| Title | Size | Downloads |
|---|---|---|
| H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual-Release 22XX Series(V1.00)-Port Security-Port Binding Operation.pdf | 190.12 KB |
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 12-Port Security-Port Binding Operation | 190.12 KB |
Table of Contents
Port Security Configuration Task List
Setting the Maximum Number of MAC Addresses Allowed on a Port
Setting the Port Security Mode
Configuring Port Security Features
Configuring Guest VLAN for a Port in macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode
Ignoring the Authorization Information from the RADIUS Server
Configuring Security MAC Addresses
Displaying and Maintaining Port Security Configuration
Port Security Configuration Example
Port Security Configuration Example
Guest VLAN Configuration Example
Displaying and Maintaining Port Binding Configuration
Port Binding Configuration Example
Port Binding Configuration Example
When configuring port security, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Port Security Configuration Task List
l Displaying and Maintaining Port Security Configuration
l Port Security Configuration Example
Port Security Overview
Introduction
Port security is a security mechanism for network access control. It is an expansion to the current 802.1x and MAC address authentication.
Port security allows you to define various security modes that enable devices to learn legal source MAC addresses, so that you can implement different network security management as needed.
With port security enabled, packets whose source MAC addresses cannot be learned by your switch in a security mode are considered illegal packets, The events that cannot pass 802.1x authentication or MAC authentication are considered illegal.
With port security enabled, upon detecting an illegal packet or illegal event, the system triggers the corresponding port security features and takes pre-defined actions automatically. This reduces your maintenance workload and greatly enhances system security and manageability.
Port Security Features
The following port security features are provided:
l NTK (need to know) feature: By checking the destination MAC addresses in outbound data frames on the port, NTK ensures that the switch sends data frames through the port only to successfully authenticated devices, thus preventing illegal devices from intercepting network data.
l Intrusion protection feature: By checking the source MAC addresses in inbound data frames or the username and password in 802.1x authentication requests on the port, intrusion protection detects illegal packets or events and takes a pre-set action accordingly. The actions you can set include: disconnecting the port temporarily/permanently, and blocking packets with the MAC address specified as illegal.
l Trap feature: When special data packets (generated from illegal intrusion, abnormal login/logout or other special activities) are passing through the switch port, Trap feature enables the switch to send Trap messages to help the network administrator monitor special activities.
Port Security Modes
Table 1-1 describes the available port security modes:
Table 1-1 Description of port security modes
|
Security mode |
Description |
Feature |
|
noRestriction |
In this mode, access to the port is not restricted. |
In this mode, neither the NTK nor the intrusion protection feature is triggered. |
|
autolearn |
In this mode, the port automatically learns MAC addresses and changes them to security MAC addresses. This security mode will automatically change to the secure mode after the amount of security MAC addresses on the port reaches the maximum number configured with the port-security max-mac-count command. After the port security mode is changed to the secure mode, only those packets whose source MAC addresses are security MAC addresses learned can pass through the port. |
In either mode, the device will trigger NTK and intrusion protection upon detecting an illegal packet. |
|
secure |
In this mode, the port is disabled from learning MAC addresses. Only those packets whose source MAC addresses are security MAC addresses learned and static MAC addresses can pass through the port. |
|
|
userlogin |
In this mode, port-based 802.1x authentication is performed for access users. |
In this mode, neither NTK nor intrusion protection will be triggered. |
|
userLoginSecure |
MAC-based 802.1x authentication is performed on the access user. The port is enabled only after the authentication succeeds. When the port is enabled, only the packets of the successfully authenticated user can pass through the port. In this mode, only one 802.1x-authenticated user is allowed to access the port. When the port changes from the noRestriction mode to this security mode, the system automatically removes the existing dynamic MAC address entries and authenticated MAC address entries on the port. |
In any of these modes, the device triggers the NTK and Intrusion Protection features upon detecting an illegal packet or illegal event. |
|
userLoginSecureExt |
This mode is similar to the userLoginSecure mode, except that there can be more than one 802.1x-authenticated user on the port. |
|
|
userLoginWithOUI |
This mode is similar to the userLoginSecure mode, except that, besides the packets of the single 802.1x-authenticated user, the packets whose source MAC addresses have a particular OUI are also allowed to pass through the port. When the port changes from the normal mode to this security mode, the system automatically removes the existing dynamic/authenticated MAC address entries on the port. |
|
|
macAddressWithRadius |
In this mode, MAC address–based authentication is performed for access users. |
|
|
macAddressOrUserLoginSecure |
In this mode, both MAC authentication and 802.1x authentication can be performed, but 802.1x authentication has a higher priority. 802.1x authentication can still be performed on an access user who has passed MAC authentication. No MAC authentication is performed on an access user who has passed 802.1x authentication. In this mode, there can be only one 802.1x-authenticated user on the port, but there can be several MAC-authenticated users. |
|
|
macAddressOrUserLoginSecureExt |
This mode is similar to the macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode, except that there can be more than one 802.1x-authenticated user on the port. . |
|
|
macAddressElseUserLoginSecure |
In this mode, a port performs MAC authentication or 802.1x authentication of an access user. If either authentication succeeds, the user is authenticated. In this mode, there can be only one 802.1x-authenticated user on the port, but there can be several MAC-authenticated users. |
|
|
macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt |
This mode is similar to the macAddressElseUserLoginSecure mode, except that there can be more than one 802.1x-authenticated user on the port. |
|
|
macAddressAndUserLoginSecure |
In this mode, a port firstly performs MAC authentication for a user and then performs 802.1x authentication for the user if the user passes MAC authentication. The user can access the network after passing the two authentications. In this mode, up to one user can access the network. |
|
|
macAddressAndUserLoginSecureExt |
This mode is similar to the macAddressAndUserLoginSecure mode, except that more than one user can access the network. |
![]()
l When the port operates in the userlogin-withoui mode, Intrusion Protection will not be triggered even if the OUI address does not match.
l In the macAddressElseUserLoginSecure or macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt security mode, the MAC address of a user failing MAC authentication is set as a quiet MAC address. If the user initiates 802.1x authentication during the quiet period, the switch does not authenticate the user.
l A port with port security configured permits all ordinary Layer 2 packets to be forwarded whose source MAC addresses are dynamic ones configured on the port.
Port Security Configuration Task List
Complete the following tasks to configure port security:
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
|
Required |
||
|
Setting the Maximum Number of MAC Addresses Allowed on a Port |
Optional |
|
|
Required |
||
|
Optional Choose one or more features as required. |
||
|
Configuring Guest VLAN for a Port in macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode |
Optional |
|
|
Ignoring the Authorization Information from the RADIUS Server |
Optional |
|
|
Optional |
||
Enabling Port Security
Configuration Prerequisites
Before enabling port security, you need to disable 802.1x and MAC authentication globally.
Enabling Port Security
Follow these steps to enable port security:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enable port security |
port-security enable |
Required Disabled by default |
![]()
Enabling port security resets the following configurations on the ports to the defaults (shown in parentheses below):
l 802.1x (disabled), port access control method (macbased), and port access control mode (auto)
l MAC authentication (disabled)
In addition, you cannot perform the above-mentioned configurations manually because these configurations change with the port security mode automatically.
![]()
l For details about 802.1x configuration, refer to the sections covering 802.1x and System-Guard.
l For details about MAC authentication configuration, refer to the sections covering MAC authentication configuration.
Setting the Maximum Number of MAC Addresses Allowed on a Port
Port security allows more than one user to be authenticated on a port. The number of authenticated users allowed, however, cannot exceed the configured upper limit.
By setting the maximum number of MAC addresses allowed on a port, you can
l Control the maximum number of users who are allowed to access the network through the port
l Control the number of Security MAC addresses that can be added with port security
This configuration is different from that of the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be leaned by a port in MAC address management.
Follow these steps to set the maximum number of MAC addresses allowed on a port:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Set the maximum number of MAC addresses allowed on the port |
port-security max-mac-count count-value |
Required Not limited by default |
Setting the Port Security Mode
Follow these steps to set the port security mode:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Set the OUI value for user authentication |
port-security oui OUI-value index index-value |
Optional In userLoginWithOUI mode, a port supports one 802.1x user plus one user whose source MAC address has a specified OUI value. |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Set the port security mode |
port-security port-mode { autolearn | mac-and-userlogin-secure | mac-and-userlogin-secure-ext | mac-authentication | mac-else-userlogin-secure | mac-else-userlogin-secure-ext | secure | userlogin | userlogin-secure | userlogin-secure-ext | userlogin-secure-or-mac | userlogin-secure-or-mac-ext | userlogin-withoui } |
Required By default, a port operates in noRestriction mode. In this mode, access to the port is not restricted. You can set a port security mode as needed. |
![]()
l Before setting the port security mode to autolearn, you need to set the maximum number of MAC addresses allowed on the port with the port-security max-mac-count command.
l When the port operates in the autoLearn mode, you cannot change the maximum number of MAC addresses allowed on the port.
l After you set the port security mode to autolearn, you cannot configure any static or blackhole MAC addresses on the port.
l If the port is in a security mode other than noRestriction, before you can change the port security mode, you need to restore the port security mode to noRestriction with the undo port-security port-mode command.
If the port-security port-mode mode command has been executed on a port, none of the following can be configured on the same port:
l Maximum number of MAC addresses that the port can learn
l Reflector port for port mirroring
l Link aggregation
Configuring Port Security Features
Configuring the NTK feature
Follow these steps to configure the NTK feature:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Configure the NTK feature |
port-security ntk-mode { ntkonly | ntk-withbroadcasts | ntk-withmulticasts } |
Required By default, NTK is disabled on a port, namely all frames are allowed to be sent. |
Configuring intrusion protection
Follow these steps to configure the intrusion protection feature:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Set the corresponding action to be taken by the switch when intrusion protection is triggered |
port-security intrusion-mode { blockmac | disableport | disableport-temporarily } |
Required By default, intrusion protection is disabled. |
|
Return to system view |
quit |
— |
|
Set the timer during which the port remains disabled |
port-security timer disableport timer |
Optional 20 seconds by default |
![]()
The port-security timer disableport command is used in conjunction with the port-security intrusion-mode disableport-temporarily command to set the length of time during which the port remains disabled.
![]()
If you configure the NTK feature and execute the port-security intrusion-mode blockmac command on the same port, the switch will be unable to disable the packets whose destination MAC address is illegal from being sent out that port; that is, the NTK feature configured will not take effect on the packets whose destination MAC address is illegal.
Configuring the Trap feature
Follow these steps to configure port security trapping:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enable sending traps for the specified type of event |
port-security trap { addresslearned | dot1xlogfailure | dot1xlogoff | dot1xlogon | intrusion | ralmlogfailure | ralmlogoff | ralmlogon } |
Required By default, no trap is sent. |
Configuring Guest VLAN for a Port in macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode
Users fails the authentication can access certain specified VLAN. This VLAN is called guest VLAN. For details about guest VLAN, refer to the sections covering 802.1x and System-Guard.
A port in macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode supports guest VLAN configurations. The port can connect multiple users; but services only one user at a time.
1) When the first user of the port initiates 802.1x or MAC address authentication:
l If the user fails the authentication, the port is added to the guest VLAN, and all the other users of the port are authorized to access the guest VLAN.
l If the user passes the authentication, authentication requests from other users are not handled because only one user is allowed to pass authentication using the port. The other users will fail the authentication, but the port will not be added to the guest VLAN.
2) After the port is added to the guest VLAN:
l The users of the port can initiate 802.1x authentication. If a user passes authentication, the port leaves the guest VLAN and is added to the original VLAN, that is, the one the port belongs to before it is added to the guest VLAN). The port then does not handle other users' authentication requests.
l MAC address authentication is also allowed. However, MAC authentication in this case cannot be triggered by user requests; the switch will use the first MAC address learned in the guest VLAN to initiate MAC address authentication at a certain interval. If the authentication succeeds, the port leaves the guest VLAN.
Follow these steps to configure a guest VLAN for a port in macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Set the interval at which the switch triggers MAC address authentication after a port is added to the guest VLAN |
port-security timer guest-vlan-reauth interval |
Optional |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Set the security mode to macAddressOrUserLoginSecure |
port-security port-mode userlogin-secure-or-mac |
Required |
|
Specify a VLAN as the guest VLAN of the port |
port-security guest-vlan vlan-id |
Required |
Note that:
l Only an existing VLAN can be specified as a guest VLAN. Make sure the guest VLAN of a port contain the resources that the users need.
l If one user of the port has passed or is undergoing authentication, you cannot specify a guest VLAN for it.
l When a user using a port with a guest VLAN specified fail the authentication, the port is added to the guest VLAN.
l Multiple users may connect to one port in the macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode for authentication; however, after a guest VLAN is specified for the port, only one user can pass the security authentication. In this case, the authentication client software of the other 802.1x users displays messages about the failure; MAC address authentication does not have any client software and therefore no such messages will be displayed.
l To change the security mode from macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode of a port that is assigned to a guest VLAN, execute the undo port-security guest-vlan command first to remove the guest VLAN configuration.
l For a port configured with both the port-security guest-vlan and port-security intrusion-mode disableport commands, when authentication of a user fails, only the intrusion detection feature is triggered. The port is not added to the specified guest VLAN.
l It is not recommended to configure the port-security guest-vlan and port-security intrusion-mode blockmac commands simultaneously for a port. Because when the authentication of a user fails, the blocking MAC address feature will be triggered and packets of the user will be dropped, making the user unable to access the guest VLAN.
Ignoring the Authorization Information from the RADIUS Server
After an 802.1x user or MAC-authenticated user passes Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) authentication, the RADIUS server delivers the authorization information to the device. You can configure a port to ignore the authorization information from the RADIUS server.
Follow these steps to configure a port to ignore the authorization information from the RADIUS server:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Ignore the authorization information from the RADIUS server |
port-security authorization ignore |
Required By default, a port uses the authorization information from the RADIUS server. |
Configuring Security MAC Addresses
A port in autolearn mode performs MAC address learning and maintains a security MAC address forwarding table. You can also manually configure security MAC address entries. By default, the security MAC address entries will never be aged, one security MAC address can only be added to the forwarding table of one port. This feature allows binding a security MAC address with a port in the same VLAN.
After the security port is set to autolearn, the port changes its way of learning MAC addresses as follows.
The port deletes original dynamic MAC addresses;
l If the amount of security MAC addresses has not yet reach the maximum number, the port will learn new MAC addresses and turn them to security MAC addresses;
l If the amount of security MAC addresses reaches the maximum number, the port will not be able to learn new MAC addresses and the port mode will be changed from autolearn to secure.
![]()
The security MAC addresses manually configured are written to the configuration file; they will not get lost when the port is up or down. As long as the configuration file is saved, the security MAC addresses can be restored after the switch reboots.
Configuring a security MAC address entry manually
Before configuring a security MAC address entry for a port manually, ensure that:
l Port security is enabled.
l The maximum number of security MAC addresses allowed on the port is set.
l The security mode of the port is set to autolearn.
Configuring a security MAC address
Follow these steps to configure a security MAC address:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Add a security MAC address |
In system view |
mac-address security mac-address interface interface-type interface-number vlan vlan-id |
Either is required. By default, no security MAC address is configured. |
|
In Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
||
|
mac-address security mac-address vlan vlan-id |
|||
Configuring an aging time for learned security MAC address entries
By default, learned security MAC address entries will never be aged; they are deleted only when the port security feature is disabled or the security mode is not autolearn any more.
You can configure an aging time for security MAC address entries. When the timer of an entry expires, the entry is removed from the security MAC address table.
Follow these steps to configure an aging time for learned security MAC address entries:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enable port security |
port-security enable |
— |
|
Configure the aging time for learned security MAC address entries |
port-security timer autolearn age |
Required Aging of MAC address entries is disabled by default. |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Set the maximum number of MAC addresses allowed on the port |
port-security max-mac-count count-value |
Required By default, there is no limit on the number of MAC addresses. |
|
Set the security mode of the port to autolearn |
port-security port-mode autolearn |
Required By default, a port operates in noRestriction mode, and access to the port is not restricted. |
![]()
After you execute the port-security timer autolearn command, you can display security MAC address entries by the display mac-address security command. Though the aging time field displayed has a value of "NOAGED", the aging of security MAC address entries is enabled already.
Displaying and Maintaining Port Security Configuration
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Display information about port security configuration |
display port-security [ interface interface-list ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display information about security MAC address configuration |
display mac-address security [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] |
Port Security Configuration Example
Port Security Configuration Example
Network requirements
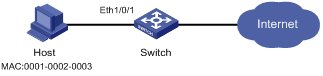
Implement access user restrictions through the following configuration on Ethernet 1/0/1 of the switch.
l Allow a maximum of 80 users to access the port without authentication and permit the port to learn and add the MAC addresses of the users as security MAC addresses.
l To ensure that Host can access the network, add the MAC address 0001-0002-0003 of Host as a security MAC address to the port in VLAN 1.
l After the number of security MAC addresses reaches 80, the port stops learning MAC addresses. If any frame with an unknown MAC address arrives, intrusion protection is triggered and the port will be disabled and stay silent for 30 seconds.
Network diagram
Figure 1-1 Network diagram for port security configuration
Configuration procedure
# Enter system view.
<Switch> system-view
# Enable port security.
[Switch] port-security enable
# Enter Ethernet1/0/1 port view.
[Switch] interface Ethernet 1/0/1
# Set the maximum number of MAC addresses allowed on the port to 80.
[Switch-Ethernet1/0/1] port-security max-mac-count 80
# Set the port security mode to autolearn.
[Switch-Ethernet1/0/1] port-security port-mode autolearn
# Add the MAC address 0001-0002-0003 of Host as a security MAC address to the port in VLAN 1.
[Switch-Ethernet1/0/1] mac-address security 0001-0002-0003 vlan 1
# Configure the port to be silent for 30 seconds after intrusion protection is triggered.
[Switch-Ethernet1/0/1] port-security intrusion-mode disableport-temporarily
[Switch-Ethernet1/0/1] quit
[Switch] port-security timer disableport 30
Guest VLAN Configuration Example
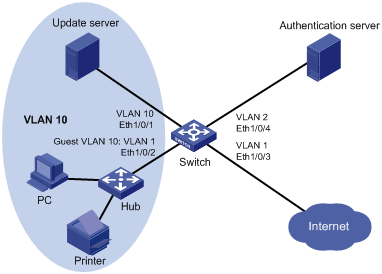
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1-2, Ethernet 1/0/2 connects to a PC and a printer, which are not used at the same time. Configure the port to operate in macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode and specify a guest VLAN for the port.
l The PC must pass 802.1x authentication to connect to the network while the printer must pass MAC address authentication to achieve network connectivity.
l The switch’s port Ethernet 1/0/3 connects to the Internet. This port is assigned to VLAN 1. Normally, the port Ethernet 1/0/2 is also assigned to VLAN.
l VLAN 10 is intended to be a guest VLAN. It contains an update server for users to download and upgrade their client software. When a user fails authentication, port Ethernet 1/0/2 is added to VLAN 10. Then the user can access only VLAN 10. The port goes back to VLAN 1 when the user passes authentication.
Figure 1-2 Network diagram for guest VLAN configuration
Configuration procedure
![]()
The following configuration steps include configurations of AAA and RADIUS. For details about these commands, refer to AAA Command. The configurations on the 802.1x client and the RADIUS server are omitted.
# Configure RADIUS scheme 2000.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] radius scheme 2000
[Switch-radius-2000] primary authentication 10.11.1.1 1812
[Switch-radius-2000] primary accounting 10.11.1.1 1813
[Switch-radius-2000] key authentication abc
[Switch-radius-2000] key accounting abc
[Switch-radius-2000] user-name-format without-domain
[Switch-radius-2000] quit
# Configure the ISP domain and apply the scheme 2000 to the domain.
[Switch] domaim system
[Switch-isp-system] scheme radius-scheme 2000
[Switch-isp-system] quit
# Set the username type for MAC address authentication to MAC address that requires no hyphened lowercase MAC addresses as the username and password.
[Switch] mac-authentication authmode usernameasmacaddress usernameformat without-hyphen lowercase
# Configure the ISP domain for MAC address authentication.
[Switch] mac-authentication domain system
# Enable port security.
[Switch] port-security enable
# Specify the switch to trigger MAC address authentication at an interval of 60 seconds.
[Switch] port-security timer guest-vlan-reauth 60
# Create VLAN 10 and assign the port Ethernet 1/0/1 to it.
[Switch] vlan 10
[Switch–vlan10] port Ethernet 1/0/1
# Set the security mode of the port Ethernet 1/0/2 to macAddressOrUserLoginSecure.
[Switch] interface Ethernet1/0/2
[Switch-Ethernet1/0/2] port-security port-mode userlogin-secure-or-mac
# specify VLAN 10 as the guest VLAN of the port.
[Switch-Ethernet1/0/2] port-security guest-vlan 10
You can display the guest VLAN configuration information by the display current-configuration or display interface ethernet 1/0/2 command.
If a user fails the authentication, you can use the display vlan 10 command to view if the guest VLAN specified for the port is effective.
2 Port Binding Configuration
When configuring port binding, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Displaying and Maintaining Port Binding Configuration
l Port Binding Configuration Example
![]()
Currently, only the S3100-EI series support port binding.
Port Binding Overview
Introduction
Binding is a simple security mechanism. Through the binding configuration on the switch, you can filter the packets forwarded on the ports. When a port receives a packet, it searches the binding entry. If the information carried in the packet matches the information in the binding entry, the port forwards the packet. Otherwise, the port discards the packet.
Currently, the switch provides the following binding policies:
l Port-IP binding: binds a port to an IP address. On the bound port, the switch forwards only the packets sourced from the bound IP address.
l Port-MAC binding: binds a port to a MAC address. On the bound port, the switch forwards only the packets sourced from the bound MAC address.
l Port-MAC-IP binding: binds a MAC address and an IP address to a port. On the port, if the source IP address of a received packet matches a binding entry, the port forwards the packet only if the source MAC address of the packet also matches the entry. If the source IP address of a packet does not match any entry in the port-MAC-IP binding table, the port forwards the packet.
l IP-MAC binding: binds an IP address to a MAC address. The switch forwards only the packets sourced from the bound source MAC address and source IP address.
![]()
When a port is bound, the binding applies only to the port.
Configuring Port Binding
Follow these steps to configure port binding:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Bind the MAC address and IP address of a user to a specific port |
In system view |
am user-bind mac-addr mac-address { ip-addr ip-address s | ipv6 ipv6-address } [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
Either is required. By default, no user MAC address or IP address is bound to a port. |
|
In Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
||
|
am user-bind { mac-addr mac-address [ ip-addr ip-address | ipv6 ipv6-address ] | ip-addr ip-address | ipv6 ipv6-address } |
|||
![]()
l An IP address can be bound to only one port at a time.
l A MAC address can be bound to only one port at a time.
l For the same port, port-IP-MAC binding is mutually exclusive with port-IP binding.
Displaying and Maintaining Port Binding Configuration
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Display port binding information |
display am user-bind [ interface interface-type interface-number | ip-addr ip-address | mac-addr mac-address ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display IPv6 port binding information |
display am user-bind ipv6 [ interface interface-type interface-number | ipv6-address | mac-address mac-address | unit unit-id ] |
Port Binding Configuration Example
Port Binding Configuration Example
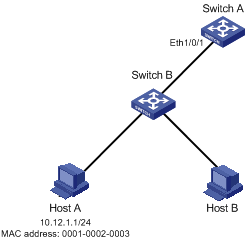
Network requirements
It is required to bind the MAC and IP addresses of Host A to Ethernet 1/0/1 on Switch A, so as to prevent malicious users from using the IP address they steal from Host A to access the network.
Network diagram
Figure 2-1 Network diagram for port binding configuration
Configuration procedure
Configure Switch A as follows:
# Enter system view.
<SwitchA> system-view
# Enter Ethernet 1/0/1 port view.
[SwitchA] interface Ethernet 1/0/1
# Bind the MAC address and the IP address of Host A to Ethernet 1/0/1.
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/1] am user-bind mac-addr 0001-0002-0003 ip-addr 10.12.1.1

