- Table of Contents
-
- 07-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Security Overview
- 02-AAA Configuration
- 03-802.1X Configuration
- 04-MAC Authentication Configuration
- 05-Port Security Configuration
- 06-Public Key Configuration
- 07-PKI Configuration
- 08-SSH Configuration
- 09-SSL Configuration
- 10-User Isolation Configuration
- 11-Portal Configuration
- 12-IPsec Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-Port Security Configuration | 235.16 KB |
Setting port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses on a port
Setting the port security mode
Configuring port security features
Configuring intrusion protection
Configuring secure MAC addresses
Configuring port security for WLAN ports
Setting the port security mode of a WLAN port
Ignoring authorization information from the server
Displaying and maintaining port security
Port security configuration examples
userLoginSecure mode configuration example
macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt mode configuration example
userLoginSecureExt mode configuration example on a WLAN port
Cannot set the port security mode
Cannot configure secure MAC addresses
Cannot change port security mode when a user is online
Overview
Port security combines and extends 802.1X and MAC authentication to provide MAC-based network access control. It applies to networks that require different authentication methods for different users on a port, such as a WLAN.
Port security prevents unauthorized access to a network by checking the source MAC address of inboundtraffic and prevents access to unauthorized devices by checking the destination MAC address of outboundtraffic.
Port securitycan control MAC address learning and authentication on a port to make sure the port learns only source trusted MAC addresses.
A frame is illegal if its source MAC addresscannot be learned in a port security mode, or if it is from a client that has failed 802.1X or MAC authentication. The port security feature automatically takes a pre-defined action on illegal frames. This automatic mechanism enhances network security and reduces human intervention.
Port security is available on Ethernet and WLAN ports. Supportedport types depend on the command. For more information, see Security Command Reference.
For scenarios that require only 802.1X authentication or MAC authentication, H3C recommends you use the 802.1X authentication or MAC authentication feature rather than port security.
For more information about 802.1X and MAC authentication, see "Configuring 802.1X" and "Configuring MAC authentication."
Configuring port security
Port security supports the need to know (NTK) feature, intrusion protection, and port security traps.
NTK
NTKprevents traffic interception by checking the destination MAC address in outbound frames. The feature ensures that frames are sent only to hoststhat have passedauthentication or whose MAC addresseshave been learned or configured on the access device.
Intrusion protection
The intrusion protection feature checks the source MAC address in inbound framesfor illegal frames and takesapre-definedactionon each detected illegal frame. The actioncanbe disabling the port temporarily, disabling the port permanently, or blocking frames fromthe illegalMAC address for three minutes (not user configurable).
Port security traps
To monitor user behavior, configure the port security module to send traps for port security events such as login, logoff, and MAC authentication.
Port security modes
Port security supports the following categories of security mode:
· MAC learning control—IncludesautoLearn and secure. MAC address learning is permitted on portsin autoLearn mode and disabled on ports in secure mode.
· Authentication—ImplementsMAC authentication, 802.1X authentication, or a combination of the two authentication methods.
Upon receiving a frame, the port in a security mode searches the MAC address table for the source MAC address. If a match is found, the port forwards the frame. If no match is found, the port learns the MAC address or performs authentication,depending on the security mode. If the frame is illegal, the port takes thepre-defined NTK, intrusion protection, or trapping action.
The maximum number of users a port supports equals the maximum number of MAC addresses that port security allows or the maximum number of concurrent users the authentication modein use allows, whichever is smaller. For example, if 802.1X allows more concurrent users than port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses on the port in userLoginSecureExt mode, port security's limit takes effect.
Table 1 describes the port security modesand the security features.
|
Purpose |
Security mode |
Featuresthat can be triggered |
|
|
Turning off the port security feature |
noRestrictions(the default mode). In this mode, port security is disabled on the port and access to the port is not restricted. |
N/A |
|
|
autoLearn |
NTK/intrusion protection |
||
|
secure |
|||
|
userLogin |
N/A |
||
|
userLoginSecure |
NTK/intrusion protection |
||
|
userLoginSecureExt |
|||
|
userLoginWithOUI |
|||
|
macAddressWithRadius |
NTK/intrusion protection |
||
|
Performinga combination of MAC authentication and 802.1X authentication |
Or |
macAddressOrUserLoginSecure |
NTK/intrusion protection |
|
macAddressOrUserLoginSecureExt |
|||
|
Else |
macAddressElseUserLoginSecure |
||
|
macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt |
|||
|
|
TIP: · userLogin specifies 802.1X authentication and port-based access control. · macAddress specifies MAC authentication. · Else specifies that the authentication method before Else is applied first. If the authentication fails, whether to turn to the authentication method following Else depends on the protocol type of the authentication request. · Typically, in a security mode with Or, theauthenticationmethod to be used depends on the protocol type of the authentication request. For wireless users, the network access device always use 802.1X authentication first. · userLogin with Secure specifies 802.1X authentication and MAC-based access control. · Ext indicates allowing multiple 802.1X users to be authenticated and serviced at the same time. A security mode withoutExt allows only one user to pass 802.1X authentication. |
Controlling MAC address learning
1. autoLearn
A port in this mode can learn MAC addresses, and allows frames from learned or configured MAC addressesto pass. The automatically learned MAC addresses are secure MAC addresses. You can also configure secure MAC addresses by using the port-security mac-address security command. A secure MAC address never ages out by default.
When the number of secure MAC addresses reaches the upper limit, the port transitions tosecure mode.
The dynamic MAC address learning function in MAC address management is disabledon ports operating in autoLearn mode, but you can configure MAC addresses by using the mac-address dynamic and mac-address static commands.
2. secure
MAC addresslearning is disabled on aport in secure mode. You configure MAC addresses by using the mac-address staticand mac-address dynamic commands.For more information about configuring MAC address table entries, see Layer 2 Configuration Guide.
A port in secure mode allows only frames sourced from secure MAC addresses and manually configured MAC addresses to pass.
Performing 802.1X authentication
1. userLogin
A port in this mode performs 802.1X authentication and implements port-based access control. The port can service multiple 802.1X users. Once an 802.1X user passes authentication on the port, any subsequent 802.1X users can access the network through the port without authentication.
2. userLoginSecure
A port in this mode performs 802.1X authentication and implements MAC-based access control. The port services only one user passing 802.1X authentication.
3. userLoginSecureExt
This mode is similar to the userLoginSecure mode except that this mode supports multiple online 802.1X users.
4. userLoginWithOUI
This mode is similar to the userLoginSecure mode. The difference is that a port in this mode also permits frames from one user whose MAC address contains a specificOUI.
¡ For wired users, the port performs 802.1X authentication upon receiving 802.1X frames, and performs OUI check upon receiving non-802.1X frames.
¡ For wireless users, the port performs OUI check at first. If the OUI check fails, the port performs 802.1X authentication.
Performing MAC authentication
macAddressWithRadius: A port in this mode performs MAC authentication and services multiple users.
Performinga combination of MAC authentication and 802.1X authentication
1. macAddressOrUserLoginSecure
This mode is the combination of the macAddressWithRadius and userLoginSecure modes.
¡ For wiredusers, the port performs MAC authentication 30 seconds after receivingnon-802.1X frames and performs 802.1X authentication upon receiving 802.1Xframes.
¡ For wireless users, the port performs 802.1X authentication first. If 802.1X authentication fails, MAC authentication is performed.
2. macAddressOrUserLoginSecureExt
This mode is similar to the macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode except that thismode supportsmultiple 802.1Xand MAC authentication users.
3. macAddressElseUserLoginSecure
This mode is the combination of the macAddressWithRadius and userLoginSecure modes, with MAC authentication having a higher priority as the Else keyword implies.
¡ For wired users, the port performs MAC authentication 30 seconds after receivingnon-802.1X frames.
¡ For wireless users, the port performs MAC authentication upon receiving non-802.1X frames. Upon receiving 802.1X frames, the port performs MAC authentication, and if the MAC authentication fails, it performs 802.1X authentication.
4. macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt
This mode is similar to the macAddressElseUserLoginSecure mode except that this mode supportsmultiple 802.1Xand MAC authentication users as the keyword Ext implies.
|
|
NOTE: An OUI, as defined by the IEEE, is the first 24 bits of the MAC address, which uniquely identifies a device vendor. |
Support for WLAN
|
|
CAUTION: Do not configure static MAC address entries for wireless users that use the 802.1X or MAC authentication service. If the source MAC address and the VLAN of a wireless user match a static MAC address entry in the MAC address table, the user cannot pass 802.1X authentication or MAC authentication. |
Table 2 describes the port security modes that apply only to WLAN-BSS ports. These port security modes implementswireless access security at the linklayer.
Table 2 Port security modes for WLAN ports
|
Security mode |
Description |
Features that can be triggered |
|
presharedKey |
Auser must use a pre-configured static key, also called"the pre-shared key (PSK)," to negotiate the session key with the device and can access the networkonly after the negotiation succeeds. |
NTK/intrusion protection |
|
macAddressAndPresharedKey |
A user must pass MAC authentication,and then use the pre-configured PSK to negotiate with the device. Only when the negotiation succeeds, can the user access the network. |
|
|
userLoginSecureExtOrPresharedKey |
A user interacts with the device, choosingthe UserLoginSecuremode orusing the PSK to negotiate with the device. |
PSK users refer to users that have passed authentication in presharedKey mode. The maximum number of PSK users on a port varies with security modes.
· presharedKey mode—The maximum number of PSK users on the port isthe port specification limit on the number of wireless users or port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses, whichever is smaller.
· macAddressAndPresharedKey mode—The maximum number of PSK users on the port isthe MAC authentication feature's limit on the number of concurrent users or port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses, whichever is smaller.
· userLoginSecureExtOrPresharedKey mode—The number of PSK users on the port cannot exceed the port limit on the number of wireless users, the number of 802.1X users cannot exceed the 802.1X feature's limit on the number of concurrent users, and the total number of PSK and 802.1X users cannot exceed port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses on the port.
Configuration task list
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
|
Required. |
||
|
Setting port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses on a port |
Optional. |
|
|
Required. |
||
|
Optional. Configureone or more features as required. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
|
Required for WLAN ports. |
||
|
Optional. |
||
Enabling port security
When port security is enabled, you cannot manually enable 802.1X or MAC authentication, or change the access control mode or port authorization state. The port security automatically modifies these settings in different security modes.
Before you enable port security, disable 802.1X and MAC authentication globally.
To enable port security:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable port security. |
port-security enable |
By default, port security is enabled. |
You can use the undo port-security enable command to disable port security when no online users are present.
Enabling or disabling port security resets the following security settings to the default:
· 802.1X access control mode is MAC-based, and the port authorizationstate is auto.
· Port security mode is noRestrictions.
For more information aboutConfiguring 802.1X, see "Configuring 802.1X."
For more information about MAC authentication configuration, see "Configuring MAC authentication."
Setting port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses on a port
You can set the maximum number of MAC addresses that port security allows on a port for the following purposes:
· Controlling the number of concurrent users on the port. The maximum number of concurrent users on the port equals this limit or the limit of the authentication mode (802.1X for example) in use, whichever is smaller.
· Controlling the number of secure MAC addresses on the port in autoLearn mode.
The port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses on a portis independent of the MAC learning limit described in MAC address table configurationin the Layer 2 Configuration Guide.
To set the maximum number of secure MAC addresses allowed on a port:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interfaceinterface-typeinterface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the limit of port security on the number of MAC addresses. |
port-security max-mac-countcount-value |
Not limited by default. |
Setting the port security mode
After enabling port security, you can change the port security mode of a port only when the port is operating in noRestrictions (the default) mode. To change the port security mode for a port in any other mode, first use the undo port-security port-mode command to restore the default port security mode.
You can specify a port security mode when port security is disabled, but your configuration cannot take effect.
You cannot change the port security mode of a port when online users are present.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you seta port security mode for a port, complete the following tasks:
· Disable 802.1X and MAC authentication.
· Checkthat the port does not belong to any aggregation group.
· If you are configuring the autoLearn mode, set port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses. You cannot change the setting when the port is operating in autoLearn mode.
Configuration procedure
Toenablea port security mode:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Set an OUI value for user authentication. |
port-securityouioui-value index index-value |
Required for the userlogin-withoui mode. Not configured by default. To set multiple OUI values, repeat this step. |
|
3. Enter interface view. |
interfaceinterface-type interface-number |
· To specify the autoLearn, secure, userlogin, or userlogin-withOUI mode, you must enterLayer 2 Ethernet interface view. · To specify themac-and-psk, psk, or userlogin-secure-ext-or-pskmode, you must enter WLAN-BSS interface view. |
|
4. Setthe port security mode. |
port-securityport-mode { autolearn | mac-and-psk | mac-authentication | mac-else-userlogin-secure | mac-else-userlogin-secure-ext| psk |secure | userlogin | userlogin-secure | userlogin-secure-ext|userlogin-secure-ext-or-psk |userlogin-secure-or-mac | userlogin-secure-or-mac-ext | userlogin-withoui } |
By default, a port operates in noRestrictions mode. |
Configuring port security features
Configuring NTK
The NTK feature checks destination MAC addresses in outbound frames tomake sure frames areforwarded only to authenticated devices.Any unicastframe with an unknown destination MAC address is discarded. Not all port security modes support triggering the NTK feature. For more information, see Table 1.
The NTK feature supports the following modes:
· ntkonly—Forwards only unicast frames with authenticateddestinationMAC addresses.
· ntk-withbroadcasts—Forwards only broadcast frames and unicastframes with authenticateddestination MAC addresses.
· ntk-withmulticasts—Forwards only broadcast frames, multicast frames, and unicastframes with authenticateddestinationMAC addresses.
To configure the NTK feature:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interfaceinterface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the NTK feature. |
port-security ntk-mode { ntk-withbroadcasts | ntk-withmulticasts| ntkonly} |
Bydefault, NTK is disabled on a port and all frames are allowed to be sent. |
Configuring intrusion protection
Intrusion protection enables a device to take one of the following actions in response to illegal frames:
· blockmac—Adds the source MAC addresses of illegal frames to the blocked MAC addresses list and discards the frames. All subsequent frames sourced from a blocked MAC address will be dropped. A blocked MAC address is restored to normal state after being blocked for three minutes. The interval is fixed and cannot be changed.
· disableport—Disables the port until you bring it up manually.
· disableport-temporarily—Disables the port for a specificperiod of time. The period can be configured with the port-security timer disableport command.
On a port operating in either the macAddressElseUserLoginSecure mode or the macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt mode, intrusion protection is triggered only after both MAC authentication and 802.1X authentication fail for the same frame.
To configure the intrusion protection feature:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interfaceinterface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the intrusion protectionfeature. |
port-security intrusion-mode {blockmac |disableport | disableport-temporarily } |
By default, intrusion protection is disabled. The disableport keyword is not supported on a WLAN-BSS interface. |
|
4. Return to system view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
5. Set the silence timeout period during which a port remains disabled. |
port-security timerdisableporttime-value |
Optional. 20 seconds by default. |
Enabling port security traps
You can configure the port security module to send traps for the followingcategoriesof events:
· addresslearned—Learning of new MAC addresses.
· dot1xlogfailure/dot1xlogon/dot1xlogoff—802.1X authentication failure, success, and 802.1X user logoff.
· ralmlogfailure/ralmlogon/ralmlogoff—MAC authentication failure, MAC authentication user logon, and MAC authentication user logoff.
· intrusion—Detection of illegal frames.
Toenable port security traps:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable port security traps. |
port-security trap { addresslearned | dot1xlogfailure| dot1xlogoff | dot1xlogon | intrusion | ralmlogfailure | ralmlogoff | ralmlogon } |
By default, port security traps aredisabled. |
Configuring secure MAC addresses
Secure MAC addresses are configured or learned in autoLearn mode and can survive link down/up events. You can bind a secure MAC address to only one port in a VLAN.
|
|
IMPORTANT: When the maximum number of secure MAC address entries is reached, the port changes to secure mode, and no more secure MAC addresses can be added or learned. The port allows only frames sourced from a secure MAC address or a MAC address configuredby using the mac-address dynamic or mac-address static command to pass through. |
Secure MAC addresses fall into static, sticky and dynamic secure MAC addresses.
Table 3 A comparison of static, sticky, and dynamicsecure MAC addresses
|
Type |
Address sources |
Aging mechanism |
Can be saved and survive a device reboot? |
|
Static |
Manually added |
Not available. They never age out unless you manually remove them, change the port security mode, or disable the port security feature. |
Yes. |
|
Sticky |
Manually added, converted from dynamic secure MAC addresses, or automatically learned when the dynamic secure MAC function (port-security mac-address dynamic) is disabled. |
Sticky MAC addresses by defaultdo not age out, but you can configure an aging timer or use the aging timer togetherwith the inactivity aging function to delete old sticky MAC addresses: · If only an aging timer is configured, the aging timer counts up regardless of whether traffic data has been sent from the sticky MAC address. · If both an aging timer and the inactivity aging functionare configured, the aging timer restarts once traffic data is detected from the sticky MAC address. |
Yes. The secure MAC aging timer restarts at a reboot. |
|
Dynamic |
Converted from sticky MAC addresses or automatically learned after the dynamic secure MAC function is enabled. |
Same as sticky MAC addresses. |
No. All dynamic secure MAC addresses are lost at reboot. |
Configuration prerequisites
· Enable port security.
· Set port security's limit on the number of MAC addresses onthe port. Perform this task before you enable autoLearn mode.
· Set the port security mode to autoLearn.
Configuration procedure
To configure a secure MAC address:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Set the secureMAC aging timer. |
port-security timer autolearn aging time-value |
Optional. By default, secureMAC addresses do note age out, and you can remove them only by performing the undo port-security mac-address security command, changing the port security mode, or disabling the port security feature. |
|
3. Configure a secure MAC address. |
·
Approach 1 (in system view): · Approach 2 (in interface view): a. interfaceinterface-type interface-number b. port-security mac-address security[sticky] mac-address vlan vlan-id c. quit |
Use either approach. No secure MAC address exists by default. |
|
4. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet port view. |
Interface interface-typeinterface-number |
N/A |
|
5. Enableinactivity aging. |
port-security mac-address aging-type inactivity |
Optional. By default, the inactivity aging function is disabled. |
|
6. Enable the dynamic secure MAC function. |
port-security mac-address dynamic |
Optional. By default, sticky MAC addresses can be saved to the configuration file, and once saved, can survive a device reboot. |
Configuring port security for WLAN ports
Table 4 describes the key negotiationand PSK requirementsfor different port security modes on WLAN ports.
Table 4 Port security configuration for WLAN ports
|
Port security mode |
Description |
|
presharedKey, userLoginSecureExt, userLoginSecureExtOrPresharedKey, and macAddressAndPresharedKey |
OnWPA or RSN networks using any of these modes, key negotiation must be enabled. · In presharedKeyand macAddressAndPresharedKeymodes, you need to configure the PSK. · In userLoginSecureExt mode, you do not need to configure the PSK. · In userLoginSecureExtOrPresharedKey mode, you can determine whether to configure any PSK. |
|
Port security modes other than presharedKey, userLoginSecureExtOrPresharedKey, and macAddressAndPresharedKey |
No key negotiation is performed and you do not need to enable key negotiation. |
For more information about WLAN service templates, see WLANConfiguration Guide.
By default, an 802.1X-enabled access device periodically multicasts Identity EAP-Request packets out of ports to detect 802.1X clients and trigger authentication. To save the bandwidth of WLAN ports, H3C recommends you disable the multicast trigger function (see "Configuring 802.1X").
Setting the port security mode of a WLAN port
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interfaceinterface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set a port security mode for the WLAN port. |
port-securityport-mode { mac-and-psk | mac-authentication | mac-else-userlogin-secure | mac-else-userlogin-secure-ext| psk |userlogin-secure|userlogin-secure-ext|userlogin-secure-ext-or-psk| userlogin-secure-or-mac| userlogin-secure-or-mac-ext } |
By default, a port operates in noRestrictions mode. |
Enabling key negotiation
After a user passes 802.1Xauthentication, a WLAN-BSS port usesEAPOL-Key frames to negotiate the link-layer session keywith the user if the key negotiation function is enabled.
· If key negotiation is enabled, an authenticated user is allowed to access to the port only after the key negotiation succeeds.
· If key negotiation is disabled, a user can directly access the port after passing authentication.
Toenable key negotiation:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter WLAN-BSS interface view. |
interfaceinterface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable key negotiation of the 11key type. |
port-security tx-key-type 11key |
Disabled by default. |
Configuring a PSK
A PSK pre-configured on the device is used to negotiate the session key between the user and the device.
To configure a PSK:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter WLAN-BSSinterface view. |
interfaceinterface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure a PSK. |
port-security preshared-key { pass-phrase | raw-key }[ cipher | simple ]key |
By default, no PSK is configured. |
Ignoring authorization information from the server
You can configure a port to ignore the authorization information received from the server (an RADIUS server or the local device) after an 802.1X user or MAC authentication user passes authentication.
Toconfigure a port to ignore authorization information from the server:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interfaceinterface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Ignore the authorization information receivedfrom the authenticationserver. |
port-security authorization ignore |
By default, a port uses the authorization information receivedfrom the authentication server. |
Displaying and maintaining port security
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display port security configuration information, operation information, and statistics about one or more ports or all ports. |
display port-security [ interfaceinterface-list ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display information about secure MAC addresses. |
display port-security mac-address security [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display information about blocked MAC addresses. |
display port-security mac-address block [ interface interface-type interface-number] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display information about PSK users. |
display port-security preshared-key user [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
Port security configuration examples
userLoginSecure mode configuration example
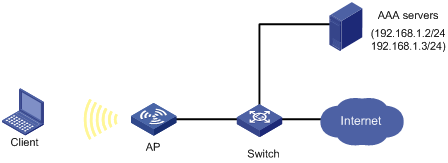
Network requirements
The WLAN client connects to the wireless port of the AP. The AP authenticates the client (using 802.1X client) by the RADIUS server. If the authentication succeeds, the client is authorized to access the Internet.
· RADIUS server 192.168.1.2/24 functions as the primary authentication server and the secondary accounting server, and RADIUS server 92.168.1.3/24 functions as the secondary authentication server and the primary accounting server. The shared key for authentication is name and that for accounting is money.
· All users use the default RADIUS scheme in the ISP domain named sun for authentication, authorization, and accounting. The domain can accommodate up to 30 users.
· The RADIUS server response timeout time is five seconds and the maximum number of RADIUS packet retransmission attempts isfive.The AP sends real-time accounting packets to the RADIUS server at an interval of 15 minutes, and sends usernames without domain names to the RADIUS server.
Configure port WLAN-BSS 1 of the AP to:
· Allow only authenticated 802.1X users' packets to pass through.
· Allows only one 802.1X user to log on.
Figure 1 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
|
|
NOTE: · The following configuration steps cover some AAA/RADIUS configuration commands. For more information, seeAAA in Security Command Reference. · Configuration steps on the host and RADIUS servers are not shown. · Do not use the Windows wireless client because it does support the service template of clear type for 802.1X authentication. Use other kind of 802.1X client in this example. |
# Enable port security.
<AP> system-view
[AP]port-security enable
# Create service template 108 of the clear type, configure its SSID as userLoginSecure, enableopen system authentication, and enable the service template.
[AP] wlan service-template 108 clear
[AP-wlan-st-108] ssid userLoginSecure
[AP-wlan-st-108] authentication-method open-system
[AP-wlan-st-108] service-template enable
[AP-wlan-st-108] quit
# Create a WLAN-BSS interface and set its port security mode to userLoginSecure.
[AP] interface wlan-bss 1
[AP-WLAN-BSS1]port-security port-mode userlogin-secure
[AP-WLAN-BSS1] quit
# Bind interface WLAN-BSS 1 with service template 108on interface WLAN-Radio 1/0/1.
[AP] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[AP-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] service-template 108 interface wlan-bss1
[AP-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] quit
# Configure a RADIUS scheme named radsun.
<AP> system-view
[AP]radius scheme radsun
[AP-radius-radsun]primary authentication 192.168.1.2
[AP-radius-radsun]primary accounting 192.168.1.3
[AP-radius-radsun]secondary authentication 192.168.1.3
[AP-radius-radsun]secondary accounting 192.168.1.2
[AP-radius-radsun]key authentication name
[AP-radius-radsun]key accounting money
[AP-radius-radsun]timer response-timeout 5
[AP-radius-radsun]retry 5
[AP-radius-radsun]timer realtime-accounting 15
[AP-radius-radsun]user-name-format without-domain
[AP-radius-radsun]quit
# Configure an authentication domain named sun.
[AP]domain sun
[AP-isp-sun]authentication default radius-scheme radsun
[AP-isp-sun]authorization default radius-scheme radsun
[AP-isp-sun]accounting default radius-scheme radsun
[AP-isp-sun]access-limit enable 30
[AP-isp-sun] quit
# Configure the authentication domainsun as the default domain.
[AP] domain default enable sun
Verifying the configuration
# Display the configuration information of the RADIUS scheme named radsun.
[AP]display radius scheme radsun
SchemeName : radsun
Index : 0 Type : standard
Primary Auth Server:
IP: 192.168.1.2 Port: 1812 State: active
Encryption Key : N/A
Probe username : N/A
Probe interval : N/A
Primary Acct Server:
IP: 192.168.1.3 Port: 1813 State: active
Encryption Key : N/A
Probe username : N/A
Probe interval : N/A
Second Auth Server:
IP: 192.168.1.3 Port: 1812 State: active
Encryption Key : N/A
Probe username : N/A
Probe interval : N/A
Second Acct Server:
IP: 192.168.1.2 Port: 1813 State: active
Encryption Key : N/A
Probe username : N/A
Probe interval : N/A
Auth Server Encryption Key : ******
Acct Server Encryption Key : ******
Accounting-On packet disable, send times : 50 , interval : 3s
Interval for timeout(second) : 5
Retransmission times for timeout : 5
Interval for realtime accounting(minute) : 15
Retransmission times of realtime-accounting packet : 5
Retransmission times of stop-accounting packet : 500
Quiet-interval(min) : 5
Username format : without-domain
Data flow unit : Byte
Packet unit : one
# Display the configuration information of the ISP domain named sun.
[AP] display domain sun
Domain: sun
State: Active
Access-limit: 30
Accounting method: Required
Default authentication scheme : radius:radsun
Default authorization scheme : radius:radsun
Default accounting scheme : radius:radsun
Domain User Template:
Idle-cut : Disabled
Session-time : exclude-idle-time
Self-service : Disabled
Authorization attributes:
# Display port security configuration information.
[AP] display port-security interface wlan-bss 1
Equipment port-security is enabled
Trap is disabled
Disableport Timeout: 20s
OUI value:
WLAN-BSS1 is link-up
Port mode is userLoginSecure
NeedToKnow mode is disabled
Intrusion Protection mode is NoAction
Max MAC address number is not configured
Stored MAC address number is 0
Authorization is permitted
After an 802.1X user gets online, you can see that the number of secure MAC addresses is 1.
# Display 802.1X user information.
[AP] display dot1x interface wlan-bss 1
Equipment 802.1X protocol is enabled
EAP authentication is enabled
Proxy trap checker is disabled
Proxy logoff checker is disabled
Configuration: Transmit Period 30 s, Handshake Period 15 s
Quiet Period 60 s, Quiet Period Timer is disabled
Supp Timeout 30 s, Server Timeout 100 s
Reauth Period 3600 s
The maximal retransmitting times 2
The maximum 802.1X user resource number is 128 per slot
Total current used 802.1X resource number is 1
WLAN-BSS1 is link-up
802.1X protocol is enabled
Proxy trap checker is disabled
Proxy logoff checker is disabled
Handshake is enabled
Periodic reauthentication is disabled
The port is an authenticator
Authentication Mode is Auto
Port Control Type is Mac-based
802.1X Multicast-trigger is enabled
Mandatory authentication domain: NOT configured
Guest VLAN: NOT configured
Auth-Fail VLAN: NOT configured
Max number of on-line users is 128
EAPOL Packet: Tx 188, Rx 55
Sent EAP Request/Identity Packets : 129
EAP Request/Challenge Packets: 14
EAP Success Packets: 2, Fail Packets: 37
Received EAPOL Start Packets : 10
EAPOL LogOff Packets: 3
EAP Response/Identity Packets : 21
EAP Response/Challenge Packets: 20
Error Packets: 0
1. Authenticated user : MAC address: 000e-35b2-8be9
Controlled User(s) amount to 1
macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt mode configuration example
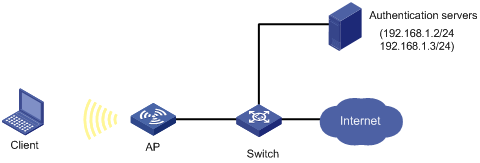
Network requirements
The WLAN client connects to the wireless port of the AP. The AP authenticates the client by the RADIUS server. If the authentication succeeds, the client is authorized to access the Internet.
Configure port WLAN-BSS1 of the APto:
· Allows multiple concurrent MAC authenticated users to log on.
· For 802.1X users, perform MAC authentication first and then, if MAC authentication fails, 802.1X authentication. Allow only one 802.1X user to log on.
· Use MAC-based accounts for MAC authentication. The MAC addresses must be hyphenated and in lower case.
· Set the total number of MAC authenticated users and 802.1X-authenticated users to 64.
· Enable NTK to prevent frames from being sent to unknown MAC addresses.
Figure 2 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
|
|
NOTE: · Configurations about RADIUS scheme and ISP domain are similar to those described in"userLoginSecure mode configuration example."(Details not shown.) · Configurations on the host and RADIUS servers are not shown. · Do not use the Windows wireless client because it does support the service template of clear type for 802.1X authentication. Use other kind of 802.1X client in this example. |
# Enable port security.
<AP> system-view
[AP] port-security enable
# Create service template 108 of the clear type, configure its SSID as macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt, enableopen system authentication, and enable the service template.
[AP] wlan service-template 108 clear
[AP-wlan-st-108] ssid macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt
[AP-wlan-st-108] authentication-method open-system
[AP-wlan-st-108] service-template enable
[AP-wlan-st-108] quit
# Create a WLAN-BSS interface, and set the maximum number of secure MAC addresses on the port to 64.
[AP] interface wlan-bss1
[AP-WLAN-BSS1]port-security max-mac-count 64
# Specify the port security mode as macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt.
[AP-WLAN-BSS1]port-security port-mode mac-else-userlogin-secure-ext
# Set the NTK mode of the port to ntkonly.
[AP-WLAN-BSS1]port-security ntk-mode ntkonly
[AP-WLAN-BSS1] quit
# Bind interface WLAN-BSS 1 with service template 108.
[AP] interface wlan-radio1/0/1
[AP-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] service-template 108 interface wlan-bss1
[AP-WLAN-Radio1/0/1] quit
# Use MAC-based user accounts for MAC authentication users, and each MAC address must be hyphenated.
[AP]mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address with-hyphen
# Configure an ISP domain named sun for MAC authentication.
[AP] mac-authentication domain sun
Verifying the configuration
# Display port security configuration information.
<AP>display port-security interface wlan-bss1
Equipment port-security is enabled
Trap is disabled
Disableport Timeout: 20s
OUI value:
WLAN-BSS1 is link-up
Port mode is macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt
NeedToKnow mode is NeedToKnowOnly
Intrusion Protection mode is NoAction
Max MAC address number is 64
Stored MAC address number is 0
Authorization is permitted
# Display MAC authentication information. (Suppose you have configured a MAC user account with the username 00-0e-35-b2-8b-e9 on the server.)
<AP>display mac-authentication interface wlan-bss 1
MAC address authentication is enabled.
User name format is MAC address in lowercase, like xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx
Fixed username:aaa
Fixed password:******
Offline detect period is 300s
Quiet period is 60s
Server response timeout value is 100s
The max allowed user number is 128 per slot
Current user number amounts to 1
Current domain is sun
Silent MAC User info:
MAC Addr From Port Port Index
WLAN-BSS1 is link-up
MAC address authentication is enabled
Authenticate success: 1, failed: 13
Max number of on-line users is 128
Current online user number is 1
MAC Addr Authenticate State Auth Index
000e-35b2-8be9 MAC_AUTHENTICATOR_SUCCESS 18
# If no MAC user account with the username 00-21-27-08-B5-0F is configured on the server. The user fails MAC authentication, and the passes 802.1X authentication. Display 802.1X authentication information.
<AP>display dot1x interface wlan-bss 1
Equipment 802.1X protocol is enabled
CHAP authentication is enabled
Proxy trap checker is disabled
Proxy logoff checker is disabled
Configuration: Transmit Period 30 s, Handshake Period 15 s
Quiet Period 60 s, Quiet Period Timer is disabled
Supp Timeout 30 s, Server Timeout 100 s
Reauth Period 3600 s
The maximal retransmitting times 2
The maximum 802.1X user resource number is 128 per slot
Total current used 802.1X resource number is 1
WLAN-BSS1 is link-up
802.1X protocol is enabled
Proxy trap checker is disabled
Proxy logoff checker is disabled
Handshake is disabled
Periodic reauthentication is disabled
The port is an authenticator
Authentication Mode is Auto
Port Control Type is Mac-based
802.1X Multicast-trigger is disabled
Mandatory authentication domain: NOT configured
Max number of on-line users is 128
EAPOL Packet: Tx 19, Rx 7
Sent EAP Request/Identity Packets : 14
EAP Request/Challenge Packets: 2
EAP Success Packets: 1, Fail Packets: 2
Received EAPOL Start Packets : 1
EAPOL LogOff Packets: 0
EAP Response/Identity Packets : 4
EAP Response/Challenge Packets: 1
Error Packets: 0
1. Authenticated user : MAC address: 0021-2708-b50f
Controlled User(s) amount to 1
userLoginSecureExt mode configuration example on a WLAN port
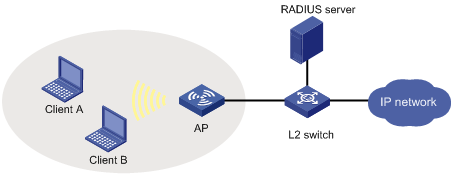
Network requirements
WLAN Clients connect to the wireless port of the AP. The AP uses the RADIUS server to authenticate its clients. If the authentication for a client succeeds, key negotiation is performed. If key negotiation succeeds, the client is authorized to access the network resources.
Figure 3 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
|
|
NOTE: · The following configuration steps cover some AAA/RADIUS configuration commands. For more information about the commands, seeAAA in Security Command Reference. · Configuration steps on the clients and RADIUS server are not shown. |
1. Perform RADIUS-related configurations. See relevant steps in "userLoginSecure mode configuration example."
2. Configure port security:
# Enable port security.
<AP> system-view
[AP]port-security enable
# Set the 802.1X authentication method to EAP.
[AP]dot1x authentication-method eap
# Enter the view of port WLAN-BSS 1.
[AP] interface wlan-bss 1
# Set the port security mode to userLoginSecureExt.
[AP-WLAN-BSS1]port-security port-mode userlogin-secure-ext
# Enable key negotiation on the port.
[AP-WLAN-BSS1]port-security tx-key-type 11key
# Disable the online handshake function and 802.1X multicast trigger function.
[AP-WLAN-BSS1]undo dot1x handshake
[AP-WLAN-BSS1]undo dot1x multicast-trigger
[AP-WLAN-BSS1] quit
3. Configure the WLAN service template:
# Create service template 1 of the crypto type, configure its SSID as sectest, and enableopen system authentication.
[AP]wlan service-template 1 crypto
[AP-wlan-st-1]ssid sectest
[AP-wlan-st-1]authentication-method open-system
# Enable the CCMP cipher suite, enable the RSN-IE in the beacon and probe responses, and enable the service template.
[AP-wlan-st-1]cipher-suite ccmp
[AP-wlan-st-1]security-ie rsn
[AP-wlan-st-1]service-template enable
[AP-wlan-st-1] quit
# Bind interface WLAN-BSS 1 with service template 1.
[AP] interface wlan-radio 1/0/1
[AP-WLAN-Radio1/0/1]service-template 1 interface wlan-bss 1
Verifying the configuration
# Display port security configuration information.
<AP>display port-security interface wlan-bss1
Equipment port-security is enabled
Trap is disabled
Disableport Timeout: 20s
OUI value:
WLAN-BSS1 is link-up
Port mode is userLoginSecureExt
NeedToKnow mode is disabled
Intrusion Protection mode is NoAction
Max MAC address number is not configured
Stored MAC address number is 0
Authorization is permitted
# If a user comes online, use the display connection command and the display wlan client command to view information about the user.
<AP>display connection ucibindex 1
Index=1 , Username=test@sun
MAC=00-17-9A-00-7B-2F
IP=40.1.1.5
IPv6=N/A
Access=8021X ,AuthMethod=EAP
Port Type=Wireless-802.11,Port Name=WLAN-BSS1
Initial VLAN=1, Authorization VLAN=N/A
ACL Group=Disable
User Profile=N/A
CAR=Disable
Priority=Disable
Accounting Username=test@sun
SessionTimeout=60(s), Terminate-Action=Radius-Request
Start=2011-06-30 17:58:44 ,Current=2011-06-30 18:47:59 ,Online=00h49m09s
Total 1 connection matched.
<AP>display wlan client
Total Number of Clients : 1
Client Information
SSID: sectest
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC Address User Name APID/RID IP Address VLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0017-9a00-7b2f test 1 /1 40.1.1.5 1
Troubleshooting port security
Cannot set the port security mode
Symptom
Cannot set the port security mode.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]port-security port-mode autolearn
Error:When we change port-mode, we should first change it to noRestrictions, then change it to the other.
Analysis
For portsoperatingin a port security mode other than noRestrictions, you cannot change the port security modedirectly using the port-security port-mode command.
Solution
Set the port security mode to noRestrictions first.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo port-security port-mode
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security port-mode autolearn
Cannot configure secure MAC addresses
Symptom
Cannot configure secure MAC addresses.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security mac-address security 1-1-2 vlan 1
Error: Security MAC address configuration failed.
Error:Can not operate security MAC address for current port mode is not autoLearn!
Analysis
Secure MAC addresses can be configured only on portsoperating in autoLearn mode.
Solution
Set the port security mode to autoLearn.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo port-security port-mode
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]port-security max-mac-count 64
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]port-security port-mode autolearn
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]port-security mac-address security 1-1-2 vlan 1
Cannot change port security mode when a user is online
Symptom
Port security mode cannot be changed when an 802.1X authenticated or MAC authenticated user is online.
[AP-WLAN-BSS1] undo port-security port-mode
Error:Cannot configure port-security for there is 802.1X user(s) on line on port WLAN-BSS1
Analysis
Changing port security mode is not allowed when an 802.1X authenticated or MAC authenticated user is online.
Solution
Disable the service template that is associated with the wireless interface to disconnect the user from the port, and then change the port security mode.
[AP-WLAN-BSS1] quit
[AP] wlan service-template 1
[AP-wlan-st-1]service-template disable
[AP-wlan-st-1] quit
[AP] interface wlan-bss 1
[AP-WLAN-BSS 1] undo port-security port-mode
