- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Text | 8.19 MB |
Installation safety recommendations
Installation site requirements
Airflow direction of the server
Temperature and humidity requirements
Equipment room height requirements
Corrosive gas concentration requirements
Installing or removing the server
Installing cable management brackets
Connecting a mouse, keyboard, and monitor
Removing the server from a rack
Powering on and powering off the server
Configuring basic BIOS settings
Installing the operating system and hardware drivers
Installing the operating system
Replacing riser cards and PCIe modules
Removing a riser card and a PCIe module
Installing a riser card and a PCIe module
Installing PCIe modules and a riser card on PCIe riser connector 3
Replacing a storage controller and a power fail safeguard module
Removing a standard storage controller and a power fail safeguard module
Installing a standard storage controller and a power fail safeguard module
Adjusting the length of the riser card
Replacing an OCP network adapter
Replacing a standard PCIe network adapter
Replacing a SATA M.2 SSD and a SATA M.2 SSD expander module
Removing a SATA M.2 SSD and a SATA M.2 SSD expander module
Installing a SATA M.2 SSD expander module and a SATA M.2 SSD
Replacing a dual SD card extended module
Removing a dual SD card extended module
Installing a dual SD card extended module
Replacing the LCD smart management module
Removing the LCD smart management module
Install the LCD smart management module
Replacing a chassis air baffle
Installing and setting up a TCM or TPM
Installation and setup flowchart
Enabling the TCM or TPM in the BIOS
Configuring encryption in the operating system
Removing and installing a blank
Removing and installing a blank
Connecting the SATA M.2 SSD cable
Connecting the OCP 3.0 ×16 network adapter cable
Connecting the PCIe signal cables
Connecting supercapacitor extension cables
Connecting cables to chassis ears
Connecting the LCD smart management module cable
Monitoring the temperature and humidity in the equipment room
Safety information
Safety sign conventions
To avoid bodily injury or damage to the server or its components, make sure you are familiar with the safety signs on the server chassis or its components.
|
Sign |
Description |
|
Circuit or electricity hazards are present. Only H3C authorized or professional server engineers are allowed to service, repair, or upgrade the server. To avoid bodily injury or damage to circuits, do not open any components marked with the electrical hazard sign unless you have authorization to do so. |
|
|
Electrical hazards are present. Field servicing or repair is not allowed. To avoid bodily injury, do not open any components with the field-servicing forbidden sign in any circumstances. |
|
|
The RJ-45 ports on the server can be used only for Ethernet connections. To avoid electrical shocks, fire, or damage to the equipment, do not connect an RJ-45 port to a telephone. |
|
|
The surface or component might be hot and present burn hazards. To avoid being burnt, allow hot surfaces or components to cool before touching them. |
|
|
The server or component is heavy and requires more than one people to carry or move. To avoid bodily injury or damage to hardware, do not move a heavy component alone. In addition, observe local occupational health and safety requirements and guidelines for manual material handling. |
|
|
The server is powered by multiple power supplies. To avoid bodily injury from electrical shocks, make sure you disconnect all power supplies if you are performing offline servicing. |
Power source recommendations
Power instability or outage might cause data loss, service disruption, or damage to the server in the worst case.
To protect the server from unstable power or power outage, use uninterrupted power supplies (UPSs) to provide power for the server.
Installation safety recommendations
To avoid bodily injury or damage to the server, read the following information carefully before you operate the server.
General operating safety
To avoid bodily injury or damage to the server, follow these guidelines when you operate the server:
· Only H3C authorized or professional server engineers are allowed to install, service, repair, operate, or upgrade the server.
· Place the server on a clean, stable table or floor for servicing.
· Make sure all cables are correctly connected before you power on the server.
· To avoid being burnt, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them.
Electrical safety
|
WARNING! If you put the server in standby mode (system power LED in amber) with the power on/standby button on the front panel, the power supplies continue to supply power to some circuits in the server. To remove all power for servicing safety, you must first press the button, wait for the system to enter standby mode, and then remove the power cords from the server. |
To avoid bodily injury or damage to the server, follow these guidelines:
· Always use the power cords that came with the server.
· Do not use the power cords that came with the server for any other devices.
· Power off the server when installing or removing any components that are not hot swappable.
Rack mounting recommendations
To avoid bodily injury or damage to the equipment, follow these guidelines when you rack mount a server:
· Mount the server in a standard 19-inch rack.
· Make sure the leveling jacks are extended to the floor and the full weight of the rack rests on the leveling jacks.
· Couple the racks together in multi-rack installations.
· Load the rack from the bottom to the top, with the heaviest hardware unit at the bottom of the rack.
· Get help to lift and stabilize the server during installation or removal, especially when the server is not fastened to the rails. As a best practice, a minimum of two people are required to safely load or unload a rack. A third person might be required to help align the server if the server is installed higher than check level.
· For rack stability, make sure only one unit is extended at a time. A rack might get unstable if more than one server unit is extended.
· Make sure the rack is stable when you operate a server in the rack.
· To maintain correct airflow and avoid thermal damage to the server, use blank panels to fill empty rack units.
ESD prevention
Preventing electrostatic discharge
To prevent electrostatic damage, follow these guidelines:
· Transport or store the server with the components in antistatic bags.
· Keep the electrostatic-sensitive components in separate antistatic bags until they arrive at an ESD-protected area.
· Place the components on a grounded surface before removing them from their antistatic bags.
· Avoid touching pins, leads, or circuitry.
Grounding methods to prevent electrostatic discharge
The following are grounding methods that you can use to prevent electrostatic discharge:
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Take adequate personal grounding measures, including wearing antistatic clothing and static dissipative shoes.
· Use conductive field service tools.
· Use a portable field service kit with a folding static-dissipating work mat.
Cooling performance
Poor cooling performance might result from improper airflow and poor ventilation and might cause damage to the server.
To ensure good ventilation and proper airflow, follow these guidelines:
· Install blanks if the following module slots are empty:
¡ Drive bays.
¡ Fan bays.
¡ PCIe slots.
¡ Power supply slots.
· Do not block the ventilation openings in the server chassis.
· To avoid thermal damage to the server, do not operate the server for long periods in any of the following conditions:
¡ Access panel open or uninstalled.
¡ Air baffles uninstalled.
¡ PCIe slots, drive bays, fan bays, or power supply slots empty.
Battery safety
The server's system board contains a system battery, which is designed with a lifespan of 3 to 5 years.
If the server no longer automatically displays the correct date and time, you might need to replace the battery. When you replace the battery, follow these safety guidelines:
· Do not attempt to recharge the battery.
· Do not expose the battery to a temperature higher than 60°C (140°F).
· Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts, or dispose of the battery in fire or water.
· Dispose of the battery at a designated facility. Do not throw the battery away together with other wastes.
Preparing for installation
Prepare a rack that meets the rack requirements and plan an installation site that meets the requirements for space and airflow, temperature, humidity, equipment room height, cleanliness, and grounding.
Rack requirements
|
IMPORTANT: To avoid affecting the server chassis, install power distribution units (PDUs) with the outputs facing backwards. If you install PDUs with the outputs facing the inside of the server, perform onsite survey to make sure the cables won't affect the server rear. |
The server is 2U high. The rack for installing the server must meet the following requirements:
· A standard 19-inch rack.
· A clearance of more than 50 mm (1.97 in) between the rack front posts and the front rack door.
· A minimum of 1200 mm (47.24 in) in depth as a best practice. For installation limits for different rack depth, see Table 2.
Table 2 Installation limits for different rack depths
|
Rack depth |
Installation limits |
|
1000 mm (39.37 in) |
· The H3C cable management arm (CMA) is not supported. · A clearance of 60 mm (2.36 in) is reserved from the server rear to the rear rack door for cabling. · The slide rails and PDUs might hinder each other. Perform onsite survey to determine the PDU installation location and the proper PDUs. If the PDUs hinder the installation and movement of the slide rails anyway, use other methods to support the server, a tray for example. |
|
1100 mm (43.31 in) |
Make sure the CMA does not hinder PDU installation at the server rear before installing the CMA. If the CMA hinders PDU installation, use a deeper rack or change the installation locations of PDUs. |
|
1200 mm (47.24 in) |
Make sure the CMA does not hinder PDU installation or cabling. If the CMA hinders PDU installation or cabling, change the installation locations of PDUs. For detailed installation suggestions, see Figure 1. |
Figure 1 Installation suggestions for a 1200 mm deep rack (top view)
|
(1) 1200 mm (47.24 in) rack depth |
|
(2) A minimum of 50 mm (1.97 in) between the front rack posts and the front rack door |
|
(3) 780 mm (30.71 in) between the front rack posts and the rear of the chassis, including power supply handles at the server rear (not shown in the figure) |
|
(4) 800 mm (31.50 in) server depth, including chassis ears |
|
(5) 960 mm (37.80 in) between the front rack posts and the CMA |
|
(6) 860 mm (33.86 in) between the front rack posts and the rear ends of the slide rails |
Installation site requirements
Airflow direction of the server
Figure 2 Airflow direction of the server

|
(1) to (4) Directions of the airflow into the chassis and power supplies |
|
(5) Direction of the airflow out of the power supplies |
|
(6) Direction of the airflow out of the chassis |
Temperature and humidity requirements
To ensure correct operation of the server, make sure the room temperature and humidity meet the requirements as described in "Appendix A Server specifications."
Equipment room height requirements
To ensure correct operation of the server, make sure the equipment room height meets the requirements as described in "Appendix A Server specifications."
Corrosive gas concentration requirements
Corrosive gases can accelerate corrosion and aging of metal components and even cause server failure. Table 3 describes common corrosive gases and their sources.
Table 3 Common corrosive gases and their sources
|
Corrosive gas |
Sources |
|
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) |
Geothermal emissions, microbiological activities, fossil fuel processing, wood pulping, sewage treatment, combustion of fossil fuel, auto emissions, ore smelting, and sulfuric acid manufacture. |
|
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) and sulfur trioxide (SO3) |
Combustion of fossil fuel, auto emissions, ore smelting, sulfuric acid manufacture, and tobacco smoke. |
|
Sulphur (S) |
Foundries and sulfur manufacture. |
|
Hydrogen Fluoride (HF) |
Fertilizer manufacture, aluminum manufacture, ceramics manufacture, steel manufacture, electronics device manufacture, and fossil fuel. |
|
Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) |
Automobile emissions, fossil fuel combustion, microbes, and chemical industry. |
|
Ammonia (NH3) |
Microbes, sewage, fertilizer manufacture, geothermal steam, refrigeration equipment, cleaning products, and reproduction (blueprint) machines. |
|
Carbonic oxide (CO) |
Combustion, automobile emissions, microbes, trees, and wood pulping. |
|
Chlorine (Cl2) and chlorine dioxide (ClO2) |
Chlorine manufacture, aluminum manufacture, papermills, refuse decomposition, and cleaning products. |
|
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) |
Automobile emissions, combustion, oceanic processes, and polymer combustion. |
|
Hydrobromic acid (HBr) and hydroiodic acid (HI) |
Automobile emissions. |
|
Ozone (O3) |
Atmospheric photochemical processes mainly involving nitrogen oxides and oxygenated hydrocarbons, automotive emissions, and electrostatic filters. |
|
Hydrocarbons (CnHn) |
Automobile emissions, fossil fuel processing, tobacco smoke, water treatment, microbes, paper mill, and many other sources, both natural and industrial. |
Requirements of corrosive gas concentration vary by server model. For information about the requirements, see the installation guide of the server.
Requirements for the data center equipment room
As a best practice, make sure the corrosive gas concentration for the data center equipment room meets the requirements of severity level G1 of ANSI/ISA 71.04-1985. The rate of copper corrosion product thickness growth must be less than 300 Å/month, and the rate of silver corrosion product thickness growth must be less than 200 Å/month. Angstrom (Å) is a metric unit of length equal to one ten-billionth of a meter.
To meet the copper and silver corrosion rates stated in severity level G1, make sure the corrosive gases in the equipment room do not exceed the concentration limits as shown in Table 4.
Table 4 Corrosive gas concentration limits in the data center equipment room
|
Corrosive gas |
Concentration (ppb) |
Remarks |
|
H2S |
<3 |
The concentration limits are calculated based on the reaction results of the gases in the equipment room with a relative humidity less than 50%. If the relative humidity of the equipment room increases by 10%, the severity level of ANSI/ISA 71.04-1985 to be meet must also increase by 1. |
|
SO2, SO3 |
<10 |
|
|
Cl2 |
<1 |
|
|
NOx |
<50 |
|
|
HF |
<1 |
|
|
NH3 |
<500 |
|
|
O3 |
<2 |
|
|
NOTE: Part per billion (ppb) is a concentration unit. 1 ppb represents a volume-to-volume ratio of 1 to 100000000. |
Requirements for the non-data center equipment room
The corrosive gas concentration for the non-data center equipment room must meet the requirements of class 3C2 of IEC 60721-3-3:2002, as shown in Table 5.
Table 5 Corrosive gas concentration limits in the non-data center equipment room
|
Gas |
Average concentration (mg/m3) |
Maximum concentration (mg/m3) |
|
SO2 |
0.3 |
1.0 |
|
H2S |
0.1 |
0.5 |
|
Cl2 |
0.1 |
0.3 |
|
HCI |
0.1 |
0.5 |
|
HF |
0.01 |
0.03 |
|
NH3 |
1.0 |
3.0 |
|
O3 |
0.05 |
0.1 |
|
NOX |
0.5 |
1.0 |
|
CAUTION: As a best practice, control the corrosive gas concentrations in the equipment room at their average values. Make sure the corrosive gas concentrations do not exceed 30 minutes per day at their maximum values. |
Guidelines for controlling corrosive gases
To control corrosive gases, follow these guidelines:
· As a best practice, do not build the equipment room in a place with a high concentration of corrosive gases.
· Make sure the equipment room is not connected to sewer, sewage, vertical shaft, or septic tank pipelines and keep it far away from these pipelines. The air inlet of the equipment room must be away from such pollution sources.
· Use environmentally friendly materials to decorate the equipment room. Avoid using organic materials that contains harmful gases, such as sulfur or chlorine-containing insulation cottons, rubber mats, sound-proof cottons, and avoid using plasterboards with high sulfur concentration.
· Place fuel (diesel or gasoline) engines separately. Do not place them in the same equipment room with the device. Make sure the exhausted air of the engines will not flow into the equipment room or towards the air inlet of the air conditioners.
· Place batteries separately. Do not place them in the same room with the device.
· Employ a professional company to monitor and control corrosive gases in the equipment room regularly.
Cleanliness requirements
Mechanically active substances buildup on the chassis might result in electrostatic adsorption, which causes poor contact of metal components and contact points. In the worst case, electrostatic adsorption can cause communication failure.
Requirements of dust particle concentration vary by server model. For information about the requirements, see the installation guide of the server.
Requirements for the data center equipment room
The concentration of dust participles in the equipment room must meet the ISO 8 cleanroom standard defined by ISO 14644-1, as described in Table 6. Make sure no zinc whiskers are in the equipment room.
Table 6 Dust particle concentration limit in the equipment room
|
Particle diameter |
Concentration limit |
|
≥ 5 µm |
≤ 29300 particles/m3 |
|
≥ 1 µm |
≤ 832000 particles/m3 |
|
≥ 0.5 µm |
≤ 3520000 particles/m3 |
Requirements for the non-data center equipment room
The concentration of dust participles (particle diameter ≥ 0.5 µm) must meet the requirement of the GB 50174-2017 standard, which is less than 17600000 particles/m3.
Guidelines for controlling cleanliness
To maintain cleanliness in the equipment room, follow these guidelines:
· Keep the equipment room away from pollution sources and do not smoke or eat in the equipment room.
· Use double-layer glass in windows and seal doors and windows with dust-proof rubber strips.
· Use dustproof materials for floors, walls, and ceilings and use matt coating that does not produce powders.
· Keep the equipment room clean and clean the air filters of the rack regularly.
· Wear ESD clothing and shoe covers before entering the equipment room. Keep the ESD clothing and shoe covers clean and replace them frequently.
Grounding requirements
Correctly connecting the server grounding cable is crucial to lightning protection, anti-interference, and ESD prevention. The server can be grounded through the grounding wire of the power supply system and no external grounding cable is required.
Storage requirements
Follow these guidelines to store storage media:
· As a best practice, do not store an HDD for 6 months or more without powering on and using it.
· As a best practice, do not store an SSD, M.2 SSD, or SD card for 3 months or more without powering on and using it. Long unused time increases data loss risks.
· To store the server chassis, an HDD, or an SSD for 3 months or more, power on it every 3 months and run it for a minimum of 2 hours each time. For information about powering on and powering off the server, see "Powering on and powering off the server."
Installation tools
Table 7 lists the tools that you might use during installation.
|
Picture |
Name |
Description |
|
T25 Torx screwdriver |
Installs or removes screws inside chassis ears, including screw rack mount ears or multifunctional rack mount ears. |
|
|
T30 Torx screwdriver |
Installs or removes captive screws on processor heatsinks. |
|
|
T15 Torx screwdriver (shipped with the server) |
Installs or removes screws on the system board. |
|
|
T10 Torx screwdriver (shipped with the server) |
Installs or removes screws on riser cards. |
|
|
Flat-head screwdriver |
Installs or removes captive screws inside multifunctional rack mount ears or replaces system batteries. |
|
|
Phillips screwdriver |
Installs or removes screws on drive carriers. |
|
|
|
Cage nut insertion/extraction tool |
Inserts or extracts the cage nuts in rack posts. |
|
Diagonal pliers |
Clips insulating sleeves. |
|
|
Tape measure |
Measures distance. |
|
|
Multimeter |
Measures resistance and voltage. |
|
|
ESD wrist strap |
Prevents ESD when you operate the server. |
|
|
Antistatic gloves |
Prevents ESD when you operate the server. |
|
|
Antistatic clothing |
Prevents ESD when you operate the server. |
|
|
Ladder |
Supports high-place operations. |
|
|
Interface cable (such as an Ethernet cable or optical fiber) |
Connects the server to an external network. |
|
|
Serial console cable |
Connects the serial connector on the server to a monitor for troubleshooting. |
|
|
Monitor |
Displays the output from the server. |
|
|
Temperature humidity meter |
Displays current temperature and humidity. |
|
|
Oscilloscope |
Displays the variation of voltage over time in waveforms. |
Installing or removing the server
Installing the server
Installing rails
Install the inner rails to the server and the outer rails to the rack. For information about installing the rails, see the document shipped with the rails.
Rack-mounting the server
1. Slide the server into the rack. For more information about how to slide the server into the rack, see the slide rails installation guide.
Figure 3 Rack-mounting the server
2. Secure the server.
a. Push the server until the multifunctional rack mount ears are flush against the rack front posts, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 4.
b. Unlock the latches of the multifunctional rack mount ears, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 4.
c. Fasten the captive screws inside the chassis ears and lock the latches, as shown by callout 3 in Figure 4.
Installing cable management brackets
Install cable management brackets if the server is shipped with cable management brackets. For information about how to install cable management brackets, see the installation guide shipped with the brackets.
Connecting external cables
Cabling guidelines
|
WARNING! To avoid electric shock, fire, or damage to the equipment, do not connect communication equipment to RJ-45 Ethernet ports on the server. |
· For heat dissipation, make sure no cables block the inlet or outlet air vents of the server.
· To easily identify ports and connect/disconnect cables, make sure the cables do not cross.
· Label the cables for easy identification of the cables.
· Wrap unused cables onto an appropriate position on the rack.
· To avoid damage to cables when extending the server out of the rack, do not route the cables too tight if you use cable management brackets.
Connecting a mouse, keyboard, and monitor
About this task
The server provides two DB15 VGA connectors for connecting a monitor. One is on the front panel and the other is on the rear panel.
The server is not shipped with a standard PS2 mouse and keyboard. To connect a PS2 mouse and keyboard, you must prepare a USB-to-PS2 adapter.
Procedure
1. Connect one plug of a VGA cable to a VGA connector on the server, and fasten the screws on the plug.
Figure 5 Connecting a VGA cable
2. Connect the other plug of the VGA cable to the VGA connector on the monitor, and fasten the screws on the plug.
3. Connect the mouse and keyboard.
¡ For a USB mouse and keyboard, directly connect the USB connectors of the mouse and keyboard to the USB connectors on the server.
¡ For a PS2 mouse and keyboard, insert the USB connector of the USB-to-PS2 adapter to a USB connector on the server. Then, insert the PS2 connectors of the mouse and keyboard into the PS2 receptacles of the adapter.
Figure 6 Connecting a PS2 mouse and keyboard by using a USB-to-PS2 adapter
Connecting an Ethernet cable
About this task
Perform this task before you set up a network environment or log in to the HDM management interface through the HDM network port to manage the server.
Procedure
1. Determine the network port on the server.
¡ To connect the server to the external network, use the Ethernet port on the network adapter.
¡ To log in to the HDM management interface, use the HDM dedicated network port. For the position of the HDM dedicated network port, see "Rear panel."
If the server is configured with an OCP network adapter, you can also use the HDM shared network port on the OCP network adapter to log in to the HDM management interface. For the position of the OCP network adapter, see "Rear panel."
2. Determine type of the Ethernet cable.
Verify the connectivity of the cable by using a link tester.
If you are replacing the Ethernet cable, make sure the new cable is the same type or compatible with the old cable.
3. Label the Ethernet cable by filling in the names and numbers of the server and the peer device on the label.
As a best practice, use labels of the same kind for all cables.
If you are replacing the Ethernet cable, label the new cable with the same number as the number of the old cable.
4. Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the network port on the server and the other end to the peer device.
Figure 7 Connecting an Ethernet cable
5. Verify network connectivity.
After powering on the server, use the ping command to test the network connectivity. If the connection between the server and the peer device fails, verify that the Ethernet cable is securely connected.
6. Secure the Ethernet cable. For information about how to secure cables, see "Securing cables."
Connecting the power cord
Guidelines
|
WARNING! To avoid damage to the equipment or even bodily injury, use the power cord that ships with the server. |
Before connecting the power cord, make sure the server and components are installed correctly.
Procedure
Multiple methods can be used for securing power cords. The following uses cable clamps as an example.
To connect the power cord:
1. Insert the power cord plug into the power receptacle of a power supply at the rear panel, as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8 Connecting the power cord
2. Connect the other end of the power cord to the power source, for example, the power strip on the rack.
3. Secure the power cord to avoid unexpected disconnection of the power cord.
a. If the cable clamp is positioned too near the power cord that it blocks the power cord plug connection, press down the tab on the cable mount and slide the clip backward.
Figure 9 Sliding the cable clamp backward
b. Open the cable clamp, place the power cord through the opening in the cable clamp, and then close the cable clamp, as shown by callouts 1, 2, 3, and 4 in Figure 10.
Figure 10 Securing the AC power cord
c. Slide the cable clamp forward until it is flush against the edge of the power cord plug, as shown in Figure 11.
Figure 11 Sliding the cable clamp forward
Securing cables
Securing cables to cable management brackets
For information about how to secure cables to cable management brackets, see the installation guide shipped with the brackets.
Securing cables to slide rails by using cable straps
You can secure cables to either left slide rails or right slide rails. As a best practice for cable management, secure cables to left slide rails.
When multiple cable straps are used in the same rack, stagger the strap location, so that the straps are adjacent to each other when viewed from top to bottom. This positioning will enable the slide rails to slide easily in and out of the rack.
To secure cables to slide rails by using cable straps:
1. Hold the cables against a slide rail.
2. Wrap the strap around the slide rail and loop the end of the cable strap through the buckle.
3. Dress the cable strap to ensure that the extra length and buckle part of the strap are facing outside of the slide rail.
Figure 12 Securing cables to a slide rail
Removing the server from a rack
1. Power down the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Disconnect all peripheral cables from the server.
3. Extend the server from the rack.
a. Open the latches of the multifunctional rack mount ears, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 13.
b. Loosen the captive screws inside the multifunctional rack mount ears, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 13.
c. Slide the server out of the rack, as shown by callout 3 in Figure 13.
Figure 13 Extending the server from the rack
4. Place the server on a clean, stable surface.
Powering on and powering off the server
Important information
If the server is connected to external storage devices, make sure the server is the first device to power off and then the last device to power on. This restriction prevents the server from mistakenly identifying the external storage devices as faulty devices.
Powering on the server
Prerequisites
Before you power on the server, you must complete the following tasks:
· Install the server and internal components correctly.
· Connect the server to a power source.
· As a best practice for the internal components to operate correctly, do not perform the power on action immediately after powering off the server. Wait for over 30 seconds for HDD drives to stop rotation and electronic components to be powered off completely.
Procedure
Powering on the server by pressing the power on/standby button
Press the power on/standby button to power on the server.
The server exits standby mode and supplies power to the system. The system power LED changes from steady amber to flashing green and then to steady green. For information about the position of the system power LED, see "LEDs and buttons."
Powering on the server from the HDM Web interface
1. Log in to HDM.
For information about how to log in to HDM, see the firmware update guide for the server.
2. Power on the server.
a. Select System > Power Management.
b. Click Power on.
For more information, see HDM online help.
Powering on the server from the remote console interface
1. Log in to HDM.
For information about how to log in to HDM, see the firmware update guide for the server.
2. Log in to a remote console and then power on the server.
For information, see HDM online help.
Configuring automatic power-on
You can configure automatic power-on from HDM or the BIOS.
To configure automatic power-on from HDM:
1. Log in to HDM.
For information about how to log in to HDM, see the firmware update guide for the server.
2. Configure automatic power-on for the server.
a. Select System > Power Management > Power Supply Info, and then click System Power Restore.
b. Select Always power on, and then click OK.
For more information, see HDM online help.
To configure automatic power-on from the BIOS:
3. Log in to the BIOS.
For information about how to log in to the BIOS, see the BIOS user guide for the server.
2. Configure automatic power-on for the server.
a. Select Server > AC Restore Settings, and then press Enter.
b. Select Always Power On, and then press Enter.
c. Press F4 to save the configuration.
For more information, see the BIOS user guide for the server.
Powering off the server
Guidelines
Before powering off the server, you must complete the following tasks:
· Back up all critical data.
· Make sure all services have stopped or have been migrated to other servers.
Procedure
Powering off the server from its operating system
1. Connect a monitor, mouse, and keyboard to the server.
2. Shut down the operating system of the server.
3. Disconnect all power cords from the server.
Powering off the server by pressing the power on/standby button
1. Press the power on/standby button and wait for the system power LED to turn into steady amber.
2. Disconnect all power cords from the server.
Powering off the server forcedly by pressing the power on/standby button
|
IMPORTANT: This method forces the server to enter standby mode without properly exiting applications and the operating system. Use this method only when the server system crashes. For example, a process gets stuck. |
1. Press and hold the power on/standby button until the system power LED turns into steady amber.
2. Disconnect all power cords from the server.
Powering off the server from the HDM Web interface
1. Log in to HDM.
For information about how to log in to HDM, see the firmware update guide for the server.
2. Power off the server.
For more information, see HDM online help.
3. Disconnect all power cords from the server.
Powering off the server from the remote console interface
1. Log in to HDM.
For information about how to log in to HDM, see the firmware update guide for the server.
2. Log in to a remote console and then power off the server.
For information about how to log in to a remote console, see HDM online help.
3. Disconnect all power cords from the server.
Configuring the server
The following information describes the procedures to configure the server after the server installation is complete.
Configuration flowchart
Figure 14 Configuration flowchart
Powering on the server
1. Power on the server. For information about the procedures, see "Powering on the server."
2. Verify that the health LED on the front panel is steady green, which indicates that the system is operating correctly. For more information about the health LED status, see "LEDs and buttons."
Configuring basic BIOS settings
You can set the server boot order and the BIOS passwords from the BIOS setup utility of the server.
|
|
NOTE: The BIOS setup utility screens are subject to change without notice. |
Setting the server boot order
The server has a default boot order. You can change the server boot order from the BIOS. For the default boot order and the procedure of changing the server boot order, see the BIOS user guide for the server.
Setting the BIOS passwords
BIOS passwords include a boot password as well as an administrator password and a user password for the BIOS setup utility. By default, no passwords are set.
To prevent unauthorized access and changes to the BIOS settings, set both the administrator and user passwords for accessing the BIOS setup utility. Make sure the two passwords are different.
After setting the administrator password and user password for the BIOS setup utility, you must enter the administrator password or user password each time you access the BIOS setup utility.
· To obtain administrator privileges, enter the administrator password.
· To obtain the user privileges, enter the user password.
For the difference between the administrator and user privileges and guidelines for setting the administrator and user passwords, see the BIOS user guide for the server.
Configuring RAID
Configure physical and logical drives (RAID arrays) for the server.
The embedded SATA controller and embedded NVMe controllers do not support RAID configuration. The supported RAID levels and RAID configuration methods vary by storage controller model. For more information, see the storage controller user guide for the server.
Installing the operating system and hardware drivers
Installing the operating system
Install a compatible operating system on the server by following the procedures described in the operating system installation guide for the server.
For the server compatibility with the operating systems, visit the query tool at http://www.h3c.com/cn/Service/Document_Software/Document_Center/Server/.
Installing hardware drivers
|
IMPORTANT: To avoid hardware unavailability caused by an update failure, always back up the drivers before you update them. |
For newly installed hardware to operate correctly, the operating system must have the required hardware drivers.
To install a hardware driver, see the operating system installation guide for the server.
Updating firmware
|
IMPORTANT: Verify the hardware and software compatibility before firmware upgrade. For information about the hardware and software compatibility, see the software release notes. |
You can update the following firmware from FIST or HDM:
· HDM.
· BIOS.
· CPLD.
· LCD.
For information about the update procedures, see the firmware update guide for the server.
Replacing hardware options
If you are replacing multiple hardware options, read their replacement procedures and identify similar steps to streamline the entire replacement procedure.
The figures used in this document are for illustration only and might differ from your product.
Adding a processor
For information about how to add a processor, see H3C UniServer R4950 G5 Server Processor Installation Quick Start.
Replacing a processor
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
Guidelines
· To avoid damage to a processor or the system board, only H3C authorized or professional server engineers can install, replace, or remove a processor.
· You can install one or two processors. If you install two processors, make sure the processors are the same model.
· The pins in the processor sockets are very fragile and prone to damage. Install a protective cover if a processor socket is empty.
· For the server to operate correctly, make sure processor 1 is in position. For more information about processor locations, see system board components in "Appendix A Server specifications."
· Make sure a protective cover is installed over each empty processor socket.
· The compatible BIOS firmware varies by processor type (Rome CPU or Milan CPU). After you change the processor type, you must update the BIOS firmware version. For information about updating BIOS firmware, see H3C Servers Firmware Update Guide.
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a processor
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the chassis.
4. Remove the chassis air baffle. Hold the air baffle by the holes at both ends, press the blue tabs, and lift the air baffle out of the chassis.
5. Remove the processor heatsink:
a. Loosen the captive screws in the sequence from 4 to 1.
b. Lift the heatsink slowly to remove it from the chassis.
6. Open the processor socket. Use a T20 Torx screwdriver to loosen the screws in the sequence shown by callouts 3 through 1 in Figure 15. The cover of the processor socket will automatically open.
Figure 15 Opening the processor socket
7. Open the bracket. Hold and lift the bracket by two fingers till the bracket is fully opened, as shown in Figure 16.
Figure 16 Opening the steel bracket
8. Remove the processor. Pinch the handle of the processor tray and pull the processor tray out from the bracket as shown in Figure 17.
|
CAUTION: To avoid damage to a processor, prevent the processor socket from falling down and do not touch the surface of the processor. |
Figure 17 Removing the processor tray
Installing a processor
1. Smear thermal grease onto the processor:
a. Clean the processor and heatsink with isopropanol wipes. Allow the isopropanol to evaporate before continuing.
b. Use the thermal grease injector to inject 0.6 ml of thermal grease to five dots on the processor, 0.12 ml for each dot.
2. Install the processor tray into the bracket. Holding the processor tray by the handle, align the processor tray with the bracket, and then insert the processor tray into the bracket as shown in Figure 18.
|
CAUTION: To avoid damage to a processor, prevent the processor socket from falling down and do not touch the surface of the processor. |
Figure 18 Installing the processor tray
3. Close the bracket. Slowly close the bracket and then press both corners of the open edge of the bracket to lock the bracket, as shown in Figure 19.
4. Install the processor. Slowly close the protective cover of the processor cover. Then, use a T20 Torx screwdriver to fasten the screws in the sequence shown by callouts 1 through 3 in Figure 20.
Figure 20 Installing the processor
5. Install the heatsink onto the server:
a. Lower down the heatsink on the processor socket as shown by callout 1 in Figure 21.
b. Use a T20 Torx screwdriver to fasten the four captive screws on the heatsink in the sequence shown by callouts 2 through 5 in Figure 21.
c. Paste bar code label supplied with the processor over the original label on the heatsink. This step is required for you to obtain H3C's processor servicing.
|
CAUTION: To avoid poor contact between the processor and the system board or damage to the pins in the processor socket, tighten the screws to a torque value of 1.6 Nm (16.1kgf.cm). |
Figure 21 Installing the heatsink

6. Install the chassis air baffle.
7. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
8. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
9. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
10. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Verifying the replacement
Log in to HDM and view the operating status of the processor to verify that the processor is operating correctly. For more information, see the HDM online help.
Replacing a DIMM
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
The server supports LRDIMMs and RDIMMs. RDIMMs can perform parity checking on addresses. Compared with RDIMMs, LRDIMMs provide larger capacity and higher bandwidth.
Both LRDIMMs and RDIMMs are referred to as DIMMs in this document, unless otherwise stated.
Guidelines
DIMM and processor compatibility
The supported DIMMs vary by processor model, as shown in Table 8.
Table 8 Supported DIMMs of a processor
|
Processor |
Supported DIMMs |
|
AMD Rome EYPC |
· DDR4 @ 3200 MHz · DDR4 @ 2933 MHz |
|
AMD Milan EYPC |
· DDR4 @ 3200 MHz · DDR4 @ 2933 MHz |
DIMM frequency
The actual operating frequency of DIMMs also depends on the maximum DIMM frequency supported by the processor and the number of DIMMs per channel.
· If the supported frequency is lower than the DIMM frequency, the DIMMs operate at the supported frequency.
· If the supported frequency is higher than the DIMM frequency, the DIMMs operate at the DIMM frequency.
· If a supported frequency is equal to the DIMM frequency, the actual operating frequency depends on the number of DIMMs per channel.
¡ For RDIMMs or LRDIMMs (excluding 3DS RDIMMs):
- If one DIMM is installed per channel, the maximum DIMM operating frequency is 3200 MHz.
- If two DIMMs are installed per channel, the maximum DIMM operating frequency is 2933 MHz.
¡ For 3DS RDIMMs:
- If one DIMM is installed per channel, the maximum DIMM operating frequency is 2933 MHz.
- If two DIMMs are installed per channel, the maximum DIMM operating frequency is 2666 MHz.
Use Figure 22 to identify the DIMM operating frequency on the server.
Figure 22 Identifying the DIMM operating frequency
For example, for DIMMs to operate at 3200 MHz, make sure the following conditions are met:
· The processors support a maximum of 3200 MHz DIMM frequency.
· DIMMs with a maximum of 3200 MHz data rate are used.
· Only one DIMM per channel is installed.
|
|
NOTE: You can access the query tool at http://www.h3c.com/cn/Service/Document_Software/Document_Center/Server/ to obtain the frequency of a DIMM and the maximum DIMM frequency supported by a processor. |
DIMM population
If only one processor is present, populate DIMMs as shown in Figure 23.
If two processors are present, populate DIMMs as shown in Figure 24 and Figure 25.
Figure 23 DIMM population schemes (one processor present)
Figure 24 DIMM population schemes (two processors present) (for processors 1)
Figure 25 DIMM population schemes (two processors present) (for processors 2)
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a DIMM
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
4. Open the DIMM slot latches and pull the DIMM out of the slot to remove the DIMM.
Figure 26 Removing a DIMM
Installing a DIMM
1. Install the DIMM. Align the notch on the DIMM with the connector key in the DIMM slot and press the DIMM into the socket until the latches lock the DIMM in place.
Figure 27 Installing a DIMM
2. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
3. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
4. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
5. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
6. (Optional.) Enter the BIOS to change the memory mode, if necessary. For more information, see the BIOS user guide of the server.
Verifying the replacement
Use one of the following methods to verify that the DIMM is installed correctly:
· Using the operating system:
¡ For the Windows operating system, click Run from the Start menu, enter msinfo32, and verify the memory capacity of the DIMM.
¡ For the Linux operating system, execute the cat /proc/meminfo command to verify the memory capacity.
· Using HDM:
Log in to HDM and verify the memory capacity of the DIMM. For more information, see the HDM online help.
· Using BIOS:
Enter the BIOS, select Chipset > North Bridge > Slot x Information, and press Enter. (x represents the ID of a processor). Then, verify the memory capacity of the DIMM.
If the memory capacity displayed is inconsistent with the actual capacity, remove and then install the DIMM, or replace the DIMM with a new DIMM.
For a DIMM in Mirror mode or enabled with memory rank sparing, the capacity displayed is smaller than the actual capacity.
Replacing the system board
Guidelines
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
To prevent electrostatic discharge, place the removed parts on an antistatic surface or in antistatic bags.
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing the system board
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the OCP network adapter.
4. Remove the power supplies.
5. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
6. Remove the chassis air baffle. Lift the air baffle to remove it from the chassis.
7. Remove all fans.
8. Remove the fan cage. Open the locking levers at the two ends of the fan cage, and then lift the fan cage out of the chassis.
9. Disconnect all cables connected to the system board.
10. Remove the cable cover.
11. Remove all components installed on the system board, for example, riser cards, DIMMs, and processors.
12. Install protective covers over the empty processor sockets.
13. Remove the system board:
a. Loosen the captive screws on the system board.
b. Hold the system board handle and slide the system board toward the server front. Then, lift the system board to remove it from the chassis.
Installing the system board
1. Install the system board:
a. Hold the system board handle and slowly place the system board in the chassis. Then, slide the system board toward the server rear until the connectors (for example, USB connectors and the Ethernet port) on it are securely seated.
|
|
NOTE: The connectors are securely seated if you cannot use the system board handle to lift the system board. |
b. Fasten the two captive screws on the system board.
2. Installed the removed cable cover.
3. Reconnect cables to the system board.
4. Remove the installed protective covers over the processor sockets. Hold a cover and lift it straight up and away from a socket.
5. Install the removed components (for example, the riser cards, DIMMs, and processors) on the system board.
6. Install the removed fan cage. Place the fan cage in the chassis and then close the locking levers at the two ends of the fan cage.
7. Install the removed chassis air baffle.
8. Install the removed fans.
9. Install the removed access panel.
10. Install the removed OCP network adapter.
11. Install the removed power supplies.
12. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
13. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
14. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing a SAS/SATA drive
The drives are hot swappable.
To configure RAID settings after the drive is replaced, see the storage controller user guide for the server.
Guidelines
If you hot swap an HDD repeatedly within 30 seconds, the system might fail to identify the drive.
If you are using the drives to create a RAID, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· To avoid degraded RAID performance or RAID creation failures, make sure all drives in the RAID are the same type (HDDs or SSDs) and have the same connector type (SAS or SATA).
· For efficient use of storage, use drives that have the same capacity to build a RAID. If the drives have different capacities, the lowest capacity is used across all drives in the RAID.
· If one drive is used by several logical drives, RAID performance might be affected and maintenance complexities will increase.
· If the installed drive contains RAID information, you must clear the information before configuring RAIDs. As a best practice, install drives that do not contain RAID information.
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Identify the position of the drive to be replaced.
Identify the RAID array information of the drive to be replaced. To replace a drive in a non-redundancy RAID array, back up data in the RAID array if the old drive is full or the new drive is of a different model.
Removing a SAS/SATA drive
1. Remove the security bezel, if any. Unlock the security bezel and then remove the security bezel out from the chassis.
2. Observe the drive LEDs to verify that the drive is not selected by the storage controller and is not performing a RAID migration or rebuilding. For more information about drive LEDs, see drive LEDs in "Appendix B Component specifications."
3. Remove the drive:
¡ To remove an SSD, press the button on the drive panel to release the locking lever, and then hold the locking lever and pull the drive out of the slot.
¡ To remove an HDD, press the button on the drive panel to release the locking lever. Pull the drive 3 cm (1.18 in) out of the slot. Wait for a minimum of 30 seconds for the drive to stop rotating, and then pull the drive out of the slot.
Figure 28 Removing a drive

4. Remove the drive carrier. Remove the screws that secure the drive and then remove the drive from the carrier.
Installing a SAS/SATA drive
|
IMPORTANT: As a best practice, install drives that do not contain RAID information. |
1. Attach the drive to the drive carrier. Place the drive in the carrier and then use four screws to secure the drive into place.
2. Install the drive:
a. Press the button on the drive panel to release the locking lever.
Figure 29 Releasing the locking lever of the drive

b. Insert the drive into the slot and push it gently until you cannot push it further, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 30.
c. Close the locking lever until it snaps into place, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 30.

3. Install the removed security bezel. Place the right edge of the security bezel into the server, secure the left edge into place, and then use a key to lock the security bezel.
Verifying the replacement
Use one of the following methods to verify that the drive has been replaced correctly:
· Verify the drive properties (including capacity) by using one of the following methods:
¡ Log in to HDM. For more information, see H3C Servers HDM online help.
¡ Access the BIOS. For more information, see the storage controller user guide for the server.
¡ Access the CLI or GUI of the server.
· Observe the drive LEDs to verify that the drive is operating correctly. For more information about drive LEDs, see drive LEDs in "Appendix B Component specifications".
Replacing an NVMe drive
Guidelines
Support for hot swapping of NVMe drives varies by operating system.
If an operating system supports hot swapping of NVMe drives, follow these guidelines:
· Use a stable speed to insert NVMe drives without any pauses during the drive insertion to prevent the operating system from getting stuck or restarted.
· Do not hot swap multiple NVMe drives at the same time. As a best practice, hot swap NVMe drives one after another at intervals longer than 30 seconds. After the operating system identifies the first NVMe drive, you can hot swap the next drive. If you insert multiple NVMe drives simultaneously, the system might fail to identify the drives.
To replace an NVMe drive in an operating system that does not support hot removal of NVMe drives, first power off the server.
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Identify the position of the drive to be replaced.
Removing an NVMe drive
1. Remove the security bezel, if any. Unlock the security bezel and then remove the security bezel from the server.
2. Remove the drive. Press the button on the drive panel to release the locking lever, and then hold the locking lever and pull the drive out of the slot.
3. Remove the drive carrier. Remove the screws that secure the drive and then remove the drive from the carrier.
Installing an NVMe drive
1. Attach the drive to the drive carrier. Place the drive in the carrier and then use four screws to secure the drive into place.
2. Insert the drive into the slot and push it gently until you cannot push it further, and then close the locking lever.
3. Install the removed security bezel. Place the right edge of the security bezel into the server, secure the left edge into place, and then use a key to lock the security bezel.
Verifying the replacement
Use the following methods to verify that the drive is installed correctly:
· Verify the drive properties (including capacity) by using one of the following methods:
¡ Access HDM. For more information, see HDM online help.
¡ Access the BIOS. For more information, see the BIOS user guide for the server.
¡ Access the CLI or GUI of the server.
· Observe the drive LEDs to verify that the drive is operating correctly. For more information, see "Drive LEDs."
Replacing a drive backplane
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a drive backplane
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the drives attached to the backplane.
4. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
5. Remove the fan cage. Open the locking levers at the two ends of the fan cage, and then lift the fan cage out of the chassis.
6. Disconnect cables from the backplane.
7. Remove the drive backplane:
a. Loosen the captive screws that secure the backplane as shown by callout 1 in Figure 31.
b. Lift the backplane to remove it from the chassis as shown by callout 2 in Figure 31.
The removal procedure is the same for a front drive backplane and a rear drive backplane. This example uses a front drive backplane.
Figure 31 Removing a front drive backplane

Installing a drive backplane
1. Install a drive backplane. Place the backplane in the slot and then fasten the captive screws as shown in Figure 32.
The installation procedure is the same for a front drive backplane and a rear drive backplane. This example uses a front drive backplane.
Figure 32 Installing a front drive backplane

2. Connect cables to the drive backplane.
3. Install the removed fan cage. Place the fan cage in the chassis and then close the locking levers at the two ends of the fan cage.
4. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
5. Install the removed drives.
6. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
7. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
8. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing a rear drive cage
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a rear drive cage
Removing a rear 2SFF drive cage
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the drives installed in the drive cage.
4. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
5. Disconnect cables from the backplane.
6. Remove the riser card bracket from the chassis.
7. Remove the rear 2SFF drive cage:
a. Loosen the screws that secure the drive cage, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 33.
b. Lift the drive cage to remove it from the chassis, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 33.
Figure 33 Removing a rear 2SFF drive cage

Removing a rear 4SFF drive cage
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the drives installed in the drive cage.
4. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
5. Disconnect cables from the backplane.
6. Remove a rear 4SFF drive cage:
a. Loosen the screws that secure the drive cage, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 34.
b. Lift the drive cage to remove it out from the chassis, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 34.
Figure 34 Removing a rear 4SFF drive cage

Removing a rear 2LFF drive cage
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the drives installed in the drive cage.
4. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
5. Disconnect cables from the backplane.
6. Remove the rear 2LFF drive cage:
a. Loosen the screws that secure the drive cage, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 35.
b. Lift the drive cage to remove it out from the chassis, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 35.
Figure 35 Removing a rear 2LFF drive cage

Removing a rear 4LFF drive cage
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the drives installed in the drive cage.
4. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
5. Disconnect cables from the backplane.
6. Remove the rear 4LFF drive cage:
a. Loosen the screws that secure the drive cage, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 36.
b. Lift the drive cage to remove it out from the chassis, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 36.
Figure 36 Removing a rear 4LFF drive cage

Installing a rear drive cage
Installing a rear 2SFF drive cage
1. Install the riser card bracket on the chassis.
2. Install the rear drive cage in the server:
a. Aligning the clip at the cage side with the edge of the riser card bracket, place the drive cage in the chassis, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 37.
b. Use screws to secure the drive cage, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 37.
Figure 37 Installing a rear 2SFF drive cage

3. Connect cables to the drive backplane.
4. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
5. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
6. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
7. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Installing a rear 4SFF drive cage
1. Install the rear drive cage in the server:
a. Aligning the clip at the cage side with the edge of the bracket in the chassis, place the drive cage in the chassis, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 38.
b. Use screws to secure the drive cage, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 38.
Figure 38 Installing a rear 4SFF drive cage

2. Connect cables to the drive backplane.
3. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
4. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
5. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
6. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Installing a rear 2LFF drive cage
1. Install the rear drive cage in the server:
a. Aligning the clip at the cage side with the edge of the bracket in the chassis, place the drive cage in the chassis, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 39.
b. Use screws to secure the drive cage, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 39.
Figure 39 Installing a rear 2LFF drive cage

2. Connect cables to the drive backplane.
3. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
4. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
5. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
6. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Installing a rear 4LFF drive cage
1. Install the rear drive cage in the server:
a. Aligning the clip at the cage side with the edge of the bracket in the chassis, place the drive cage in the chassis, as shown by callout 1 in Figure 40.
b. Use screws to secure the drive cage, as shown by callout 2 in Figure 40.
Figure 40 Installing a rear 4LFF drive cage

2. Connect cables to the drive backplane.
3. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
4. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
5. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
6. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing riser cards and PCIe modules
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
The server provides three PCIe riser connectors on the system board to connect riser cards, which hold PCIe modules. For more information about the connector locations, see system board components in "Appendix A Server specifications."
Guidelines
You can install a PCIe module in a PCIe slot for a larger-sized PCIe module. For example, an LP PCIe module can be installed in a slot for an FHFL PCIe module.
A PCIe slot can supply power to the installed PCIe module if the maximum power consumption of the module does not exceed 75 W. If the maximum power consumption exceeds 75 W, a power cord is required.
If a processor is faulty or absent, the corresponding PCIe slots are unavailable. For more information about processor and PCIe slot mapping relationship, see riser cards in "Appendix B Component specifications."
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a riser card and a PCIe module
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
4. Disconnect all cables that hinder the replacement, if any.
5. Remove the riser card installed with a PCIe module. Holding the riser card by the notch and handle, lift the riser card to remove the riser card from the chassis.
Figure 41 Removing a riser card

6. Remove the PCIe module from the riser card:
a. Open the retaining latch of the riser card as shown by callout 1 in Figure 42.
b. Pull the PCIe module out of the slot as shown by callout 2 in Figure 42.
Figure 42 Removing a PCIe module from a riser card

Installing a riser card and a PCIe module
1. Install the PCIe module on the riser card:
a. Remove the PCIe module blank.
b. Install the PCIe module into the riser card. Insert the PCIe module into the PCIe slot along the guide rails, and then close the retaining latch.
Figure 43 Installing the PCIe module

2. Install the riser card on the server:
a. Lift the riser card blank to remove it from the chassis.
b. Install the riser card on the PCIe riser connector, with the two standouts on the card aligned with the notches in the chassis.
Figure 44 Installing the riser card

3. Connect cables to the riser card or PCIe modules, if any.
4. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
5. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
6. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
7. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Installing PCIe modules and a riser card on PCIe riser connector 3
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
Guidelines
For more information, see "Guidelines."
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Procedure
1. Identify the position of the PCIe riser connector. For more information, see system board components in "Appendix A Server specifications."
2. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
3. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
4. Remove the access panel. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
5. Remove the PCIe riser card blank. Lift the blank to remove it from the chassis.
6. Install a PCIe module into the riser card:
a. Remove the PCIe module blank. Loosen the screws on the PCIe module blank, and then remove the PCIe module blank.
b. Install the PCIe module into the riser card. Insert the PCIe module into the PCIe slot along the guide rails, and fasten the screws to secure the PCIe module.
7. Install the support bracket. Align the guide pins on the support bracket with the guide holes in the chassis, place the support bracket onto the chassis, and then fasten the screws to secure the support bracket.
Figure 45 Installing the support bracket

8. Install the riser card installed with the PCIe module. Inset the riser card into the PCIe riser connector along the guide rails.
9. Connect cables to the riser card or PCIe modules, if any.
10. Install the removed PCIe riser card blank. Align the standouts on the PCIe riser card blank with the notches on the side of the chassis, and then insert the PCIe riser card blank into the chassis.
11. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
12. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
13. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
14. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing a storage controller and a power fail safeguard module
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
For some storage controllers, you can order a power fail safeguard module to prevent data loss when power outage occurs.
A power fail safeguard module provides a flash card and a supercapacitor. When a system power failure occurs, this supercapacitor can provide power for a minimum of 20 seconds. During this interval, the storage controller transfers data from DDR memory to the flash card, where the data remains indefinitely or until the controller retrieves the data.
A supercapacitor has a lifespan of 3 to 5 years. If the lifespan of a supercapacitor expires, a supercapacitor exception might occur. The system notifies users of supercapacitor exceptions by using the following methods:
· For a PMC storage controller, the status of the flash card will become Abnormal_status code. You can check the status code to identify the exception. For more information, see HDM online help.
· For an LSI storage controller, the status of the flash card of the power fail safeguard module will become Abnormal.
You can also review log messages from HDM to identify supercapacitor exceptions.
For the power fail safeguard module to take effect, replace the supercapacitor before its lifespan expires.
The supercapacitor might have a low charge after the power fail safeguard module is installed or after the server is powered up. If the system displays that the supercapacitor has low charge, no action is required. The system will charge the supercapacitor automatically. You can view the status of the supercapacitor from HDM or the BIOS.
|
IMPORTANT: After the supercapacitor replacement, verify that cache related settings are enabled for logical drives. For more information, see HDM online help. |
Guidelines
You can install one or multiple standard storage controllers. When you install standard storage controllers, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· Make sure the standard storage controllers are of the same vendor (PMC or LSI). For information about the available storage controllers and their vendors, visit the query tool at http://www.h3c.com/cn/Service/Document_Software/Document_Center/Server/.
· If you install only drives at the server front, install storage controllers on different riser cards. If you install multiple storage controllers, connect each controller to the drive backplane of the corresponding bay: lower-numbered controller to lower-numbered bay and higher-numbered controller to higher-numbered bay. For information about drive bay locations, see the front panel view in "Appendix A Server specifications."
· If you install drives both at the server front and rear, install storage controllers on the same riser card. If you install multiple storage controllers, connect each controller to the drive backplane of the corresponding bay: lower-numbered controller to lower-numbered bay and higher-numbered controller to higher-numbered bay. For information about drive bay locations, see the front panel view in "Appendix A Server specifications."
Use Table 9 to identify the supercapacitor available for a storage controller.
Table 9 Standard storage controller and supercapacitor compatibility matrix
|
Standard storage controller |
Supercapacitor |
Supercapacitor installation location |
|
RAID-LSI-9361-8i(2G)-1-X |
BAT-LSI-G2-A |
In the supercapacitor container on the air baffle |
|
RAID-LSI-9460-16i(4G) |
BAT-LSI-G3-A |
|
|
RAID-LSI-9460-8i(4G) |
||
|
RAID-P460-B4 |
BAT-PMC-G3-2U |
|
|
HBA-LSI-9300-8i-A1-X |
Not supported |
Not supported |
|
HBA-H460-B1 |
To replace the storage controller with a controller of a different model, back up data in the drives of the storage controller and clear RAID configuration.
To replace the storage controller with a controller of the same model, make sure the following configurations remain the same after replacement:
· Storage controller operating mode.
· Storage controller firmware version.
· BIOS boot mode.
· First boot option in Legacy mode.
For more information, see the storage controller user guide for the server and the BIOS user guide for the server.
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a standard storage controller and a power fail safeguard module
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
4. Disconnect all cables from the standard storage controller.
5. Remove the standard storage controller:
a. Remove the riser card where the standard storage controller resides. Holding the riser card by the notch and handle, lift the riser card to remove the riser card from the chassis.
b. Remove the standard storage controller from the riser card. Open the retaining latch on the riser card, and then pull the storage controller out from the slot.
6. Remove the power fail safeguard module or super capacitor, if any:
a. Remove the flash card on the storage controller, if any. Remove the screws that secure the flash card, and then remove the flash card.
b. Remove the supercapacitor. Pull the clip on the supercapacitor holder, and take the supercapacitor out of the holder.
c. Remove the supercapacitor holder. Lift the retaining latch at the bottom of the supercapacitor holder, and slide the holder to remove it.
Installing a standard storage controller and a power fail safeguard module
1. Install the supercapacitor on the supercapacitor holder:
a. Install the supercapacitor holder on the chassis air baffle. Place the supercapacitor holder in the chassis and slide it to the server rear until it snaps into place.
b. Connect one end of a supercapacitor extension cable to the supercapacitor.
c. Install the supercapacitor to the supercapacitor holder. Tilt the supercapacitor and insert one end of the supercapacitor into the holder. Pull the clip on the holder and insert the other end into the holder, and then release the clip.
2. Install the removed flash card on the power fail safeguard module:
a. Install the internal threaded studs supplied with the power fail safeguard module on the standard storage controller.
b. Install the flash card on the standard storage controller. Insert the flash card connector into the socket and use screws to secure the flash card on the storage controller.
3. Install the standard storage controller on the riser card. Insert the standard storage controller into the PCIe slot along the guide rails, and then close the retaining latch on the riser card to secure the storage controller.
4. Install the riser card on the server.
5. Connect the cables for the standard storage controller to the drive backplane. For more information, see "Connecting drive cables."
6. Install the removed power fail safeguard module or supercapacitor. Connect the supercapacitor extension cable to the flash card. For more information, see "Connecting supercapacitor extension cables."
7. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
8. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
9. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
10. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing a GPU module
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
Guidelines
A riser card is required when you install a GPU module. You can install a GPU only in a PCIe4.0 ×16 slot that supports the 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1 link widths.
As a best practice, install GPU modules of the same model.
Use Table 10 to determine the available riser cards and PCIe slots for GPU module installation. For information about the locations of PCIe riser connectors, see system board components in "Appendix A Server specifications." For information about PCIe slots, see "Riser cards." For more information about PCIe slot locations, see the rear panel view in "Appendix A Server specifications."
Table 10 GPU module and riser card compatibility
|
Riser card |
PCIe riser connector |
PCIe slot |
|
RC-3FHHL-2U-SW-G5 |
Connector 1 |
Slot 2, 4, or 6 |
|
Connector 2 |
Slot 8, 10, or 12 |
|
|
RC-3FHHL-2U-SW-G5-1 |
Connector 3 |
Slot 14, 15, or 16 |
You can install single-slot wide GPU modules or dual-slot wide GPU modules on the server, but cannot install both of them on the same server.
· To install multiple dual-slot wide modules (a maximum of two), install them in PCIe slots in the following order: slots 5 and 2.
· To install multiple single-slot wide modules (a maximum of six), use Table 11 to determine the order to install them in PCIe slots depending the storage controller model.
Table 11 Storage controller model and PCIe slot order for GPU module installation
|
Number of GPU modules |
Storage controller model |
PCIe slot order |
|
1 |
· Embedded SATA controller · Standard storage controller |
Slot 5 |
|
2 |
· Embedded SATA controller · Standard storage controller |
Slots 5 and then 2 |
|
3 |
· Embedded SATA controller · Standard storage controller |
Slots 5, 2, and then 7 |
|
4 |
Embedded SATA controller |
Slots 2, 3, 5, and then 6 |
|
Standard storage controller |
Slots 1, 2, 5, and then 6 |
|
|
6 |
Embedded SATA controller |
Slots 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and then 6 |
|
Standard storage controller |
Slots 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, and then 7 |
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a GPU module
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the server.
4. Disconnect all cables that hinder the replacement, if any.
5. Remove the riser card where the GPU module resides. Holding the riser card by the notch and handle, lift the riser card to remove the riser card out of the chassis.
6. Remove the GPU module from the riser card:
a. Disconnect the cable from the GPU module.
b. Open the retaining latch on the riser card, and pull the GPU module out from the slot.
Adjusting the length of the riser card
Perform this task if you replace the GPU module with a new GPU module of different length.
To adjust the length of the riser card:
1. Loosen the screws on the riser card.
2. Adjust the length of the riser card.
3. Fasten the screws of the riser card.
4. Install an air baffle that fits the riser card.
Installing a GPU module
1. Install a GPU module on the riser card:
a. Insert the GPU module into the PCIe slot along the guide rails, and then close the retaining latch.
b. Connect the GPU module power cord.
2. Reconnect other cables to the riser card.
3. Install the riser card on the server. Insert the riser card into the chassis along the slot.
4. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
5. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
6. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
7. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing a network adapter
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
The OCP network adapter supports NCSI. By default, port 1 on the OCP network adapter acts as the HDM shared network port. You can configure another port on the OCP network adapter as the HDM shared network port from the HDM Web interface. For more information, see HDM online help.
Guidelines
You can install an OCP network adapter only on an OCP 3.0 network adapter connector. For information about the OCP adapter connector on the system board, see system board components in "Appendix A Server specifications."
To install a standard PCIe network adapter, a riser card is required. For more information about riser card and PCIe module compatibility, see riser cards in "Appendix B Component specifications."
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Replacing an OCP network adapter
Removing an OCP network adapter
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Disconnect all cables from the OCP network adapter.
3. Remove the OCP network adapter. Loosen the captive screws on the OCP network adapter and pull the OCP network adapter out from the chassis.
Installing an OCP network adapter
1. Install the OCP network adapter. Insert the OCP network adapter into the slot and fasten the captive screws on it.
2. Connect cables to the OCP network adapter.
3. (Optional.) Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
4. (Optional.) Configure a network port on the OCP network adapter as an HDM shared network port.
Replacing a standard PCIe network adapter
Removing a standard PCIe network adapter
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Disconnect cables from the standard PCIe network adapter.
3. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
4. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear.
5. (Optional.) Disconnect all cables that hinder the replacement, if any.
6. Remove the riser card where the PCIe network adapter resides. Lift the riser card to remove it from the chassis.
7. Remove the PCIe network adapter. Open the retaining latch on the riser card and pull the OCP network adapter out from the chassis.
Installing a standard PCIe network adapter
For the installation procedure, see "Installing a riser card and a PCIe module."
Replacing a SATA M.2 SSD and a SATA M.2 SSD expander module
Guidelines
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
An M.2 expander module is required for SATA M.2 SSDs. You must use a data cable to connect the M.2 expander module to the system board. For more information about the cabling, see "Connecting the SATA M.2 SSD cable."
SATA M.2 SSDs can be used to install the operating system.
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a SATA M.2 SSD and a SATA M.2 SSD expander module
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear.
4. Remove the SATA M.2 SSD expander module on which the SATA M.2 SSD resides:
a. Disconnect the cable from the SATA M.2 SSD expander module.
b. Remove the expander module. Remove the screws that secure the expander module and then pull the expander module out.
Figure 46 Removing the SATA M.2 SSD expander module

5. Remove the SATA M.2 SSD. As shown in callouts 1 and 2 in Figure 47, slide the locking tab, lift the SSD, and then pull the SSD out of the slot.
Figure 47 Removing the SATA M.2 SSD

Installing a SATA M.2 SSD expander module and a SATA M.2 SSD
1. Install a SATA M.2 SSD to the SATA M.2 SSD expander module. As shown in callouts 1 and 2 in Figure 48, insert the connector of the SSD into the socket, slide the locking tab, press the SSD to secure the SSD into place, and then release the locking tab.
Figure 48 Attaching a SATA M.2 SSD to a SATA M.2 SSD expander module

2. Install the expander module:
a. Align the two screw holes in the expander module with the two internal threaded studs on the chassis, put the expander module onto the chassis, and then use screws to secure the expander module.
Figure 49 Installing the SATA M.2 SSD expander module

b. Connect the SATA M.2 SSD cable. For more information, see "Connecting the SATA M.2 SSD cable."
c. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
3. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
4. Connect the power cord.
5. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing a dual SD card extended module
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a dual SD card extended module
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the chassis.
4. (Optional.) Remove the riser card cage that might hinder the replacement.
5. Remove the dual SD card extended module. Press the top clip and the side clip on the dual SD card extended module and pull the module out of the connector.
6. Remove all SD cards from the extended module. Press an SD card to release it and then pull the SD card out of the slot.
Figure 50 Removing a dual SD card extended module
Installing a dual SD card extended module
1. Install SD cards on the dual SD card extended module. Insert an SD card into the slot and gently press the SD card to secure it in the slot.
2. Install the dual SD card extended module on the server. Insert the extender module into the slot along the guide rails until you hear a click.
3. (Optional.) Install the removed riser card cage.
4. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
5. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
6. Connect the power cord.
7. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing an SD card
Guidelines
The SD cards support 1+1 redundancy. To avoid storage space waste, install two SD cards with the same capacity.
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing an SD card
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the chassis.
4. (Optional.) Remove the riser card cage that hinders the replacement.
5. Remove the dual SD card extended module. Press the top clip and the side clip on the dual SD card extended module and pull the module out of the connector.
6. Press the SD card to release it and then pull the SD card out of the slot.
Installing an SD card
1. Install a new SD card. Insert the SD card into the slot and gently press the SD card to secure it in the slot.
2. Install the dual SD card extended module on the server. Insert the extender module into the slot along the guide rails until you hear a click.
3. Install the removed riser card cage.
4. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
5. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
6. Connect the power cord.
7. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing the LCD smart management module
For more information about how to use the LCD smart management module, see LCD Smart Management Module User Guide.
Guidelines
Identify the installation location for the LCD smart management module. For more information, see the front panel view in "Appendix A Server specifications."
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing the LCD smart management module
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the chassis.
4. Remove the fan cage. Open the locking levers at the two ends of the fan cage, and then lift the fan cage out of the chassis.
5. Remove the LCD smart management module:
a. Disconnect the LCD module cable from the system board.
b. Use a T10 Torx screwdriver or tweezers to press the clip of the LCD smart management module and pull the module out from the slot.
Install the LCD smart management module
1. Install the LCD smart management module:
a. Connect one end of the LCD module cable to the LCD smart management module.
b. Push the LCD smart management module into the slot until it snaps into place.
c. Connect the other end of the cable to the LCD smart management module connector on the system board.
2. Install the fan cage. Place the fan cage in the chassis and then close the locking levers at the two ends of the fan cage.
3. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
4. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
5. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
6. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing a chassis ear
The procedure is the same for the left and right chassis ears. This section uses the left chassis ear as an example.
Removing a chassis ear
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack, if the space over the server is insufficient. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the chassis.
4. Remove the fan cage. Open the locking levers at the two ends of the fan cage, and then lift the fan cage out of the chassis.
5. Remove the chassis air baffle. Hold the air baffle by the holes at both ends, press the blue tabs, and lift the air baffle out of the chassis.
6. Remove the front I/O component cable assembly:
a. Disconnect the front I/O component cable assembly from the system board.
b. Remove the screw that secures the cable protection plate, slide the plate toward the rear of the chassis, and then remove it from the chassis.
c. Pull the I/O component cable out of the slot.
7. Remove the chassis ear. Remove the screws that secure the left chassis ear, and then pull the chassis ear until it is removed.
Installing a chassis ear
1. Install a chassis ear. Attach the chassis ear to the corresponding side of the server, and use screws to secure the chassis ear into place.
2. Install the front I/O component cable assembly:
a. Insert the front I/O component cable assembly into the cable cutout.
b. Install the cable protection plate on the chassis.
c. Connect the front I/O component cable assembly to the front I/O connector on the system board.
3. Install the fan cage.
4. Install the chassis air baffle.
5. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
6. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
7. Connect the power cord. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
8. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing a chassis air baffle
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the chassis.
4. Remove the chassis air baffle:
a. Disconnect the supercapacitor extension cable if a supercapacitor is installed on the mezzanine board.
b. Hold the air baffle by the holes at both ends, press the blue tabs, and lift the air baffle out of the chassis.
5. Install the chassis air baffle:
a. Place the chassis air baffle in the chassis.
b. Connect the disconnected supercapacitor extension cables, if any.
6. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
7. Rack-mount the server if the server has been removed. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
8. Connect the power cord if the power cord has been disconnected.
9. Power on the server if the server has been powered off. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing a fan
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
|
CAUTION: To avoid component damage or server power-off caused by overtemperature, install a fan on the server within 30 seconds after you remove one. |
The fans are hot swappable.
Guidelines
If sufficient space is available for replacement, you can replace a fan without removing the server from the rack.
Make sure the fans on the server are the same model.
The server support single-rotor fan FAN-6038-2U-G5 and dual-rotor fan FAN-6056-2U-G5. You must install FAN-6056-2U-G5 fans when one of the following conditions exists:
· The TDP of the processors on the server is equal to or greater than 240W.
· The TDP of the processors on the server is greater than 200W, and an HDD drive or NVMe SSD drive is installed at the server rear.
· The server is installed with GPU-T4 GPU modules when one 12LFF or 25SFF drive backplane, or two 8SFF UniBay drive backplanes are present.
· The server is installed with GPU-V100S-32G GPU modules.
Removing a fan
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the chassis.
4. Remove a fan. Lift the fan handle and hold the handle to pull the fan out of the slot.
Installing a fan
1. Install a new fan. Insert the fan into the slot and close the fan handle.
2. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
3. Rack-mount the server if the server has been removed. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
4. Connect the power cord if the power cord has been disconnected. For more information, see "Connecting the power cord."
5. Power on the server if the server has been powered off. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Installing and setting up a TCM or TPM
Trusted platform module (TPM) is a microchip embedded in the system board. It stores encryption information (such as encryption keys) for authenticating server hardware and software. The TPM operates with drive encryption programs such as Microsoft Windows BitLocker to provide operating system security and data protection. For information about Microsoft Windows BitLocker, visit the Microsoft website at http://www.microsoft.com.
Trusted cryptography module (TCM) is a trusted computing platform-based hardware module with protected storage space, which enables the platform to implement password calculation.
Installation and setup flowchart
Figure 51 TCM/TPM installation and setup flowchart
Guidelines
· Do not remove an installed TCM or TPM. Once installed, the module becomes a permanent part of the system board.
· To replace a failed TCM or TPM, remove the system board, and then contact H3C Support to replace the TCM or TPM and the system board.
· When installing or replacing hardware, H3C technicians cannot configure the TCM or TPM or enter the recovery key. For security reasons, only the user can perform the tasks.
· When replacing the system board, do not remove the TCM or TPM from the system board. H3C will provide a TCM or TPM with a spare system board for the replacement.
· Any attempt to remove an installed TCM or TPM from the system board breaks or disfigures the TCM or TPM security rivet. Upon locating a broken or disfigured rivet on an installed TCP or TPM, administrators should consider the system compromised and take appropriate measures to ensure the integrity of the system data.
· H3C is not liable for blocked data access caused by improper use of the TCM or TPM. For more information, see the encryption technology feature documentation provided by the operating system.
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Installing a TCM or TPM
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the chassis.
4. Remove all riser cards.
5. Remove the riser card cage.
6. Install the TCM or TPM.
The installation procedure is the same for a TPM and a TCM. The following information uses a TPM to show the procedure:
a. Press the TPM into the TPM connector on the system board.
b. Insert the rivet pin.
c. Insert the security rivet into the hole in the rivet pin and press the security rivet until it is firmly seated.
7. Install the removed riser card cage.
8. Install the removed riser cards.
9. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
10. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
11. Connect the power cord.
12. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Enabling the TCM or TPM in the BIOS
1. Enter the BIOS utility. For information about how to enter the BIOS utility, see the BIOS user guide.
2. Select Advanced > Trusted Computing, and press Enter.
3. Enable TCM or TPM. By default, the TCM and TPM are enabled for a server.
If the server is installed with a TPM, perform the following steps to enable TPM:
a. Select TPM State > Enabled, and press Enter.
b. Click Device Select, press Enter, and then select a TPM version.
If the TPM is installed with a TCM, perform the following steps to enable TCM:
c. Select TCM State > Enabled, and press Enter.
d. Click Device Select, press Enter, and then select a TPM version.
For more information, see the BIOS user guide for the server.
4. Log in to HDM to verify that the TCM or TPM is operating correctly. For more information, see HDM online help.
Configuring encryption in the operating system
For more information about this task, see the encryption technology feature documentation that came with the operating system.
The recovery key/password is generated during BitLocker setup, and can be saved and printed after BitLocker is enabled. When using BitLocker, always retain the recovery key/password. The recovery key/password is required to enter Recovery Mode after BitLocker detects a possible compromise of system integrity or firmware or hardware change.
For security purposes, follow these guidelines when retaining the recovery key/password:
· Always store the recovery key/password in multiple locations.
· Always store copies of the recovery key/password away from the server.
· Do not save the recovery key/password on the encrypted hard drive.
For more information about Microsoft Windows BitLocker drive encryption, visit the Microsoft website at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc732774.aspx.
Replacing a power supply
The power supplies are hot swappable.
Guidelines
· If more than one operating power supply is present and the server rear has sufficient space for replacement, you can replace a power supply without powering off the server.
· If only one power supply is present, install the new power supply in the slot where the original one is installed.
· Make sure the installed power supplies are the same model. HDM will perform power supply consistency check and generate a minor alarm if the power supply models are different.
· To avoid hardware damage, do not use third-party power supplies.
· The power supplies have an overtemperature protection mechanism. A power supply stops working when an overtemperature occurs and automatically recovers when the overtemperature condition is removed.
|
|
NOTE: For information about power supply specifications, see the user manual for each power supply. |
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing a power supply
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the power cord from the power supply:
a. Press the tab to disengage the ratchet from the tie mount, slide the cable clamp outward, and then release the tab.
b. Open the cable clamp and remove the power cord out of the clamp.
c. Unplug the power cord.
4. Remove the power supply. Holding the power supply by its handle and pressing the retaining latch with your thumb, pull the power supply slowly out of the slot.
Installing a power supply
1. Install a new power supply. Push the power supply into the slot until it snaps into place.
2. Rack-mount the server if the server has been removed. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
3. Connect the power cord if the power cord has been disconnected.
4. Power on the server if the server has been powered off. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
Replacing the system battery
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
The server comes with a system battery (Panasonic BR2032) installed on the system board, which supplies power to the real-time clock and has a lifespan of 3 to 5 years. If the server no longer automatically displays the correct date and time, you might need to replace the battery. As a best practice, use the Panasonic BR2032 battery to replace the old one.
|
|
NOTE: The BIOS will restore to the default settings after the replacement. You must reconfigure the BIOS to have the desired settings, including the system date and time. For more information, see the BIOS user guide for the server. |
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
When you replace a component, examine the slot and connector for damages. Make sure the pins are not damaged (bent for example) and do not contain any foreign objects.
Removing the system battery
1. Power off the server. For more information, see "Powering off the server."
2. Remove the server from the rack. For more information, see "Removing the server from a rack."
3. Remove the access panel. Press the button on the locking lever and then lift the locking lever. The access panel will automatically slide to the server rear. Then, lift the access panel to remove it from the chassis.
4. Remove the system battery. Pinch the system battery by its top edge and lift the battery out of the battery holder slowly.
|
|
NOTE: For environment protection purposes, dispose of the used-up system battery at a designated site. |
Installing the system battery
1. Install the system battery. Insert the system battery into the system battery holder on the management module.
2. Install the access panel. Place the access panel onto the server, and then slide the access panel to the server front until it snaps into place.
3. Rack-mount the server. For more information, see "Rack-mounting the server."
4. Connect the power cord.
5. Power on the server. For more information, see "Powering on the server."
6. Access the BIOS to reconfigure the system date and time. For more information, see the BIOS user guide for the server.
Removing and installing a blank
|
WARNING! To avoid bodily injury from hot surfaces, allow the server and its internal modules to cool before touching them. |
Prerequisites
Take the following ESD prevention measures:
· Wear antistatic clothing.
· Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
· Do not wear any conductive objects, such as jewelry or watches.
Removing and installing a blank
Install blanks over the empty slots if the following modules are not present and remove blanks before you install the following modules:
· Drives.
· LCD smart management module.
· Drive backplanes.
· Power supplies.
· Riser cards.
· PCIe modules.
· OCP network adapter.
Use Table 12 as a guide when you remove or install a blank for a hardware option.
Table 12 Removing or installing a blank
|
Task |
Procedure |
|
Remove a drive blank. |
Press the latches on the drive blank inward with one hand, and pull the drive blank out of the slot. |
|
Install a drive blank. |
Insert the drive blank into the slot. |
|
Remove the LCD smart management module blank. |
From the inside of the chassis, use a flat-head screwdriver to push aside the clip of the blank and push the blank outward to disengage the blank. Then, pull the blank out of the server. |
|
Install the LCD smart management module blank. |
Insert the blank into the slot with the TOP mark facing up and push the blank until you hear a click. |
|
Remove a drive backplane blank. |
From the inside of the chassis, use a flat-head screwdriver to push aside the clip of the blank and push the blank outward to disengage the blank. Then, pull the blank out of the server. |
|
Install a drive backplane blank. |
Insert the drive backplane blank into the slot and push the blank until you hear a click. |
|
Remove a power supply blank. |
Hold and pull the power supply blank out of the slot. |
|
Install a power supply blank. |
Insert the power supply blank into the slot with the TOP mark facing up. |
|
Remove a riser card blank. |
Lift the riser card blank to remove it from the connector. |
|
Install a riser card blank. |
Insert the riser card blank into the slot along guide rails. |
|
Remove a PCIe module blank. |
Open the retaining latch of the riser card and then lift the blank upwards. |
|
Install a PCIe module blank |
Insert the PCIe module blank into the slot and then close the retaining latch of the riser card. |
|
Remove an OCP network adapter blank |
Pinching the handle on the OCP network adapter blank, pull the blank out. |
|
Install an OCP network adapter blank |
Insert the OCP network adapter blank in to the slot. |
Connecting internal cables
Guidelines
Follow these guidelines when connecting the internal cables:
· Do not route the cables above the removable components, such as DIMMs.
· Route the internal cables without hindering installation or removal of other components or hindering other internal components.
· Route the cables neat and tidy in their own fixed spaces. Make sure the cables will not be squeezed or scratched by other internal components.
· Do not pull the connectors when routing the cables.
· Do not use a cable tie to bundle an excessive number of cables.
· Appropriately bind long cables. Coil and use cable ties to secure unused cables.
· Connect the drive cables until they click into place.
· Remove the cap (if any) from the target cable connector before connecting a cable to it.
· If you cannot identify the cables by labels provided with the cables, apply new labels to cables for easy identification.
Connecting drive cables
Drive cables include SAS/SATA data cables, NVMe data cables, power cords, and signal cables. The server supports various drive configurations, each with a different cable scheme. This section describes drive cabling for the following two drive configurations:
· Cabling 8SFF UniBay+8SFF UniBay drives at the front
· Cabling 25SFF drives at the front and 4SFF UniBay drives at the rear
For information about drive cabling for other drive configurations, contact Technical Support.
Cabling 8SFF UniBay+8SFF UniBay drives at the front
An 8SFF UniBay drive backplane is installed in front drive bay 2, which support eight SAS, SATA, or NVMe drives.
An 8SFF UniBay drive backplane is installed in front drive bay 3, which support eight NVMe drives.
Figure 52 Connecting the NVMe data cables for front drive bay 2

|
(1) NVMe data cable 1 (from connector NVMe-A1/A2 on the drive backplane to connector NVMe-A5/A6 on the system board) |
|
(2) NVMe data cable 2 (from connector NVMe-A3/A4 on the drive backplane to connector NVMe-A7/A8 on the system board) |
|
(3) NVMe data cable 3 (from connector NVMe-B1/B2 on the drive backplane to connector NVMe-A1/A2 on the system board) |
|
(4) NVMe data cable 4 (from connector NVMe-B3/B4 on the drive backplane to connector NVMe-A3/A4 on the system board) |
Figure 53 Connecting the NVMe data cables for front drive bay 3
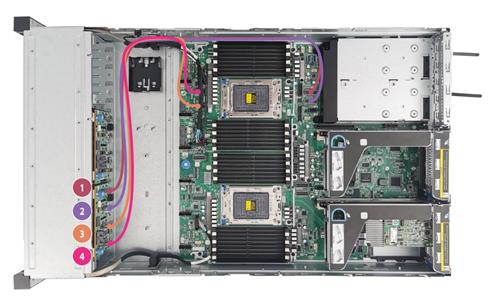
|
(1) NVMe data cable 1 (from connector NVMe-A1/A2 on the drive backplane to connector NVMe-B5/B6 on the system board) |
|
(2) NVMe data cable 2 (from connector NVMe-A3/A4 on the drive backplane to connector NVMe-B7/B8 on the system board) |
|
(3) NVMe data cable 3 (from connector NVMe-B1/B2 on the drive backplane to connector NVMe-B1/B2 on the system board) |
|
(4) NVMe data cable 4 (from connector NVMe-B3/B4 on the drive backplane to connector NVMe-B3/B4 on the system board) |
Figure 54 Connecting the SAS/SATA data cable

Figure 55 Connecting the AUX signal cables

Figure 56 Connecting the power cords

Cabling 25SFF drives at the front and 4SFF UniBay drives at the rear
The front 25SFF drive backplane supports eight SAS, SATA, or NVMe drives and 17 SAS, SATA, or NVMe drives.
The rear 4SFF UniBay drive backplane supports two SAS, SATA, or NVMe drives and two NVMe drives.
Figure 57 Connecting the SAS/SATA data cable for the front 25SFF UniBay drives

Figure 58 Connecting the AUX signal cable and power cords for the front 25SFF UniBay drives

|
(1) to (3) Power cords |
(4) AUX signal cable |
Figure 59 Connecting the NVMe data cables and SAS/SATA data cable for the rear 4SFF UniBay drives

|
(1) SAS/SATA data cable (from the rear drive backplane to the EXP connector on the front drive backplane) |
|
(2) and (3) NVMe data cable (from the rear drive backplane to the system board) |
Figure 60 Connecting the AUX signal cable and power cord for the rear 4SFF UniBay drives

|
(1) Power cord |
(2) AUX signal cable |
Connecting the SATA M.2 SSD cable
Figure 61 Connecting the SATA M.2 SSD cable

Connecting the OCP 3.0 ×16 network adapter cable
Figure 62 Connecting the OCP 3.0 ×16 network adapter cable

Connecting the PCIe signal cables
Figure 63 Connecting the PCIe signal cables

Table 13 Cabling method
|
Riser card slot |
Cable code |
Cable number |
Connector on the riser card |
Connector on the system board |
|
Riser1 |
0404A1EB |
1 |
SlimSAS port 1 |
NVMe-A1/A2 |
|
2 |
SlimSAS port 2 |
NVMe-A3/A4 |
||
|
Riser2 |
0404A1ED |
1 |
SlimSAS port 1 |
NVMe-B1/B2 |
|
2 |
SlimSAS port 2 |
NVMe-B3/B4 |
Connecting supercapacitor extension cables
Figure 64 Connecting supercapacitor extension cables

Connecting cables to chassis ears
Figure 65 Connecting cables to chassis ears

Connecting the LCD smart management module cable
Figure 66 Connecting the LCD smart management module cable

Maintenance
The following information describes the guidelines and tasks for daily server maintenance.
Guidelines
· Keep the equipment room clean and tidy. Remove unnecessary devices and objects from the equipment room.
· Make sure the temperature and humidity in the equipment room meet the server operating requirements.
· Regularly check the server from HDM for operating health issues.
· Keep the operating system and software up to date as required.
· Make a reliable backup plan:
¡ Back up data regularly.
¡ If data operations on the server are frequent, back up data as needed in shorter intervals than the regular backup interval.
¡ Check the backup data regularly for data corruption.
· Stock spare components on site in case replacements are needed. After a spare component is used, prepare a new one.
· Keep the network topology up to date to facilitate network troubleshooting.
Maintenance tools
The following are major tools for server maintenance:
· Temperature humidity meter—Monitors the operating environment of the server.
· HDM and FIST—Monitors the operating status of the server.
Maintenance tasks
Observing LED status
Observe the LED status on the front and rear panels of the server to verify that the server modules are operating correctly. For more information about the status of the front and rear panel LEDs, see "Front panel" and "Rear panel."
Monitoring the temperature and humidity in the equipment room
Use a hygrothermograph to monitor the temperature and humidity in the equipment room.
The temperature and humidity in the equipment room must meet the server requirements described in "Environment requirements."
Examining cable connections
Verify that the cables and power cords are correctly connected.
Guidelines
· Do not use excessive force when connecting or disconnecting cables.
· Do not twist or stretch the cables.
· Organize the cables appropriately. For more information, see "Cabling guidelines."
Checklist
· The cable type is correct.
· The cables are correctly and firmly connected and the cable length is appropriate.
· The cables are in good condition and are not twisted or corroded at the connection point.
Viewing the server status
For information about how to view the server status, see HDM online help.
Downloading the server log
For information about how to download the sever log, see H3C Servers HDM User Guide.
Upgrading the server firmware
For information about how to upgrade the HDM, BIOS, and CPLD firmware, see H3C Servers Firmware Update Guide.
Technical support
· Log and sensor information:
· Log information:
¡ Event logs.
¡ HDM audit logs and update logs.
¡ SDS logs.
¡ Diagnostics logs.
For information about how to collect log information, see HDM and iFIST online help.
· Sensor information.
To collect the sensor information, you must log in to the HDM Web interface. For more information, see HDM online help.
· Product serial number.
· Product model and name.
· Snapshots of error messages and descriptions.
· Hardware change history, including installation, replacement, insertion, and removal of hardware.
· Third-party software installed on the server.
· Operating system type and version.









































