against uncategorized clients.
6. Configure WIPS countermeasures against attackers.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against devices that launch broadcast deauthentication attacks.
countermeasure attack deauth-broadcast
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices that launch broadcast deauthentication attacks.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against devices that launch broadcast disassociation attacks.
countermeasure attack disassoc-broadcast
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices that launch broadcast disassociation attacks.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against honeypot APs.
countermeasure attack honeypot-ap
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against honeypot APs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against devices that launch hotspot attacks.
countermeasure attack hotspot-attack
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices that launch hotspot attacks.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against 802.11n devices with the 40 MHz bandwidth mode disabled.
countermeasure attack ht-40-mhz-intolerance
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against 802.11n devices with the 40 MHz bandwidth mode disabled.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against devices that send malformed packets.
countermeasure attack malformed-packet
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices that send malformed packets.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against devices that launch MITM attacks.
countermeasure attack man-in-the-middle
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices that launch MITM attacks.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against devices that launch Omerta attacks.
countermeasure attack omerta
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices that launch Omerta attacks.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against devices that launch power save attacks.
countermeasure attack power-save
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices that launch power save attacks.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against soft APs.
countermeasure attack soft-ap
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against soft APs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against devices that use weak IVs.
countermeasure attack weak-iv
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices that use weak IVs.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against devices that launch Windows bridge attacks.
countermeasure attack windows-bridge
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices that launch Windows bridge attacks.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against unencrypted authorized clients.
countermeasure attack unencrypted-trust-client
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against unencrypted authorized clients.
¡ Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against all attackers.
countermeasure attack all
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against all attackers.
7. Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against Ad hoc devices.
countermeasure adhoc
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against Ad hoc devices.
8. Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against the specified device.
countermeasure mac-address mac-address [ except-authorized-ap ]
By default, WIPS does not take countermeasures against devices.
9. Enable all sensors that detect an attacker to take countermeasures against the attacker.
select sensor all
By default, only the sensor that most recently detects an attacker takes countermeasures against the attacker.
Applying a countermeasure policy
About this task
Applying a countermeasure policy to a VSD enables the countermeasure policy to take effect on all radios in the VSD.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter VSD view.
virtual-security-domain vsd-name
4. Apply a countermeasure policy to the VSD.
apply countermeasure policy policy-name
By default, no countermeasure policy is applied to a VSD.
Configuring the countermeasure packet sending interval
About this task
Perform this task to enable a sensor to send countermeasure packets in a channel if it has detected rogue devices in the channel. The sensor sends countermeasure packets in the channel only within scanning periods, and you can specify the interval at which sensors send countermeasure packets. For more information about channel scanning, see channel scanning configuration in Radio Resources Management Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter countermeasure policy view.
countermeasure policy policy-name
4. Specify the interval at which sensors send countermeasure packets.
countermeasure packet-sending-interval interval
By default, sensors send countermeasure packets every 30 milliseconds.
Enabling the enhanced countermeasure mode
About this task
Perform this task to prevent dual-band clients from roaming between the two radios sharing the same SSID on a rogue AP.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Enter countermeasure policy view.
countermeasure policy policy-name
4. Enable the enhanced countermeasure mode.
countermeasure enhance
By default, the enhanced countermeasure mode is not enabled.
Detecting clients with NAT configured
About this task
Perform this task to enable an AP to detect clients with NAT configured to prevent network sharing among clients.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or AP group view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Enter AP group view.
wlan ap-group group-name
3. Enable the AP to detect clients with NAT configured.
wlan nat-detect enable
By default:
¡ In AP view, an AP uses the configuration in AP group view.
¡ In AP group view, detection on clients with NAT configured is disabled.
4. Enable WIPS to take countermeasures against clients with NAT configured.
wlan nat-detect countermeasure
By default:
¡ In AP view, an AP uses the configuration in AP group view.
¡ In AP group view, WIPS does not take countermeasures against clients with NAT configured.
Configuring the alarm-ignoring feature
About this task
With this feature configured, WIPS does not trigger any alarms for wireless devices in the alarm-ignored device list.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Add the MAC address of a device to the alarm-ignored device list.
ignorelist mac-address mac-address
By default, no MAC address is added to the alarm-ignored device list.
Configuring APs to perform WIPS scanning while providing access services
About this task
This feature enhances the WIPS detection and protection capabilities but decreases the access service capability.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Configure APs to perform WIPS scanning while providing access services.
access-scan enable
By default, APs do not perform WIPS scanning while they are providing access services.
Configuring OUIs
About this task
An Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) is the first three bytes of a device's MAC address and is used to identify the vendor of the device.
After the device starts, it automatically imports OUIs in the default OUI configuration file to the OUI library.
You can also manually configure the OUI library as follows:
· Use the import oui command to import OUIs from an OUI configuration file to the OUI library.
The system will display the numbers of imported OUIs, updated OUIs, existing OUIs, and OUIs failed to be imported.
· Use the export oui command to export OUIs in the OUI library to an OUI configuration file.
The system will display the number of OUIs successfully exported and the number of OUIs failed to be exported.
Importing OUIs
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Import OUIs from an OUI configuration file to the OUI library.
import oui file-name
Exporting OUIs
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
wips
3. Export OUIs in the OUI library to an OUI configuration file.
export oui file-name
Enabling fast learning of client association entries
About this task
Client association entries are entries saved on the AC after a client associates with an AP.
If this feature is not enabled, the sensor can learn the client association entries only after a client is associated with an AP successfully. After this feature is enabled, the sensor can learn the client association entries during the association process.
If the sensor learned the client association entries during the association process, the sensor will update the entries every time it detects an association request or response between the AP and the client.
This feature improves the association efficiency but reduces the association accuracy. As a best practice, enable this feature only when fast attack detection and countermeasures are required in the network.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WIPS view.
Wips
3. Enter attack detection policy view.
detect policy policy-name
4. Enable fast learning of client association entries.
client-association fast-learn enable
By default, fast learning of client association entries is disabled.
Verifying and maintaining WIPS
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display information about all sensors.
display wips sensor
· Display WALN attack detection statistics collected from sensors.
display wips statistics [ receive | virtual-security-domain vsd-name ]
· Display information about countermeasures that WIPS has taken against rogue devices.
display wips virtual-security-domain vsd-name countermeasure record
· Display information about wireless devices detected in a VSD.
display wips virtual-security-domain vsd-name device [ ap [ adhoc | authorized | external | mesh | misconfigured | potential-authorized | potential-external | potential-rogue | rogue | uncategorized ] | client [ [ dissociative-client ] [ authorized | misassociation | unauthorized | uncategorized ] ] | mac-address mac-address ] [ verbose ]
· Display information about detected NAT-configured clients.
display wlan nat-detect [ mac-address mac-address ]
Perform clear tasks in user view.
· Delete all embedded OUIs in the OUI library.
reset wips embedded-oui
· Clear WALN attack detection statistics collected from all sensors.
reset wips statistics
· Clear learned AP or client entries for a VSD.
reset wips virtual-security-domain vsd-name { ap { all | mac-address mac-address} | client { all | mac-address mac-address } | all }
· Clear information about countermeasures that WIPS has taken against rogue devices.
reset wips virtual-security-domain vsd-name countermeasure record
· Clear information about detected NAT-configured clients.
WIPS configuration examples
Example: Configuring device classification and countermeasures
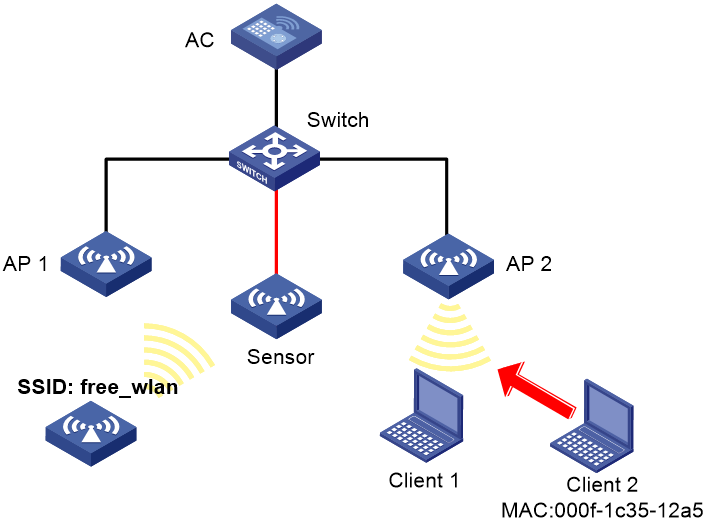
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, the sensor connects to the AC through the switch. AP 1 and AP 2 provide wireless services to clients through SSID abc. Perform the following tasks:
· Enable WIPS for the sensor.
· Configure wireless device classification to add MAC address 000f-1c35-12a5 to the static prohibited device list and SSID abc to the trusted SSID list.
· Configure countermeasures to enable WIPS to take countermeasures against potential-external APs and unauthorized clients.
Procedure
# Configure wireless services on the AC. (Details not shown.)
For more information about wireless service configuration, see "Configuring WLAN Access."
# Create a VSD named vsd1.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wips
[AC-wips] virtual-security-domain vsd1
[AC-wips-vsd-vsd1] quit
[AC-wips] quit
# Create an AP named Sensor and enable WIPS for the AP.
[AC] wlan ap Sensor model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-Sensor] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
[AC-wlan-ap-Sensor] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-Sensor-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-Sensor-radio-1] wips enable
[AC-wlan-ap-Sensor-radio-1] quit
#Add AP Sensor to VSD vsd1.
[AC-wlan-ap-Sensor] wips virtual-security-domain vsd1
[AC-wlan-ap-Sensor] quit
# Create a classification policy named class1, add the MAC address of Client 2 to the prohibited device list, and add SSID abc to the trusted SSID list.
[AC] wips
[AC-wips] classification policy class1
[AC-wips-cls-class1] block mac-address 000f-1c35-12a5
[AC-wips-cls-class1] trust ssid abc
[AC-wips-cls-class1] quit
# Apply classification policy class1 to VSD vsd1.
[AC-wips] virtual-security-domain vsd1
[AC-wips-vsd-vsd1] apply classification policy class1
[AC-wips-vsd-vsd1] quit
# Create a countermeasure policy named protect, and enable WIPS to take countermeasures against unauthorized clients and potential-external APs.
[AC-wips] countermeasure policy protect
[AC-wips-cms-protect] countermeasure unauthorized-client
[AC-wips-cms-protect] countermeasure potential-external-ap
[AC-wips-cms-protect] quit
# Apply countermeasure policy protect to VSD vsd1.
[AC-wips] virtual-security-domain vsd1
[AC-wips-vsd-vsd1] apply countermeasure policy protect
[AC-wips-vsd-vsd1] quit
[AC-wips] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display wireless device classification information for VSD vsd1.
[AC] display wips virtual-security-domain vsd1 device
Total 3 detected devices in virtual-security-domain vsd1
Class: Auth - authorization; Ext - extern; Mis - mistake;
Unauth - unauthorized; Uncate - uncategorized;
(A) - associate; (C) - config; (P) - potential
MAC address Type Class Duration Sensors Channel Status
00e0-fc00-5829 AP Auth 00h 10m 24s 1 149 Active
000f-e228-2528 AP Auth 00h 10m 04s 1 149 Active
000f-e223-1616 AP Ext(P) 00h 10m 46s 1 149 Active
000f-1c35-12a5 Client Unauth 00h 10m 02s 1 149 Active
000f-e201-0102 Client Auth 00h 10m 02s 1 149 Active
The output shows that the AP with MAC address 000f-e223-1616 is classified as a potential-external AP and the client with MAC address 000f-1c35-12a5 is classified as an unauthorized client.
# Display information about countermeasures that WIPS has taken against the devices.
[AC] display wips virtual-security-domain vsd1 countermeasure record
Total 2 times countermeasure, current 2 countermeasure record in virtual-security-domain vsd1
Reason: Attack; Ass - associated; Black - blacklist;
Class - classification; Manu - manual;
MAC address Type Reason Countermeasure AP Radio ID Time
00e0-fc00-5829 AP Class Sensor 1 2014-06-03/09:30:25
000f-e228-2528 AP Class Sensor 1 2014-06-03/19:31:56
000f-e223-1616 AP Class Sensor 1 2014-06-03/10:30:36
000f-1c35-12a5 Client Class Sensor 1 2014-06-03/09:13:26
000f-e201-0102 Client Class Sensor 1 2014-06-03/09:33:46
The output shows that WIPS has taken countermeasures against the unauthorized client with MAC address 000f-1c35-12a5 and the potential-external AP with MAC address 000f-e223-1616.
Example: Configuring malformed packet and flood attack detection
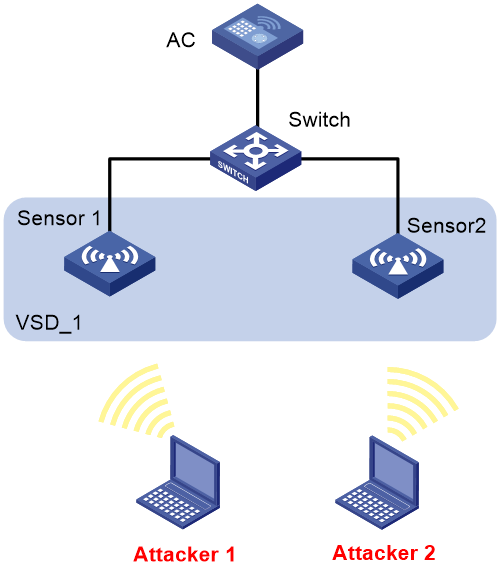
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4, configure the two APs that connect to the AC through the switch as sensors. Add Sensor 1 and Sensor 2 to VSD VSD_1. Configure malformed packet detection and flood attack detection to enable WIPS to trigger an alarm when it detects beacon flood attacks or malformed packets with duplicated IE.
Procedure
# Configure wireless services on the AC. (Details not shown.)
For more information about wireless service configuration, see "Configuring WLAN Access."
# Create an AP named sensor1 and enable WIPS for the AP.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan ap sensor1 model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1-radio-1] wips enable
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1-radio-1] return
# Create an AP named sensor2 and enable WIPS for the AP.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan ap sensor2 model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor2] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor2] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor2-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor2-radio-1] wips enable
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor2-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor2] quit
# Create a VSD named VSD_1.
[AC] wips
[AC-wips] virtual-security-domain VSD_1
[AC-wips-vsd-VSD_1] quit
# Create an attack detection policy named dtc1.
[AC-wips] detect policy dtc1
# Enable detection on malformed packets with duplicated IE, and set the quiet time to 50 seconds.
[AC-wips-dtc-dtc1] malformed duplicated-ie quiet 50
# Enable beacon flood attack detection, and set the statistics interval, threshold, and quiet time to 100 seconds, 200, and 50 seconds, respectively.
[AC-wips-dtc-dtc1] flood beacon interval 100 quiet 50 threshold 200
[AC-wips-dtc-dtc1] quit
# Apply attack detection policy dtc1 to VSD VSD_1.
[AC-wips] virtual-security-domain VSD_1
[AC-wips-vsd-VSD_1] apply detect policy dtc1
[AC-wips-vsd-VSD_1] quit
[AC-wips] quit
# Add AP sensor1 to VSD VSD_1.
[AC] wlan ap sensor1
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1] wips virtual-security-domain VSD_1
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1] quit
# Add AP sensor2 to VSD VSD_1.
[AC] wlan ap sensor2
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor2] wips virtual-security-domain VSD_1
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor2] return
Verifying the configuration
# Display packet statistics when WIPS does not detect any attacks in the WLAN. The output shows that no malformed packet or flood attack message exists.
<AC> display wips statistics receive
Information from sensor 1
Information about attack statistics:
Detected association-request flood messages: 0
Detected authentication flood messages: 0
Detected beacon flood messages: 0
Detected block-ack flood messages: 0
Detected cts flood messages: 0
Detected deauthentication flood messages: 0
Detected disassociation flood messages: 0
Detected eapol-start flood messages: 0
Detected null-data flood messages: 0
Detected probe-request flood messages: 0
Detected reassociation-request flood messages: 0
Detected rts flood messages: 0
Detected duplicated-ie messages: 0
Detected fata-jack messages: 0
Detected illegal-ibss-ess messages: 0
Detected invalid-address-combination messages: 0
Detected invalid-assoc-req messages: 0
Detected invalid-auth messages: 0
Detected invalid-deauth-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-disassoc-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-ht-ie messages: 0
Detected invalid-ie-length messages: 0
Detected invalid-pkt-length messages: 0
Detected large-duration messages: 0
Detected null-probe-resp messages: 0
Detected overflow-eapol-key messages: 0
Detected overflow-ssid messages: 0
Detected redundant-ie messages: 0
Detected AP spoof AP messages: 0
Detected AP spoof client messages: 0
Detected AP spoof ad-hoc messages: 0
Detected ad-hoc spoof AP messages: 0
Detected client spoof AP messages: 0
Detected weak IV messages: 0
Detected excess AP messages: 0
Detected excess client messages: 0
Detected sig rule messages: 0
Information from sensor 2
Information about attack statistics:
Detected association-request flood messages: 0
Detected authentication flood messages: 0
Detected beacon flood messages: 0
Detected block-ack flood messages: 0
Detected cts flood messages: 0
Detected deauthentication flood messages: 0
Detected disassociation flood messages: 0
Detected eapol-start flood messages: 0
Detected null-data flood messages: 0
Detected probe-request flood messages: 0
Detected reassociation-request flood messages: 0
Detected rts flood messages: 0
Detected duplicated-ie messages: 0
Detected fata-jack messages: 0
Detected illegal-ibss-ess messages: 0
Detected invalid-address-combination messages: 0
Detected invalid-assoc-req messages: 0
Detected invalid-auth messages: 0
Detected invalid-deauth-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-disassoc-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-ht-ie messages: 0
Detected invalid-ie-length messages: 0
Detected invalid-pkt-length messages: 0
Detected large-duration messages: 0
Detected null-probe-resp messages: 0
Detected overflow-eapol-key messages: 0
Detected overflow-ssid messages: 0
Detected redundant-ie messages: 0
Detected AP spoof AP messages: 0
Detected AP spoof client messages: 0
Detected AP spoof ad-hoc messages: 0
Detected ad-hoc spoof AP messages: 0
Detected client spoof AP messages: 0
Detected weak IV messages: 0
Detected excess AP messages: 0
Detected excess client messages: 0
Detected sig rule messages: 0
# Display packet statistics when WIPS detects beacon flood attacks and malformed packets with duplicated IE. The output shows that the number of detected messages is 28 for malformed packets with duplicated IE and the number of detected messages is 18 for beacon flood attacks.
<AC> display wips statistics receive
Information from sensor 1
Information about attack statistics:
Detected association-request flood messages: 0
Detected authentication flood messages: 0
Detected beacon flood messages: 18
Detected block-ack flood messages: 0
Detected cts flood messages: 0
Detected deauthentication flood messages: 0
Detected disassociation flood messages: 0
Detected eapol-start flood messages: 0
Detected null-data flood messages: 0
Detected probe-request flood messages: 0
Detected reassociation-request flood messages: 0
Detected rts flood messages: 0
Detected duplicated-ie messages: 0
Detected fata-jack messages: 0
Detected illegal-ibss-ess messages: 0
Detected invalid-address-combination messages: 0
Detected invalid-assoc-req messages: 0
Detected invalid-auth messages: 0
Detected invalid-deauth-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-disassoc-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-ht-ie messages: 0
Detected invalid-ie-length messages: 0
Detected invalid-pkt-length messages: 0
Detected large-duration messages: 0
Detected null-probe-resp messages: 0
Detected overflow-eapol-key messages: 0
Detected overflow-ssid messages: 0
Detected redundant-ie messages: 0
Detected AP spoof AP messages: 0
Detected AP spoof client messages: 0
Detected AP spoof ad-hoc messages: 0
Detected ad-hoc spoof AP messages: 0
Detected client spoof AP messages: 0
Detected weak IV messages: 0
Detected excess AP messages: 0
Detected excess client messages: 0
Detected sig rule messages: 0
Information from sensor 2
Information about attack statistics:
Detected association-request flood messages: 0
Detected authentication flood messages: 0
Detected beacon flood messages: 0
Detected block-ack flood messages: 0
Detected cts flood messages: 0
Detected deauthentication flood messages: 0
Detected disassociation flood messages: 0
Detected eapol-start flood messages: 0
Detected null-data flood messages: 0
Detected probe-request flood messages: 0
Detected reassociation-request flood messages: 0
Detected rts flood messages: 0
Detected duplicated-ie messages: 28
Detected fata-jack messages: 0
Detected illegal-ibss-ess messages: 0
Detected invalid-address-combination messages: 0
Detected invalid-assoc-req messages: 0
Detected invalid-auth messages: 0
Detected invalid-deauth-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-disassoc-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-ht-ie messages: 0
Detected invalid-ie-length messages: 0
Detected invalid-pkt-length messages: 0
Detected large-duration messages: 0
Detected null-probe-resp messages: 0
Detected overflow-eapol-key messages: 0
Detected overflow-ssid messages: 0
Detected redundant-ie messages: 0
Detected AP spoof AP messages: 0
Detected AP spoof client messages: 0
Detected AP spoof ad-hoc messages: 0
Detected ad-hoc spoof AP messages: 0
Detected client spoof AP messages: 0
Detected weak IV messages: 0
Detected excess AP messages: 0
Detected excess client messages: 0
Detected sig rule messages: 0
Example: Configuring signature-based attack detection
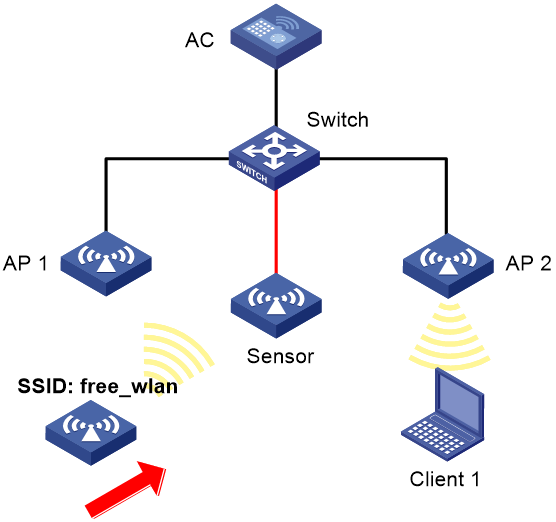
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, AP 1 and AP 2 provide wireless services for clients through SSID abc. Enable WIPS for the sensor, and configure a signature to enable WIPS to trigger an alarm when it detects beacon frames whose SSIDs are not abc.
Procedure
# Configure wireless services on the AC. (Details not shown.)
For more information about wireless service configuration, see "Configuring WLAN Access."
# Create an AP named sensor1 and enable WIPS for the AP.
<AC> system-view
[AC] wlan ap sensor1 model WA6320
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1-radio-1] wips enable
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1-radio-1] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1 ] quit
# Create a VSD named vsd1.
[AC] wips
[AC-wips] virtual-security-domain vsd1
[AC-wips] quit
# Add the AP sensor1 to the VSD vsd1.
[AC] wlan ap sensor1
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1] wips virtual-security-domain vsd1
[AC-wlan-ap-sensor1] quit
# Create signature 1, and configure a subsignature to match beacon frames and a subsignature to match frames whose SSIDs are not abc.
[AC] wips
[AC-wips] signature rule 1
[AC-wips-sig-rule-1] frame-type management frame-subtype beacon
[AC-wips-sig-rule-1] ssid not equal abc
[AC-wips-sig-rule-1] quit
# Create a signature policy named sig1, and bind signature 1 to signature policy sig1.
[AC-wips] signature policy sig1
[AC-wips-sig-sig1] apply signature rule 1
# Enable WIPS to detect packets that match the signature, and set the statistics collection interval, quiet time, and alarm threshold to 5 seconds, 60 seconds, and 60, respectively.
[AC-wips-sig-sig1] detect signature interval 5 quiet 60 threshold 60
[AC-wips-sig-sig1] quit
# Apply signature policy sig1 to VSD vsd1.
[AC] wips
[AC-wips] virtual-security-domain vsd1
[AC-wips-vsd-vsd1] apply signature policy sig1
[AC-wips-vsd-vsd1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the AC receives an alarm from the sensor when the sensor detects the wireless service with SSID free_wlan.
WIPS/5/WIPS_SIGNATURE: -VSD=vsd1-RuleID=1; Signature rule matched.
# Display attack detection information collected from sensors. The output shows that the number of detected messages is 26 for packets that match the signature.
[AC] display wips statistics receive
Information from sensor
Information about attack statistics:
Detected association-request flood messages: 0
Detected authentication flood messages: 0
Detected beacon flood messages: 0
Detected block-ack flood messages: 0
Detected cts flood messages: 0
Detected deauthentication flood messages: 0
Detected disassociation flood messages: 0
Detected eapol-start flood messages: 0
Detected null-data flood messages: 0
Detected probe-request flood messages: 0
Detected reassociation-request flood messages: 0
Detected rts flood messages: 0
Detected duplicated-ie messages: 0
Detected fata-jack messages: 0
Detected illegal-ibss-ess messages: 0
Detected invalid-address-combination messages: 0
Detected invalid-assoc-req messages: 0
Detected invalid-auth messages: 0
Detected invalid-deauth-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-disassoc-code messages: 0
Detected invalid-ht-ie messages: 0
Detected invalid-ie-length messages: 0
Detected invalid-pkt-length messages: 0
Detected large-duration messages: 0
Detected null-probe-resp messages: 0
Detected overflow-eapol-key messages: 0
Detected overflow-ssid messages: 0
Detected redundant-ie messages: 0
Detected AP spoof AP messages: 0
Detected AP spoof client messages: 0
Detected AP spoof ad-hoc messages: 0
Detected ad-hoc spoof AP messages: 0
Detected client spoof AP messages: 0
Detected weak IV messages: 0
Detected excess AP messages: 0
Detected excess client messages: 0
Detected sig rule messages: 26