- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Text | 552.26 KB |
Table of Contents
About the H3C WA Documentation Set
Examining the Installation Site
Temperature and Humidity Requirements
Grounding and Lightning Protection
Powering on the AP and Connecting It to a Network
Configuring Basic Functions for an AP Operating in Fit Mode
Configuring Basic Functions for an AP Operating in Fat Mode
Specifying an IP Address for an AP
Saving the Current Configuration
Software Maintenance Approaches
Factory Default Configuration of a Fat AP
Removing the Factory Default Configuration
Fit/Fat Working Mode Switching
Switching the Working Mode Through the BootWare Menu
Switching the Working Mode at the CLI
Upgrading Applications Through the Serial Port
Modifying Serial Communication Parameters
Upgrading Applications Through TFTP at the CLI
Setting Up an Upgrade Environment
Displaying the System Files and Available Space of the Storage Medium
Upgrading the Applications Through FTP at the CLI
Upgrading an Application Using FTP at the CLI
Setting Up an Upgrade Environment
Displaying the System Files and Available Space of the Storage Medium
Logging In to the FTP Server from the AP
Upgrading an Application by Using FTP with the Default Configuration
Upgrading an Application Through the Web Interface
Automatically Managing and Upgrading the Applications Through an AC or a US
Associating the Fit AP with an AC or a US
Automatically Upgrading the Application of the AP Through the AC or US
Maintaining Application and Configuration Files
Setting the Application File Type
The H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Getting Started Guide describes the installation preparation, login, command line interface (CLI), basic configurations, software maintenance, and troubleshooting for the H3C WA Series WLAN access points.
This preface includes:
l Audience
l About the H3C WA Documentation Set
Audience
This documentation is intended for:
l Network planners
l Field technical support and servicing engineers
l Network administrators working with the WA series
Document Organization
The H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Getting Started Guide comprises these chapters:
|
Chapter |
Content |
|
About This Document |
Briefs the audience, document organization, related documentation, and conventions. |
|
Product Overview |
Presents the models and supported working modes of each series. |
|
Installation Preparations |
Describes the preparations and check before installation. |
|
Installing an AP |
Briefs the installation method, and reference for installation. |
|
Logging In to an AP |
Describes the supported user interfaces and login methods, and provides the reference. |
|
Configuring Basic Functions |
Briefs the basic configurations in both fit and fat AP modes, and the default configurations in fat mode. |
|
Software Maintenance |
Guides you through the application and configuration file upgrade at the CLI and through the web interface, fit and fat AP switch, and dealing with password loss. |
|
Troubleshooting |
Briefs how to troubleshoot problems. |
|
Index |
Provides a list of detailed subjects and the page numbers containing text on the subject. |
Related Documentation
1) To configure a WA series WLAN access point through the Web interface, see H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Web-Based Configuration Guide.
|
Manual |
Description |
|
H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Web-Based Configuration Guide |
Guides you to configure software features through the web management interface, details the configuration items of the WA series access points, and gives configuration examples for the corresponding features. |
2) To know the hardware structure and installation procedure of a WA series WLAN access point, see the supplied documentation, or log in to http://www.h3c.com to get the relevant installation manual or quick start.
|
Manual |
Description |
|
H3C WA2200 Series WLAN Access Points Installation Manual |
Describes the hardware configuration, interfaces and LEDs, installation preparations, grounding and lightning protection, installation of outdoor antennas, connection of external cables, indoor installation, and outdoor installation of the WA2200 series WLAN access points (802.11a/b/g). |
|
H3C WA2210X-GE WLAN Access Point Installation Manual |
Describes the hardware configuration, interfaces and LEDs, installation preparations, grounding and lightning protection, installation of outdoor antennas, connection of external cables, and outdoor installation of the WA2210X-GE WLAN access point (802.11b/g). |
|
H3C WA2600 Series Enhanced WLAN Access Points Installation Manual |
Describes the hardware configuration, interfaces and LEDs, installation preparations, grounding and lightning protection, connection of external cables, and installation of the H3C WA2600 series enhanced WLAN access points (802.11a/b/g/n). |
|
H3C WA2600 Series Indoor WLAN Access Points Installation Manual |
Describes the hardware configuration, interfaces and LEDs, installation preparations, connection of external cables, and indoor installation of the H3C WA2600 series indoor WLAN access points (802.11a/b/g/n). |
|
H3C WA2620-AGN WLAN Access Point Quick Start |
Describes the interfaces and LEDs, installation preparations, and installation of the H3C WA2620-AGN WLAN access point (802.11a/b/g/n). |
3) To obtain other information about WA series WLAN access points, log in to http://www.h3c.com to get the related documentation.
Conventions
The manual uses the following conventions:
GUI conventions
|
Convention |
Description |
|
Boldface |
Window names, button names, field names, and menu items are in Boldface. For example, the New User window appears; click OK. |
|
> |
Multi-level menus are separated by angle brackets. For example, File > Create > Folder. |
Symbols
|
Convention |
Description |
|
|
Means reader be extremely careful. Improper operation may cause bodily injury. |
|
|
Means reader be careful. Improper operation may cause data loss or damage to equipment. |
|
|
Means an action or information that needs special attention to ensure successful configuration or good performance. |
|
|
Means a complementary description. |
|
|
Means techniques helpful for you to make configuration with ease. |
About the H3C WA Documentation Set
The H3C WA documentation set includes:
|
Category |
Documents |
Purposes |
|
Product description and specifications |
Describe product specifications and benefits. |
|
|
Provide an in-depth description of software features and technologies. |
||
|
Hardware specifications and installation |
Provides regulatory information and the safety instructions that must be followed during installation. |
|
|
Guides you through initial installation and setup procedures to help you quickly set up and use your AP with the minimum configuration. |
||
|
Guides you through hardware specifications and installation methods to help you install your AP. |
||
|
Software configuration |
Describe software features and configuration procedures. |
|
|
Provide a quick reference to all available commands. |
||
|
Operations and Maintenance |
Provide information about the product release, including the version history, hardware and software compatibility matrix, version upgrade information, technical support information, and software upgrading. |
Obtaining Documentation
You can access the most up-to-date H3C product documentation on the World Wide Web at http://www.h3c.com.
Click the links on the top navigation bar to obtain different categories of product documentation:
[Technical Support & Documents > Technical Documents] – Provides hardware installation, software upgrading, and software feature configuration and maintenance documentation.
[Products & Solutions] – Provides information about products and technologies, as well as solutions.
[Technical Support & Documents > Software Download] – Provides the documentation released with the software version.
Documentation Feedback
You can e-mail your comments about product documentation to info@h3c.com.
We appreciate your comments.
Developed by Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd (hereinafter referred to as H3C), H3C WA series wireless local area network (WLAN) access points (APs) (hereinafter referred to as the WA series) can be widely applied in wireless networks providing WLAN services to users. The WA series can operate in both fat and fit modes. When they serve as fit APs, they need to cooperate with wireless controllers or unified switches; when they serve as fat APs, they can independently provide wireless access for WLAN users. The WA series allow you to switch between the two modes at the CLI to accommodate to different network sizes. Thus, flexibility is achieved.
H3C WA series WLAN access points include WA2110-AG, WA2200 series, and WA2600 series. Table 2-1 shows the applicable models and working mode.
l The WA2110-AG supports 802.11a/b/g, and serves as fit APs to cooperate with wireless controllers or unified switches.
l The WA2200 series supports 802.11a/b/g, and can switch between the fit and fat modes to accommodate to different network sizes.
l The WA2600 series supports 802.11a/b/g/n, and can operate in both fat and fit modes. It provides an access rate of six times the traditional 802.11a/b/g network and covers a larger area. The WA 2600 series adopts 10 GE Ethernet interfaces as its uplink interfaces to implement wireless multi-media application.
Table 2-1 AP model and operating mode
|
Series |
Model |
Operating in fit or fat mode |
|
|
WA2110-AG |
WA2110-AG |
Only in fit mode |
|
|
WA2200 series |
WA2200 series access points (indoors) |
WA2210-AG |
Both |
|
WA2220-AG |
Both |
||
|
WA2200 series access points (outdoors) |
WA2210X-G |
Both |
|
|
WA2220X-AG |
Both |
||
|
WA2600 series |
WA2600 series access points (indoors) |
WA2610-AGN |
Both |
|
WA2612-AGN |
Both |
||
|
WA2620-AGN |
Both |
||
|
WA2600 series access points (enhanced) |
WA2610E-AGN |
Both |
|
|
WA2620E-AGN |
Both |
||
|
WA2610E-GNP |
Both |
||
This chapter describes the preparations for installing WA series WLAN access points, including the preparation of installation tools and environment examination.
![]()
The installation preparations for the H3C WA series access points depend on the installation environments (indoor or outdoor). For more information about the installation preparations of an AP model, see the installation guide or quick start of the AP.
Installation Preparations
Before installing your AP:
l Power on your AP, and connect it to an Ethernet. Check the corresponding LED status on your AP, and make sure that your AP works normally.
l Save the installation position, MAC address, and serial number of your AP, to facilitate the management and maintenance of APs by administrators.
l Determine whether installation accessories (for example, or power adapter) are needed according to the installation position and power supply mode of your AP. Order them in advance because some installation accessories are not shipped with your AP, and you need to purchase them yourself.
Preparing Installation Tools
When installing the AP, you may need the tools listed in Table 3-1. Choose the appropriate tools according to the installation environment.
Table 3-1 List of installation tools
|
Type of tool |
Indoor installation |
outdoor installation |
|
General tools |
1-meter-long rulers, marking pens, knives, a percussion drill with appropriate bits, screw driver, and adjustable spanner |
Digging tool, adjustable spanner, vices, and screw driver |
|
Special tools |
Cable strippers, crimping pliers, and RJ-45 crimping pliers |
Cable stripper, crimping pliers, RJ-45 crimping pliers, waterproof tape, and fiber fusion splicer |
|
Auxiliary tools |
Ladders and rubber hammers |
Ladders |
![]()
If you install the AP on a desk, none of the above tools is required. If you install the AP on top of or under eave of a building, no digging tool is required.
Examining the Installation Site
Before installation, examine the installation site to make sure that the AP will work in a good environment. You can examine the installation site from the following three aspects.
Installation Site Selection
Keep the AP away from places that are susceptible to high temperature, dust, inflammable, explosive, electromagnetic interference (high power radar, radio station, and transformer), unstable voltage, heavy vibration, or loud noise. The installation site should be dry, without any leakage, dripping, or dew. The AP should be at least 500 m (0.31 mi) away from the seaside and should not face the direction of sea wind.
In engineering design, the site should be selected according to the network planning and technical requirements of communications equipment, as well as the considerations such as climate, hydrology, geology, earthquake, electric power, and transportation.
Temperature and Humidity Requirements
The temperature and humidity requirements depend on your AP model. For more information, see the installation guide or quick start of your AP.
Power Supply
The power supply mode depends on your AP model. For more information, see the installation guide or quick start of your AP.
Grounding and Lightning Protection
Table 3-2 Grounding and lightning protection requirements
|
SN |
Item |
Requirements |
|
1 |
Grounding resistance |
l The earth resistance is usually required to be less than 5 ohms, and less than 10 ohms in an area with less than 20 thunderstorm days a year. If a piece of angle steel is buried as the earthing conductor, the earth resistance is required to be less than 10 ohms. In an area with a higher earth resistance, reduce the earth resistance by using brine or resistance reducing agent around the earthing conductor. l The top of the earthing conductor should be at least 0.7 m (2.30 ft) away from the ground surface. In cold areas, the earthing conductor should be buried below the frozen soil layer. |
|
2 |
Device protection ground (PGND) |
l If a grounding strip is available, connect the yellow and green ground cable of the AP to the grounding strip. If you need to make a grounding cable, the cable should be with a cross-section area of at least 6 mm2 (0.24 in2) and a length of no longer than 3 m (9.84 ft). l If no grounding strip is available, bury a piece of angle steel/steel tube at least 0.5 m (1.64 ft) long in the earth to serve as the earthing conductor. In the case of a piece of angle steel, the size should be at least 50 mm × 50 mm × 5 mm (1.97 in. × 1.97 in. × 0.20 in.); in the case of a piece of steel tube, it must be zinc-plated and have a wall thickness of at least 3.5 mm (0.14 in.). Weld the yellow and green ground cable of the AP onto the earthing conductor and use anti-erosion treatment on the welding joint. The grounding cable should be as short as possible and must not be coiled. l Ensure that the grounding points of all the lightning arresters of the AP and the peer device of the AP are well grounded. |
|
3 |
Grounding lead-in |
A grounding lead-in is a metal conductor connecting a grounding net and a grounding strip. The grounding cable of the AP should be connected to the grounding strip. The grounding lead-in must be 30 m (98.43 ft) or shorter. A piece of zinc-coated flat steel with a cross-section area of 40 × 4 mm (1.57 × 0.16 in) or 50 × 5 mm (1.97 × 0.20 in) is recommended. Connect the grounding strip and the grounding lead-in of the AP through the yellow and green ground cable with an area of 35 mm2 (1.38 in.), or weld them directly. Use anti-erosion treatment on the welding joint. |
|
4 |
Power grounding (AC) |
l Use a power cord with a protective earth (PE). Do not use a power cord with only an L line and an N line. l The neutral line of the power cord should not be connected with the PGND of other communications equipment. The L and N lines cannot be connected |
|
5 |
Lightning arrester |
In plain areas, the protection angle of the lightning rod should be less than 45 degrees. In mountainous areas or lightning areas, the protection angle should be less than 30 degrees. The lightning protection grounding (for example, the grounding of the lightning rod) should be connected to the earthing conductor of the equipment room. |
|
6 |
Feeder |
l The antenna support is already prepared according to the design requirements. l A feeder lightning rod is already installed and grounded according to the design requirements. |
|
7 |
Outdoor lightning arrester |
Power lightning arrester, port lightning protector, and feeder lightning arrester are recommended for outdoor installations. The power lightning arrester and the feeder lightning arrester should be near the AP, and the network interface lightning arrester should be near the peer device of the AP. The network interface lightning arrester should be installed where the network cable is just led out of the room. |
|
8 |
Network cable |
Use a shielded twisted pair cables for an AP used outdoors. Ensure that the devices at the two ends of the cable are well grounded. |
After you have completed the preparations, you can start installing the AP.
You can directly place an indoor model (including the enhanced model) on a desk. The rubber feet on the bottom of the AP help you to place it horizontally. Or you can fix it onto a wall, a ceiling, or a lifting pole by using the wall-mounting bracket. Support for the installation method depends on your AP model. For more information, see the installation guide or quick start of your AP.
![]()
Some installation accessories (for example, wall-mounting brackets) are not shipped with your AP. Determine whether to order them as needed.
Before logging in to an AP, power on the AP and connect it to a network. For more information, see Powering on the AP and Connecting It to a Network.
When an AP works in the fit AP mode, you cannot directly log in to and manage it, but you can control it through an access controller or a unified switch associated with it.
You can use any of the following methods to log in to a WA series WLAN access point working in the fat AP mode:
l Logging in through the console port
l Logging in through telnet
l Logging in through SSH
l Logging in through web-based network management system
l Logging in through NMS
Powering on the AP and Connecting It to a Network
After installing the AP, perform the following steps before logging in to the AP.
Step1 the AP and connect it to an Ethernet.
![]()
For how to connect the power supply and connect your AP to a network, see the installation guide or quick start of the AP.
Step2 Check the LEDs on the AP.
1) Power LED
l When the AP is powered on, the power LED is steady on.
l If the power LED is not on, it is possibly because the AP is not powered on.
2) Ethernet LED
l If the Ethernet LED is steady on, the AP is connected to the Ethernet.
l If the Ethernet LED is blinking, the AP is connected to the Ethernet, and data is being transmitted and received.
![]()
For the description of the LEDs on the AP, see the installation guide or quick start of the AP.
Logging In to an AP
For more information about how to log in to an AP, see Logging In to the AP in the Fundamentals Configuration Guide in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Configuration Guides.
The WA series WLAN access points, except the WA2110-AG that can only operate in fit mode, can operate in both fat and fit modes, and you can switch the operating mode of an AP as needed.
Configuring Basic Functions for an AP Operating in Fit Mode
An AP operating in fit mode has zero configuration. When it is associated with an access controller (AC) or unified switch (US), it does not need or save any configuration. All configurations are performed on the AC or US.
Configuring Basic Functions for an AP Operating in Fat Mode
An AP operating in fat mode has the default configuration as follows:
![]()
The default output depends on your AP model.
#
version 5.20, Release 1104P01
#
sysname WA2612-AGN
#
domain default enable system
#
telnet server enable
#
port-security enable
#
vlan 1
#
domain system
access-limit disable
state active
idle-cut disable
self-service-url disable
#
user-group system
#
local-user admin
password simple h3capadmin
authorization-attribute level 3
service-type telnet
#
wlan rrm
dot11a mandatory-rate 6 12 24
dot11a supported-rate 9 18 36 48 54
dot11b mandatory-rate 1 2
dot11b supported-rate 5.5 11
dot11g mandatory-rate 1 2 5.5 11
dot11g supported-rate 6 9 12 18 24 36 48 54
#
wlan service-template 1 clear
ssid H3C
service-template enable
#
interface NULL0
#
interface Vlan-interface1
ip address 192.168.0.50 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
#
interface WLAN-BSS32
port link-type hybrid
port hybrid vlan 1 untagged
#
interface WLAN-Radio1/0/1
service-template 1 interface wlan-bss 32
#
load xml-configuration
#
user-interface con 0
user-interface vty 0 4
authentication-mode scheme
#
return
Table 6-1 Description of the default configuration
|
Field |
Description |
|
version 5.20, Release 1104P01 |
The AP software version currently in use |
|
sysname WA2612-AGN |
The default sysname is the AP model. |
|
domain default enable system |
The default enabled domain is system. |
|
telnet server enable |
By default, telnet server is enabled. |
|
port-security enable |
By default, port security is enabled. |
|
vlan 1 |
VLAN 1 is the default VLAN, and you cannot create and delete a default VLAN. |
|
domain system access-limit disable state active idle-cut disable self-service-url disable |
Basic configurations in the default domain system: The number of associated clients is not limited. Specify the current domain to be in the active state. Disable the idle-cut function for the current ISP domain. Disable the location function of the self-service server. |
|
user-group system |
system is the default user group. You cannot delete the default user group but you can modify its configuration. |
|
local-user admin password simple h3capadmin authorization-attribute level 3 service-type telnet |
The default configuration of the local user is as follows: l The username is admin. l The password is h3capadmin, case sensitive. l The user level is 3 (manage level). l The service type is telnet. |
|
wlan rrm dot11a mandatory-rate 6 12 24 dot11a supported-rate 9 18 36 48 54 dot11b mandatory-rate 1 2 dot11b supported-rate 5.5 11 dot11g mandatory-rate 1 2 5.5 11 dot11g supported-rate 6 9 12 18 24 36 48 54 |
The default 802.11a/b/g settings are as shown on the left column. The default rates depend on your AP model. |
|
wlan service-template 1 clear ssid H3C service-template enable |
By default, service template 1 with the authentication mode open system and SSID H3C is configured on the AP. |
|
interface NULL0 |
The interface type supported by the AP. |
|
interface Vlan-interface1 ip address 192.168.0.50 255.255.255.0 |
By default, the default IP address of VLAN-interface 1 is 192.168.0.50, and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. |
|
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 |
The interface type supported by the AP. |
|
interface WLAN-BSS32 port link-type hybrid port hybrid vlan 1 untagged |
By default, WLAN-BSS32 is a hybrid port, and removes VLAN tags before forwarding packets from VLAN 1. |
|
interface WLAN-Radio1/0/1 service-template 1 interface wlan-bss 32 |
By default, service template 1 is associated with radio interface WLAN BSS 32. |
|
load xml-configuration |
The AP loads the configuration file with extension .xml after startup. |
|
user-interface con 0 user-interface vty 0 4 authentication-mode scheme |
The AP supports console and VTY user interfaces. By default, the authentication mode for VTY login is AAA. |
Besides the default configurations, you need to perform the following configurations to use a fat AP in your network:
l Specifying an IP Address for an AP
l Saving the Current Configuration
Specifying an IP Address for an AP
Follow these steps to specify an IP address for the AP:
|
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Create VLANs |
vlan vlan-id1 [ to vlan-id2 ] |
Optional Using this command can create multiple VLANs in batches. |
|
Create a VLAN interface and enter VLAN interface view |
interface vlan-interface vlan-interface-id |
Required l If the VLAN interface already exists, you enter its view directly. l If the VLAN interface does not exist, you need to create a VLAN and then enter VLAN interface view. |
|
Assign an IP address to the VLAN interface |
ip address ip-address { mask | mask-length } |
Required IP address 192.168.0.50 is assigned to VLAN-interface 1 by default. No IP address is configured for other VLAN interfaces. |
|
Configure the description of the current VLAN |
description text |
Optional VLAN interface name is used by default, for example, Vlan-interface1 Interface. |
|
Bring up the VLAN interface |
undo shutdown |
Optional By default, a VLAN interface is in the up state. In this case, the VLAN interface is up so long as one port in the VLAN is up and goes down if all ports in the VLAN go down. An administratively shut down VLAN interface however will be in the down state until you bring it up, regardless of how the state of the ports in the VLAN changes. |
Configuring WLAN Service
WLAN service configuration includes WLAN global configuration, country code, service template, and radio configuration.
Follow these steps to configure WLAN service:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure global WLAN parameters |
||
|
Specifies the time for which the link between AP and client ( power-save or awake ) can be idle |
wlan client idle-timeout interval |
Optional By default, the idle timeout interval is 3600 seconds. |
|
Configure the keep alive timeout interval for the device |
wlan client keep-alive interval |
Optional By default, keep alive function is disabled. |
|
Enable the fat AP to respond to the probe requests with the SSID null sent by the client |
wlan broadcast-probe reply |
Optional. By default, . the fat AP respond the probe requests with the SSID null sent by the client. |
|
Specify the country code |
wlan country-code code |
Required By default, the country code is CN. For more information about country code and country, see WLAN Service in the WLAN Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References. |
|
Create a WLAN service template. |
wlan service-template service-template-number { clear | crypto } |
Required By default, a clear-type service-template has been configured. |
|
Disable the advertising of SSID in beacon frames |
beacon ssid-hide |
Optional By default, the SSID is advertised in the beacon frames. If the advertising of the SSID in beacon frames is disabled, the SSID must be configured for the clients to associate with the AP. |
|
Specify the maximum number of associated clients in a BSS |
client max-count max-number |
Optional |
|
Enable the authentication method |
authentication-method { open-system | shared-key } |
Required By default, open system authentication is enabled. l If the current service template is of clear type, you can only enable open system authentication. l If the current service template is of crypto type, you can enable open system or shared key authentication. |
|
Enable the service template |
service-template enable |
Required By default, the service-template is disabled. |
|
Enter radio interface view |
interface wlan-radio interface-number |
— |
|
Specify a radio type for the radio |
radio-type { dot11a | dot11an | dot11b | dot11g | dot11gn } |
Required Support for this command depends on your device model. |
|
Map a service template to the current radio |
service-template service-template-number interface wlan-bss interface-number |
Required |
|
Specify a channel number for the radio |
channel { channel-number | auto } |
Optional By default, auto mode is enabled. The working channel of a radio varies with country codes and radio types. The channel list depends on your device model. |
|
Specify the maximum radio power |
max-power max-power |
Optional By default, the maximum radio power varies with country codes, channels, AP models, radio types and antenna types. If 802.11n is adopted, the maximum radio power also depends on the bandwidth mode. |
|
Specify the type of preamble |
preamble { long | short } |
Optional By default, the short preamble is supported. Only 802.11b/g supports this configuration. |
Saving the Current Configuration
You can modify the configuration on your device at the CLI. To use the modified configuration for the next startup, you must save it (using the save command) to the configuration file.
You can save the configuration in either of the following two modes:
l Fast saving mode: Fast saving mode is implemented by using the save command without providing the safely keyword. The mode saves the file quickly but is likely to lose the existing configuration file if the device reboots or the power fails during the process.
l Safe mode. Safe mode is implemented by using the save command with the safely keyword. The mode saves the file more slowly that the fast saving mode but can retain the configuration file on the device even if the device reboots or the power fails during the process.
The fast saving mode is suitable for environments where power supply is stable. The safe mode, however, is preferred in environments where stable power supply is unavailable or remote maintenance is involved.
Follow a step below to save the current configuration:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Save the current configuration to the specified file, but the configuration file is not set as the file to be used at the next startup |
save file-url |
Required Use either command Available in any view |
|
Save the current configuration to the root directory of the storage medium and specify the file as the startup configuration file to be used at the next system startup up |
save [ safely ] [ backup | main ] |
![]()
l The configuration file must be with extension .cfg
l For the device that supports the main keyword, the execution of the save [ safely ] and save [ safely ] main commands has the same effect: The system saves the current configuration and specifies the configuration file as the main startup configuration file to be used at the next system startup.
l During the execution of the save [ backup | main ] command, the startup configuration file to be used at the next system startup may be lost if the device reboots or the power supply fails. In this case, the device boots with the null configuration, and after the device reboots, you need to re-specify a startup configuration file for the next system startup
![]()
l The terminal output information may vary on your AP model.
l The configurations made on the WA2200 series throughout this chapter apply to WLAN APs. For the software maintenance process, see the specific configuration examples.
Introduction
Files Managed by the AP
BootWare program file
The BootWare program file is used by the AP to boot the applications; it is stored in the Flash of the device. The complete BootWare program file consists of the basic section and the extended section.
Application files
The AP provides one type of application file for device boot: main application file, which is stored in the Flash. Two main application files can exist in the AP as it supports fit and fat. For example, two main application files exist on a WA2200: WA2200_fit.bin or WA2200_fat.bin. When the AP works in the fat AP mode, you can use the boot-loader file file-url { main | backup } command to specify either of them as the main application file.
Configuration files
With a file extension of .cfg, the configuration files contain the configuration information of the AP. Typically, the default configuration file is written into the Flash before the AP is delivered. The factory default configuration file is startup.cfg.
Software Maintenance Approaches
You can maintain the AP software in the following four ways:
l Upgrading the application files using the XMODEM protocol through a serial port
l Upgrading application files by using TFTP or FTP at the CLI.
l Upgrading application files through the web interface.
l Upgrading the application files automatically through an AC or a US (applicable to the fit mode only)
![]()
The WA series APs support upgrading the BootWare and application files of a specific version through upgrade package. Thus you do not need to upgrade the BootWare program separately.
Figure 7-1 Software upgrade flowchart

BootWare Menus
BootWare Main Menu
Upon power-on or reboot of the AP, the console terminal connected with the AP displays the following information:
System is starting...
Booting Normal Extend BootWare...
The Extend BootWare is self-decompressing...................Done!
****************************************************************************
* *
* H3C WA2200 BootWare, Version 2.09 *
* *
****************************************************************************
Copyright (c) 2004-2010 Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Compiled Date : Apr 21 2010
CPU Type : PPC 405EP
CPU L1 Cache : 32KB
CPU Clock Speed : 266MHz
Memory Type : SDRAM
Memory Size : 64MB
Memory Speed : 133MHz
BootWare Size : 512KB
Flash Size : 16MB
PCB Version : Ver.B
BootWare Validating...
Press Ctrl+B to enter extended boot menu...
Starting to get the main application file--flash:/wa2200_fat.bin!.......................
.............................
The main application file is self-decompressing.........................................
........................................................................................
........................................................................................
........................................................................................
........................................................................................
........................................................................................
........................................................................................
........................................................................................
........................................................................................
........................................................................................
.............................Done!
System application is starting...
User interface con0 is available.
Press ENTER to get started.
![]()
l You need to press Ctrl+B within one second when the prompt “Press Ctrl+B to enter extended boot menu” appears. Otherwise, the system will enter the application decompression process, instead of the extended BootWare menu.
l After the system enters the application decompression process, if you want to enter the extended BootWare menu, you need to reboot the AP.
l The extended boot menu is referred to as BootWare main menu in this manual unless otherwise stated.
At the prompt above, press Ctrl+B. The system prompts you to enter the BootWare password:
Please input BootWare password:
After you provide the correct password, the system enters the BootWare main menu.
The initial BootWare password is null. If you fail to enter the correct BootWare password three times in a row, the system will be halted and you need to restart the device manually.
Note: The current operating device is flash
Enter < Storage Device Operation > to select device.
===========================<EXTEND-BOOTWARE MENU>=========================
|<1> Boot System |
|<2> Enter Serial SubMenu |
|<3> Enter Ethernet SubMenu |
|<4> File Control |
|<5> Modify BootWare Password |
|<6> Skip Current System Configuration |
|<7> BootWare Operation Menu |
|<8> Clear Super Password |
|<9> Storage Device Operation |
|<0> Reboot |
==========================================================================
Enter your choice(0-9):
Table 7-1 BootWare main menu
|
Menu item |
Description |
|
<1> Boot System |
Load the application from the Flash |
|
<2> Enter Serial SubMenu |
Enter the serial submenu. For more information, see Serial interface submenu. |
|
<3> Enter Ethernet SubMenu |
Enter Ethernet submenu. For more information, see Ethernet interface submenu. |
|
<4> File Control |
File control submenu. For more information, see File control submenu. |
|
<5> Modify BootWare Password |
Modify BootWare password |
|
<6> Skip Current System Configuration |
Boot the system with the system configuration ignored. This operation is valid this time, and you need to configure it next time. This option is generally used when you lose the password. |
|
<7> BootWare Operation Menu |
BootWare operation submenu. For more information, see BootWare operation submenu. |
|
<8> Clear Super Password |
Clear the super password. The super password is used in user level switching. No super password is set by default. This setting is valid for the first reboot of the AP only. The super password will be restored after a second reboot. |
|
<9> Storage Device Operation |
Storage device operation submenu. For more information, see Storage device operation submenu. |
|
<0> Reboot |
Reboot the AP |
BootWare Submenus
Serial interface submenu
You can upgrade the application program, change the serial interface baud rate and so on through this submenu.
Select 2 from the BootWare main menu to enter the serial interface submenu.
1) Serial interface submenu of the WA2600 series indoor APs
================<Enter Serial SubMenu>========================
|Note:the operating device is flash |
|<1> Download Application Program To SDRAM And Run |
|<2> Update Main Application File |
|<3> Update Backup Application File |
|<4> Update Secure Application File |
|<5> Modify Serial Interface Parameter |
|<0> Exit To Main Menu |
==============================================================
Enter your choice(0-5):
2) Serial interface submenu of the WA2200 series and WA2600 series enhanced APs
===================<Enter Serial SubMenu>====================
|Note:the operating device is flash |
| <1> Download Application Program To SDRAM And Run |
| <2> Update Main Application File |
| <3> Modify Serial Interface Parameter |
| <0> Exit To Main Menu |
=============================================================
Enter your choice(0-3):
Ethernet interface submenu
Select 3 from the BootWare main menu to enter the Ethernet interface submenu.
1) Ethernet interface submenu of the WA2600 series indoor APs
==================<Enter Ethernet SubMenu>===================
|Note:the operating device is flash |
| <1> Download Application Program To SDRAM And Run |
| <2> Update Main Application File |
| <3> Update Backup Application File |
| <4> Update Secure Application File |
| <5> Modify Ethernet Parameter |
| <0> Exit To Main Menu |
| < Ensure The Parameter Be Modified Before Downloading! > |
=============================================================
Enter your choice(0-5):
2) Ethernet interface submenu of the WA2200 series and WA2600 series enhanced APs
===================<Enter Ethernet SubMenu>==================
|Note:the operating device is flash |
| <1> Download Application Program To SDRAM And Run |
| <2> Update Main Application File |
| <3> Modify Ethernet Parameter |
| <0> Exit To Main Menu |
| < Ensure The Parameter Be Modified Before Downloading! > |
=============================================================
Enter your choice(0-3):
File control submenu
You can view and set the application file types and delete the files through this submenu.
Select 4 from the BootWare main menu to enter the file control submenu.
========================<File CONTROL>=======================
|Note:the operating device is Flash |
| <1> Display All File(s) |
| <2> Set Application File type |
| <3> Delete File |
| <0> Exit To Main Menu |
=============================================================
BootWare operation submenu
Select 7 from the BootWare main menu to enter the BootWare operation submenu.
=========================<BootWare Operation Menu>========================
|Note:the operating device is flash |
|<1> Backup Full BootWare |
|<2> Restore Full BootWare |
|<3> Update BootWare By Serial |
|<4> Update BootWare By Ethernet |
|<0> Exit To Main Menu |
==========================================================================
Enter your choice(0-4):
![]()
The WA2200 series and WA2600 series do not support BootWare backup.
Storage device operation submenu
Select 9 from the BootWare main menu to enter the storage device control submenu:
========================<Device CONTROL>=====================
| <1> Display All Available Nonvolatile Storage Device(s) |
| <2> Set The Operating Device |
| <3> Set The Default Boot Device |
| <0> Exit To Main Menu |
=============================================================
Enter your choice(0-3):
Factory Default Configuration
The factory default configuration is the default configuration of the device at system boot before any settings are made to the device. The factory default configuration enables you to use all the basic functions upon AP power-on.
l If you perform configurations and save the configurations on the AP, the AP uses the configuration file you have saved for next startup.
l If you remove the current configuration file, namely, no configuration file exists on the AP, the AP starts with the factory default configuration upon next startup.
l If you disable the AP from booting with the default configuration (see Removing the Factory Default Configuration), it boots with null configuration.
l The filename you specified when saving the configuration file is used as the configuration filename for next startup. This startup mode is prior to the startup with the factory default configuration.
l If no configuration file exists on the Flash of the AP, it boots with the factory default configuration. The factory default configuration is set by the vendor of the AP, and you cannot modify it.
Factory Default Configuration of a Fat AP
l For the factory default configuration of a fat AP, see Configuring Basic Functions for an AP Operating in Fat Mode.
l A fit AP has zero configuration. All the configuration and management are performed by ACs or USs.
Removing the Factory Default Configuration
Upon AP boot, when the prompt “Press Ctrl+B to enter extended boot menu...” appears, press Ctrl+B. The system prompts you to enter the BootWare password:
Please input BootWare password:
After you provide the correct password, the system enters the BootWare main menu (the initial BootWare password is null, and you can directly press Enter):
===========================<EXTEND-BOOTWARE MENU>===========================
|<1> Boot System |
|<2> Enter Serial SubMenu |
|<3> Enter Ethernet SubMenu |
|<4> File Control |
|<5> Modify BootWare Password |
|<6> Skip Current System Configuration |
|<7> BootWare Operation Menu |
|<8> Clear Super Password |
|<9> Storage Device Operation |
|<0> Reboot |
============================================================================
Enter your choice(0-9):
Select 6 to disable the AP from booting with the default configuration. It boots with null configuration, shown as follows:
Enter your choice(0-9):6
Flag Set Success.
Fit/Fat Working Mode Switching
The AP can work in the fat mode, or cooperate with an AC or a US to work in the fit mode, and it can switch between the fit mode and the fat mode.
![]()
Before working mode switching, identify the current working mode of the AP to determine whether it needs to perform a mode switching.
Switching the Working Mode Through the BootWare Menu
The working mode of the AP depends on the main application file in its Flash. If the main application file in the Flash is XXXX_fit.bin, the AP works in the fit mode; if the main application file in the Flash is XXXX_fat.bin, the AP works in the fat mode.
When setting the working mode through the BootWare menu, you need to judge whether the main application file in the Flash is consistent with the working mode. During the upgrade process, do not change the main application filename, thus to avoid inconsistency of the working mode that has been configured and the current working mode.
Select 4 from the BootWare main menu to enter the file control submenu:
==============================<File CONTROL>==============================
|Note:the operating device is flash |
|<1> Display All File(s) |
|<2> Set Application File type |
|<3> Delete File |
|<0> Exit To Main Menu |
==========================================================================
Enter your choice(0-3):
The following example illustrates the switching from the fat mode to fit mode.
1) Display the application program type in the BootWare menu:
Select 2 to enter the application program type submenu:
'M' = MAIN 'B' = BACKUP 'S' = SECURE 'N/A' = NOT ASSIGNED
==========================================================================
|NO. Size(B) Time Type Name |
|1 7884208 Aug/08/2008 20:00:00 M wa2200_fat.bin |
|2 3923104 Apr/26/2000 12:11:16 B wa2200_fit.bin |
|0 Exit |
==========================================================================
Enter file No:
Table 7-2 Application program types
|
Type |
Description |
|
'M' = MAIN |
Main (M) application program that the system loads when startup. The newly downloaded program is the M program by default. |
|
'B' = BACKUP |
Backup (B) application program. If the system finds no M program at startup, it loads the B application program automatically. |
|
'S' = SECURE |
Secure (S) application program. If all the application programs in the Flash are “N/A”, the system automatically loads the S application program at startup. |
|
'N/A' = NOT ASSIGNED |
Indicates the application program type is not specified. |
2) Set the selected file as the main application program (loaded when the system starts).
Type application program number 2 to enter the file attribute modification submenu:
Enter file No:2
Modify the file attribute:
==========================================================================
|<1> +Main |
|<2> -Main |
|<3> +Backup |
|<4> -Backup |
|<0> Exit |
==========================================================================
Enter your choice(0-4):
Table 7-3 File attribute submenu
|
Menu item |
Description |
|
<1> +Main |
Specify the current application program as the main application program |
|
<2> -Main |
Cancel the main application program type of the current application program and specify the program type as N/A |
|
<3> +Backup |
Specify the current application program as the backup application program |
|
<4> -Backup |
Cancel the backup application program type of the current application program and specify the program type as N/A |
|
<0> Exit |
Exit the current submenu |
Select 1 to specify the current application program wa2200_fit.bin as the main application program. The system then sets file wa2200_fit.bin with attribute B to a file with attribute M+B, and file wa2200_fat.bin with attribute M automatically changes to a file with attribute N/A.
Enter your choice(0-4):1
Set the file attribute success!
The system displays a successful prompt and returns to the file control submenu. Select 1 to display all files.
===============================<File CONTROL>=============================
|Note:the operating device is flash |
|<1> Display All File(s) |
|<2> Set Application File type |
|<3> Delete File |
|<0> Exit To Main Menu |
==========================================================================
Enter your choice(0-3): 1
Display all file(s) in flash:
'M' = MAIN 'B' = BACKUP 'S' = SECURE 'N/A' = NOT ASSIGNED
==========================================================================
|NO. Size(B) Time Type Name |
|1 7884208 Aug/08/2008 20:00:00 N/A wa2200_fat.bin |
|2 428 Apr/26/2000 12:00:34 N/A private-data.txt |
|3 3923104 Apr/26/2000 12:11:16 M+B wa2200_fit.bin |
==========================================================================
![]()
If you modify the main application file name by using the rename command, the system cannot be started. For more information about the rename command, see SSH2.0 in the Security Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
Switching the Working Mode at the CLI
Set the working mode to fit AP
To set the working mode of the AP working in the fat mode to the fit mode, use the boot-loader file file-url { main | backup } command:
On a WA2200 series:
<Sysname>boot-loader file wa2200_fit.bin main
This command will set the boot file. Continue? [Y/N]:y
The specified file will be used as the main boot file at the next reboot on slot 1!
![]()
l Fat and fit files cannot be stored in the Flash at the same time due to the space limitation of the Flash of the AP. Therefore, before you switch the working mode of the AP from fat AP to fit AP, you need to delete the fat file in the Flash to release the space of the Flash. When deleting the fat file, use the delete /unreserved plus name of the file to be deleted in user view (you can view the file name using the dir command in user view). Then, use TFTP to download the fit file, and set the working mode of the AP to the fit AP mode.
l When you switch the working mode of the AP at the CLI, the configuration file used for next startup is set to null. After you reboot the AP, the system starts with the factory default configuration of the current mode.
Set the working mode to fat AP
To set the working mode of the AP working in the fit AP mode to the fat AP mode, you can execute the wlan ap-execute ap-name conversion-to-fatap command on the AC or US:
For example, set the working mode of ap1_003 to the fat AP mode:
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] wlan ap excute ap1_003 concersion-to-fatap
![]()
l After setting the working mode of the AP at the CLI, you need to restart the AP to make your configuration take effect.
l You can use the wlan ap-execute ap-name conversion-to-fatap command on an AC or a US to set the working mode of the AP to fat AP only in the case that the AP running as a fit AP is associated with the AC or US and the fat AP version is stored in the Flash.
Upgrading Applications Through the Serial Port
XMODEM Overview
To upgrade applications through a serial port, use the XMODEM protocol.
XMODEM is a file transfer protocol that is widely used because of its simplicity and good performance. XMODEM transfers files via serial ports. It supports two types of data packets (128 bytes and 1 KB), two check methods (checksum and CRC), and error packet retransmission mechanism (generally the maximum number of transmission attempts is ten).
The XMODEM transmission procedure is completed by the cooperation of a receiving program and a sending program. The receiving program sends a negotiation character to negotiate a check method. After the negotiation, the sending program starts to send data packets. Upon receiving a complete packet, the receiving program checks the packet using the agreed method.
l If the check succeeds, the receiving program sends an ACK character and the sending program proceeds to send the next packet.
l If the check fails, the receiving program sends a NAK character and the sending program retransmits the packet.
Modifying Serial Communication Parameters
In actual applications, you need to make the serial interface baud rate higher to save updating time or make it lower to guarantee transmission reliability. This section introduces how to adjust the serial interface baud rate.
Enter the BootWare main menu.
l For the WA2200 series, WA2600 enhanced APs, and WA2600 outdoor APs, select 2 to enter the serial interface submenu, and then select 3 from the submenu to modify the baud rate.
l For the WA2600 series indoor APs, select 2 to enter the serial interface submenu, and then select 5 from the submenu to modify the baud rate.
===============================<BAUDRATE SET>===============================
|Note:'*'indicates the current baudrate |
| Change The HyperTerminal's Baudrate Accordingly |
|---------------------------<Baudrate Avaliable>------------------------- |
|<1> 9600(Default)* |
|<2> 19200 |
|<3> 38400 |
|<4> 57600 |
|<5> 115200 |
|<0> Exit |
============================================================================
Enter your choice(0-5):
Select an appropriate baud rate. For example, select 5 for 115200 bps. The following information appears:
Baudrate has been changed to 115200 bps.
Please change the terminal's baudrate to 115200 bps, press ENTER when ready.
Now that the serial interface baud rate of the AP has been changed to 115,200 bps while that of the terminal is still 9,600 bps, the AP and the terminal cannot communicate with each other. Change the baud rate to 115,200 bps in HyperTerminal.
Step1 Disconnect the terminal connection in HyperTerminal, as shown below:
Figure 7-2 Disconnect the terminal connection
Step2 Choose File > Properties. In the Properties dialog box, click Configure… and select 115,200 in the Bits per second drop-down list box.
Figure 7-3 Modify the baud rate
Step3 Select Call > Call to reestablish the connection.
Figure 7-4 Reconnect the call
Then, press Enter in the serial interface submenu.
![]()
After downloading files with a changed baud rate, timely change the baud rate back to 9,600 bps in HyperTerminal to ensure the normal display on the console screen when the system boots or reboots.
Upgrading an Application
Upgrading an application through the serial port is implemented in the submenu of the serial port.
Enter the BootWare main menu, and select 2 to enter the serial port submenu. For more information about this menu, see Serial interface submenu.
Upgrade main application wa2200_fat.bin:
Step1 Change the communication baud rate by referring to Modifying Serial Communication Parameters. Select 2 from the serial interface submenu. The following prompt appears:
Please Start To Transfer File, Press <Ctrl+C> To Exit.
Waiting...CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
Step2 Select Transfer > Send file… in the HyperTerminal window. The following dialog box appears:
Figure 7-5 Send File dialog box
Step3 Click Browse… to select the application file to be downloaded, and select Xmodem from the Protocol drop-down list. Then click Send. The following dialog box appears:
Figure 7-6 Download the file using XMODEM
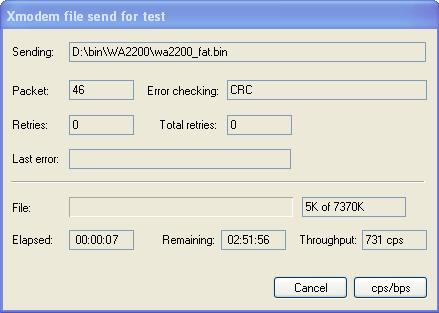
Upon successful download, the system displays the following information:
Download successfully!
7546496 bytes downloaded!
The system prompts you to name the application downloaded to the current storage medium:
Input the File Name:
1) If the input file name is different from the existing one, the downloaded application is given this name, for example:
Input the File Name:wa2200_fat.bin
Updating File flash:/ wa2200_fat.bin......................................................
........................................................................................
........................................................................................
..............................Done!
Return to the BootWare main menu, and enter the file control submenu to set the application as the main application. The system will boot with this application at the next boot. For more information about how to set the main application, see Set the selected file as the main application program (loaded when the system starts)..
2) If the input file name is the same as the existing one, the system prompts:
The file is exist,will you recover it? [Y/N]
l If you select Y, the system overwrites the original application, and the AP boots with the new application at the next boot.
l If you select N, the system prompts:
Cancel to overwrite the file.
Failed!
The system cancels overwriting the existing application, and the upgrade fails.
![]()
The size of an application is typically big. Even if you change the baud rate to 115200 bps, the upgrade process takes about 30 minutes. Therefore, it is recommended that you upgrade an application through an Ethernet.
Upgrading Applications Through TFTP at the CLI
The Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a TCP/IP protocol used for file transfer between client and server. It provides a simple and low-overhead file transfer service. TFTP provides unreliable data transfer over UDP and does not provide any access authorization and authentication mechanism. It employs the timeout retransmission method to implement best-effort delivery of data. Compared with FTP, TFTP has a much smaller software size.
Setting Up an Upgrade Environment
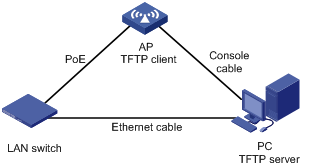
Set up an upgrade environment as shown in Figure 7-7 and Figure 7-8.
Figure 7-7 Set up an upgrade environment
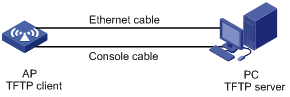
Figure 7-8 Set up an upgrade environment
l As shown in Figure 7-7, AP serves as the TFTP client, and the PC serves as the TFTP server. Connect the Ethernet interface on the AP to the PC by using a crossover Ethernet cable. Ensure the connectivity between the AP and the PC. In the example, the IP address of VLAN-interface 1 of the AP is 192.168.0.2, and that of the PC is 192.168.0.1.
l As shown in Figure 7-8, AP serves as the TFTP client, and the PC serves as the TFTP server. Connect AP and PC through a PoE switch. In the example, the IP address of VLAN-interface 1 of AP is 192.168.0.2, and that of the PC is 192.168.0.1.
Enable TFTP Server on the PC and set the path where the application file is stored.
![]()
The TFTP server software is not provided with the AP. Make sure that it is available by yourself.
Displaying the System Files and Available Space of the Storage Medium
Use the dir command on the console terminal to view the files contained in the current file system and the available space.
<Sysname>dir
Directory of flash:/
0 -rw- 7884208 Apr 26 2000 12:04:49 wa2200_fat.bin
1 -rw- 1093 Apr 26 2000 12:01:37 startup.cfg
2 -rw- 9126 Apr 26 2000 12:01:27 config.cwmp
3 -rw- 33 Apr 26 2000 12:01:27 system.xml
14986 KB total (7234 KB free)
<Sysname>
Table 7-4 dir command output description
|
Field |
Description |
|
Directory of flash:/ |
The current directory name |
|
rw |
r: The file or directory is readable. w: The file or directory is writable. |
|
14986 KB total (7234 KB free) |
If the available space of the flash is not enough, the upgrade fails. |
Upgrading an Application.
You can download an application from a TFTP server to your AP, and upgrade the original application with the new one. The configuration takes effect at the next boot of the AP.
# Download application file wa2200_fat.bin from the PC to the AP.
<Sysname>tftp 192.168.0.1 get wa2200_fat.bin
The file wa2200_fat.bin exists. Overwrite it? [Y/N]:y
Verifying server file...
Deleting the old file, please wait...
...................................
File will be transferred in binary mode
Downloading file from remote TFTP server, please wait...................
..........................................
TFTP: 7884208 bytes received in 13 second(s)
File downloaded successfully.
<Sysname>.
![]()
l If the file name already exists on the AP, the system prompts whether to overwrite the file on the AP. You need to choose Y or N for confirmation.
l For information about the tftp command, see FTP and TFTP in the Fundamentals Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
l You can update a configuration file in the way you update an application file. A configuration file can be modified by a text editor. You can modify a configuration file and then download the modified configuration file to the AP, and the modification takes effect after the AP reboots.
Backing Up an Application
To back up an application, you can upload the application from your AP to a TFTP server.
# Upload application file wa2200_fat.bin on the AP to the PC, and save it as wa2200_fat.bin.
<H3C> tftp 192.168.0.1 put wa2200_fat.bin wa2200_fat.bin
File will be transferred in binary mode
Sending file to remote TFTP server. Please wait...
TFTP: 7884208 bytes sent in 13 second(s).
File uploaded successfully.
![]()
l When you back up an application, if the file name already exists on the AP, the system does not output any information, but directly overwrites the existing file.
l For information about the tftp command, see FTP and TFTP in the Fundamentals Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
l To back up a configuration file, use the same method.
Table 7-5 Output description of commands for application upgrade and backup when the AP serves as a TFTP client
|
Output |
Description |
|
tftp 192.168.0.1 get wa2200_fat.bin |
Download the file to be upgraded from the server. |
|
The file wa2200_fat.bin exists. Overwrite it? [Y/N]: |
Prompt you whether to overwrite the existing file. |
|
TFTP: 7884208 bytes received in 13 second(s) |
The file is downloaded and upgraded. |
|
tftp 192.168.0.1 put wa2200_fat.bin wa2200_fat.bin |
Upload the file from the AP to the TFTP server. |
|
TFTP: 7884208 bytes sent in 13 second(s). |
The file is uploaded and backed up successfully. |
Upgrading the Applications Through FTP at the CLI
When the application file is large, you can also upgrade it using FTP to save upgrade and maintenance time.
As an application layer protocol in the TCP/IP suite, the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is mainly used for file transfer between remote hosts. FTP provides reliable, connection-oriented data transfer service over TCP. Compared with TFTP, the FTP software is much bigger.
![]()
The AP can only serve as the FTP client, rather the FTP server to provide FTP services.
Upgrading an Application Using FTP at the CLI
Setting Up an Upgrade Environment
Set up an upgrade environment by referring to Figure 7-9 and Figure 7-10.
Figure 7-9 Set up an upgrade environment

Figure 7-10 Set up an upgrade environment

l As shown in Figure 7-9, the AP serves as the FTP client, and the PC serves as the FTP server. Connect the Ethernet interface on the AP to the PC by using a crossover Ethernet cable. Ensure the connectivity between the AP and the PC. In the example, the IP address of VLAN-interface 1 is 192.168.0.2, and that of the PC is 192.168.0.1.
l In the upgrade environment shown in Figure 7-10, AP serves as the FTP client, and the PC serves as the FTP server. AP and the PC are connected through a PoE switch. Ensure the connectivity between the AP and the PC. In the example, the IP address of VLAN-interface 1 is 192.168.0.2, and that of the PC is 192.168.0.1.
![]()
The FTP server is not installed on the AP by default. You need to purchase and install it yourself.
Displaying the System Files and Available Space of the Storage Medium
Use the dir command on the console terminal to view the files contained in the current file system and the available space. For more information about the output description of the dir command, see Table 7-4.
<Sysname>dir
Directory of flash:/
0 -rw- 7884208 Apr 26 2000 12:04:49 wa2200_fat.bin
1 -rw- 1093 Apr 26 2000 12:01:37 startup.cfg
2 -rw- 9126 Apr 26 2000 12:01:27 config.cwmp
3 -rw- 33 Apr 26 2000 12:01:27 system.xml
14986 KB total (7234 KB free)
<Sysname>
Logging In to the FTP Server from the AP
Log in to the FTP server using FTP from the AP.
<Sysname>ftp 192.168.0.1
Trying 192.168. 0.1..
Press CTRL+K to abort
Connected to 192.168. 0.1.
220 3Com 3CDaemon FTP Server Version 2.0
User(192.168. 0.1:(none)):ftpuser
331 User name ok, need password
Password:
230 User logged in
[ftp]
Upgrading an Application
You can download an application from an FTP server to your AP, and overwrite the original application with the new one. The configuration takes effect at the next boot of the AP.
# Download application file wa2200_fat.bin from the PC to the AP.
<Sysname>ftp
[ftp]get wa2200_fat.bin
flash:/wa2200_fat.bin has been existing. Overwrite it? [Y/N]:y
227 Entering passive mode (192,168,0,1,4,128)
125 Using existing data connection
.....................................................226 Closing data connection; File transfer successful.
FTP: 7884208 byte(s) received in 271.703 second(s), 29.00K byte(s)/sec.
[ftp]quit
221 Service closing control connection
![]()
l If the file name already exists on the AP, the system prompts whether to overwrite the file on the AP. You need to choose Y or N for confirmation.
l For information about the get command, see FTP and TFTP in the Fundamentals Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
l You can update a configuration file in the way you update an application file. A configuration file can be modified by a text editor. You can modify a configuration file and then download the modified configuration file to the AP, and the modification takes effect after the AP reboots.
Backing Up an Application
To back up an application, you can upload the application from your AP to an FTP server.
# Upload application file wa2200_fat.bin on the AP to the PC, and save it as wa2200_fat.bin.
<Sysname>ftp
[ftp]put wa2200_fat.bin
227 Entering passive mode (192,168, 0,1,5,34)
125 Using existing data connection
...............................................226 Closing data connection; File transfer successful.
FTP: 7884208 byte(s) sent in 271.703 second(s), 29.00Kbyte(s)/sec
[ftp]quit
221 Service closing control connection
![]()
l When you back up an application, if the file name already exists on the AP, the system does not output any information, but directly overwrites the existing file.
l For information about the tftp command, see FTP and TFTP in the Fundamentals Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
l To back up a configuration file, use the same method.
Table 7-6 Output description of commands for application upgrade and backup when the AP serves as the FTP client
|
Output |
Description |
|
[ftp]get wa2200_fat.bin wa2200_fat.bin |
Download the file to be upgraded from the FTP server. |
|
flash:/wa2200_fat.bin has been existing. Overwrite it? [Y/N]: |
Prompt you whether to overwrite the file with the same name. |
|
FTP: 7884208 byte(s) received in 271.703 second(s), 29.00K byte(s)/sec. |
The file is downloaded and upgraded. |
|
[ftp] put wa2200_fat.bin wa2200_fat.bin |
Upload the file from the AP to the FTP server for backup. |
|
FTP: 7884208 byte(s) sent in 271.703 second(s), 29.00Kbyte(s)/sec |
The file is uploaded and backed up. |
|
[ftp]quit |
Exit FTP client view. |
|
221 Service closing control connection |
Close the service control connection. |
Upgrading an Application by Using FTP with the Default Configuration
This function is applicable to the case that an application is deleted completely and a new application needs to be downloaded. For this approach of upgrading an application, the working mode of the AP must be fat AP.
Set up an upgrade environment
Set up an upgrade environment as shown in Figure 7-9 and Figure 7-10.
Enable FTP server on the PC and set the path where the application file is stored.
Upgrade the application
Upon power-on of the WA2200 series, the following is displayed:
System is starting...
Booting Normal Extend BootWare...
The Extend BootWare is self-decompressing...................Done!
****************************************************************************
* *
* H3C WA2200 BootWare, Version 2.09 *
* *
****************************************************************************
Copyright (c) 2004-2010 Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Compiled Date : Apr 21 2010
CPU Type : PPC 405EP
CPU L1 Cache : 32KB
CPU Clock Speed : 266MHz
Memory Type : SDRAM
Memory Size : 64MB
Memory Speed : 133MHz
BootWare Size : 512KB
Flash Size : 16MB
PCB Version : Ver.B
BootWare Validating...
Press Ctrl+B to enter extended boot menu...
# When the prompt “Press Ctrl+B to enter extended boot menu...” appears, press Ctrl+B to enter the BootWare menu. If you do not press Ctrl+B within one second, the system displays the following information:
Starting to get the main application file--flash:/wa2200_fat.bin!
The main application file does not exist--flash:/wa2200_fat.bin!
Starting to get the backup application file--flash:/backup.app!
The backup application file does not exist--flash:/backup.app!
Starting to get the secure application file--flash:/secure.app!
The secure application file does not exist--flash:/secure.app!
Booting App fails!
# The system uses the default configuration to download the application.
Protocol (FTP or TFTP) : ftp
Load File Name : wa2200_fat.bin
Target File Name : wa2200_fat.bin
Server IP Address : 192.168.0.1
Local IP Address : 192.168.0.50
Gateway IP Address : 0.0.0.0
FTP User Name : wa2200
FTP User Password : wa2200
Loading..........................................................Done!
7884208 bytes downloaded!
Table 7-7 Description on the display information of setting Ethernet interface parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Protocol (FTP or TFTP) |
Downloading flag |
|
Load File Name |
Name of the file to be loaded |
|
Target File Name |
Target file name. Name of the file to be downloaded from the TFTP or FTP server. |
|
Server IP Address |
IP address of the TFTP or FTP server |
|
Local IP Address |
Default IP address of the AP |
|
Gateway IP Address |
Gateway IP address, no need to set. |
|
FTP User Name |
Default FTP username |
|
FTP User Password |
Default password of the FTP user |
# Upon successful download, the application is automatically upgraded.
Updating File flash:/wa2200_fat.bin.........................................
........................Done!
# The upgrade is completed, and the system starts up automatically.
Upgrading an Application Through the Web Interface
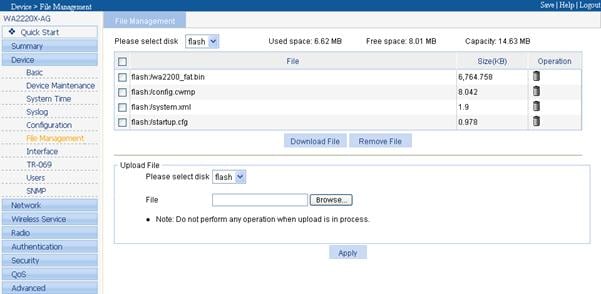
Take a WA2200 series as an example to complete application upgrade. Select Device > File Manage from the navigation tree to enter the file management page, as shown in Figure 7-11.
Displaying File List
On the top of the page, if you select a disk (APs support only flash at present) from the drop-down list, the used space, free space, and total capacity of the disk will be displayed at the right of the drop-down list, and all files saved in this disk (displayed in the format of path + filename) and their sizes will be in the list below the drop-down list.
Downloading a File
Select Device > File Manage from the navigation tree to enter the file management page, as shown in Figure 7-11. Select a file from the list, click the Download File button, and then a File Download dialog box appears. You can select to open the file or to save the file locally. You can download only one file at one time.
Figure 7-12 File download
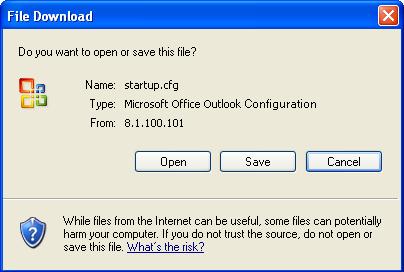
Uploading a File
Select Device > File Manage from the navigation tree to enter the file management page, as shown in Figure 7-11. In the Upload File area at the bottom of the page, you can select a disk on which the file is saved, and then select the file path and filename by clicking Browse. Click Apply to upload the file to the specified storage device.
![]()
Uploading a file takes some time. You are recommended not to perform any operation on the web interface during the upgrading procedure.
Removing a File
Select Device > File Manage from the navigation tree to enter the file management page, as shown in Figure 7-11. You can remove a file by using one of the following ways:
l
Click the ![]() icon to remove a file.
icon to remove a file.
l Select one or multiple files from the file list, and then click Remove File.
Automatically Managing and Upgrading the Applications Through an AC or a US
You cannot directly manage the AP working in the fit mode, but you can by associating it with an AC or a US.
Figure 7-13 Fit AP and AC (or US) network diagram

![]()
You can use a DHCP server in the network to assign IP addresses for the PC and the fit AP.
Configure IP addresses in the same network segment for the TFTP server and the TFTP client. In this example, configure the IP address of the TFTP server as 192.168.0.1 and 192.168.0.2 for the Ethernet interface of AC or US connecting with the TFTP server. You can use the ping command to check whether the AP and the AC are connected successfully.
Associating the Fit AP with an AC or a US
Viewing the system information of the fit AP
Since a fit AP is uniquely associated with the AC or US by the serial-ID of the fit AP, you need to first view the serial-ID of the fit AP. Each model of the WA2200 series has a model number. The serial-ID and the model number of a fit AP are set before delivery and are printed on the barcode at the back of the AP.
Associating the fit AP with the AC or US
Follow these steps to associate the fit AP with the AC or US:
1) Enter system view.
<Sysname> system-view
2) On the AC or US, create AP view for the fit AP, with the view type consistent with the model number of the fit AP. For example, create AP view with the name aptest2 and the type WA2220X_AG.
[Sysname]wlan ap aptest2 model WA2220X-AG
3) Configure the corresponding serial-ID of the fit AP in AP view, for example, 210235A29G007C000020.
[Sysname-wlan-ap-aptest2]serial-id 210235A29G007C000020
4) Configure the first RF interface in AP view and enable and the RF interface. For example, set the RF type of the first RF interface in AP view named aptest2 to 802.11a and the channel number to 149 (with country code CN), and enable the RF interface.
[Sysname-wlan-ap-aptest2]radio 1 type dot11a
[Sysname-wlan-ap-aptest2-radio-1]channel 149
[Sysname-wlan-ap-aptest2-radio-1]radio enable
After the above operations, AP view named aptest2 is associated with the fit AP whose serial-ID is 210235A29G007C000020 and you can associate the fit AP with the AC or US.
Automatically Upgrading the Application of the AP Through the AC or US
After the above configuration, you can automatically upgrade the application of the fit AP through command lines on the AC or US.
![]()
l Automatic upgrade of the AP is triggered only when the application version of the AC or US is inconsistent with that of the AP.
l Automatic upgrade is completed by the AC or US. Do not perform any configuration on the AP.
Download the application to the Flash of the AC or US
The AC or US serves as the TFTP client, and the file server serves as the TFTP server. You can access the TFTP server from the client by typing corresponding commands, and download the application to the AC or US.
Upgrade the application of the AP
After setting an upgrade environment, perform the following operations on the terminal:
Use the dir command on the console terminal to view the files contained in the current file system and the available space.
<Sysname> dir
Directory of flash:/
0 -rw- 9102056 Jan 03 2008 10:54:34 main.bin
1 -rw- 588 Nov 29 2007 10:28:05 startup.cfg
2 -rw- 26348 Dec 06 2007 10:37:53 default.diag
31750 KB total (20874 KB free)
Download application wa2200_fit.bin of the AP from the TFTP server to the AC or US:
<Sysname> tftp 192.168.0.1 get wa2200_fit.bin
File will be transferred in binary mode
Downloading file from remote TFTP server, please wait...|
TFTP: 3262168 bytes received in 17 second(s)
File downloaded successfully.
<Sysname>
The file wa2200_fit.bin exists. Overwrite it? [Y/N]:y
Verifying server file...
Deleting the old file, please wait...
File will be transferred in binary mode
Downloading file from remote TFTP server, please wait...\
TFTP: 3262168 bytes received in 17 second(s)
File downloaded successfully.
<Sysname>
![]()
l If a file system with the same name exists on the AC or US, the system prompts you whether to overwrite the existing one. Select Y/N for confirmation.
l For more information about the tftp command, see FTP and TFTP in the Fundamentals Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
l The application of the AC or US must be saved under the directory Flash:/; otherwise, the application cannot be upgraded.
Upgrade the application of the AC or US
For more information, see chapter Maintaining Software in the corresponding AC or US installation guide.
![]()
l Before upgrade, ensure the consistency of the application versions of the AP and the AC or US; otherwise, the AP cannot work normally.
l On the AC or US, you can use the wlan apdb model-name hardware-version software-version command to set the matrix between AP version and AC (or US) version. For more information, see WLAN Service in the WLAN Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
Restart the AC or US
After AP application download and AC or US application upgrade, restart the AC or US:
<Sysname> reboot
Start to check configuration with next startup configuration file, please wait.
........DONE!
This command will reboot the device. Continue? [Y/N]:y
Now rebooting, please wait...
After AC or US reboot, all the APs associated with it will finish application upgrade and reboot automatically.
![]()
l Automatic AP upgrade results in service interruption. Therefore, perform automatic upgrade when appropriate.
l By default, when the AP is being automatically upgrade, the AC or US does not give any prompt.
l If the AP cannot work normally as a result of automatic upgrade, check whether the AP version is consistent with the AC or US version. If not, you can download the AP application to upgrade the AP, without restarting the AC or US.
Maintaining Application and Configuration Files
You can use the file control submenu to display delete file types.
Take a WA2200 series as an example. Select 4 from the BootWare main menu to enter the file control submenu. The following information appears:
===============================<File CONTROL>=============================
|Note:the operating device is flash |
|<1> Display All File(s) |
|<2> Set Application File type |
|<3> Delete File |
|<0> Exit To Main Menu |
==========================================================================
Enter your choice(0-3):
Displaying All Files
Display all files at the CLI
<Sysname>dir
Directory of flash:/
0 -rw- 7884208 Apr 26 2000 12:04:49 wa2200_fat.bin
1 -rw- 1093 Apr 26 2000 12:01:37 startup.cfg
2 -rw- 9126 Apr 26 2000 12:01:27 config.cwmp
3 -rw- 33 Apr 26 2000 12:01:27 system.xml
14986 KB total (7234 KB free)
<Sysname>
Table 7-8 dir command output description
|
Field |
Description |
|
Directory of flash:/ |
The current directory name |
|
rw |
r: The file or directory is readable. w: The file or directory is writable. |
|
14986 KB total (7234 KB free) |
If the available space of the flash is not enough, the upgrade fails. |
![]()
For more information about the dir command, see File Management in the Fundamentals Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
Display all files in the BootWare menu
Select 1 from the file control submenu. The following information appears:
Display all file(s) in flash:
'M' = MAIN 'B' = BACKUP 'S' = SECURE 'N/A' = NOT ASSIGNED
==========================================================================
|NO. Size(B) Time Type Name |
|1 7884208 Aug/08/2008 20:00:00 M wa2200_fat.bin |
|2 428 Apr/26/2000 12:00:34 N/A private-data.txt |
|3 3923104 Apr/26/2000 12:01:38 B wa2200_fit.bin |
==========================================================================
Setting the Application File Type
Set the application file attribute at the CLI
# Specify application file wa2200_fat.bin as the main boot file.
<H3C> boot-loader file wa2200_fat.bin main
This command will set the boot file of the specified board. Continue? [Y/N]:
The specified file will be used as the main boot file at the next reboot on slot 5!
![]()
For more information about the boot-loader command, see Device Management in the Fundamentals Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
Set the application file attribute in the BootWare menu
Select 2 from the file control submenu to set the application file type. For more information, see Switching the Working Mode Through the BootWare Menu.
Removing a File
Remove a file at the CLI
To remove a file, execute the delete [ /unreserved ] file-url in user view, where,
l /unreserved: Permanently deletes the files.
l file-url: Name of the file to be deleted.
# Remove file test.txt in the root directory.
<Sysname> delete test.txt
Delete flash:/test.txt?[Y/N]:y
%Delete file flash:/test.txt...Done.
File test.txt is removed into the recycle bin. To remove the deleted file from the recycle bin, use the undelete command.
# Restore the deleted file test.txt from the recycle bin.
<H3C> undelete test.txt
Undelete flash:/test.txt? [Y/N]:y
% Undeleted file flash:/test.txt.
![]()
For more information about the delete and undelete commands, see File Management in the Fundamentals Command Reference in the H3C WA Series WLAN Access Points Command References.
Remove a file in the BootWare menu
Select 3 from the file control submenu to remove a file.
Deleting the file in flash:
'M' = MAIN 'B' = BACKUP 'S' = SECURE 'N/A' = NOT ASSIGNED
==========================================================================
|NO. Size(B) Time Type Name |
|1 7884208 Aug/08/2008 20:00:00 M wa2200_fat.bin |
|2 428 Apr/26/2000 12:00:34 N/A private-data.txt |
|3 3923104 Apr/26/2000 12:01:38 B wa2200_fit.bin |
|0 Exit |
==========================================================================
Enter file No:2
Select file number 2, and the system prompts:
The file you selected is flash:/private-data.txt,Delete it? [Y/N]Y
Enter Y. If the system prompts the following, the file is deleted.
Deleting.......Done!
To Return to the Main Menu
Select 0 from the file control submenu to return to the BootWare main menu.
Dealing with Password Loss
This section describes how to deal with password loss.
User Password Loss
If you forget your user password, the system will refuse your login. In this case, set a new user password by following the steps below.
1) Enter the BootWare main menu and select 6 to bypass the current configuration in system startup.
The following information appears:
Flag Set Success.
2) When the BootWare main menu appears again, select 0 to restart the system.
System is starting...
3) Set a new user password in system view.
[Sysname]user-interface conole 0
[Sysname-ui-console0]authentication-mode password
[Sysname-ui-console0]set authentication password simple 123456
This information indicates that password authentication is used for console port login, the password is set to 123456, and it is stored in plain text.
![]()
l After reboot, the system runs with the initial default configuration, while the original configuration file is still kept in the Flash. To restore the original configuration, use the display saved-configuration command to locate the configuration file, and then copy and run it.
l If the password is stored in plain text, you can use the display current-configuration command to view the password in the current configuration. If you use the set authentication password cipher 123456 command to set your password, the password will be stored in cipher text.
4) Save your new password.
[Sysname] save
The current configuration will be written to the device. Are you sure? [Y/N]:y
Please input the file name(*.cfg)[flash:/startup.cfg]
(To leave the existing filename unchanged, press the enter key):
flash:/startup.cfg exists, overwrite? [Y/N]:y
Validating file. Please wait.........................
Configuration is saved to device successfully.
![]()
After modifying the user password, use the save command to save it.
BootWare Password Loss
Contact your local dealer if you forget the BootWare password. The technical support staff will help you log in to the access controller and set a new password.
To change the BootWare password, enter the BootWare main menu, select 5, and follow the prompts:
please input old password:
Please input new password:
Please input new password again:
Password Set Successfully.
![]()
l If you enter a wrong old password, the system prompts “Wrong password,Please input password again”.
l If you fail to input a correct password within three attempts, the system prompts “Wrong password,system halt”.
l An input BootWare password is displayed as “*”.
l The BootWare password can consist of a maximum of 32 printable characters, including letters, numerals, and symbols. If you input a password longer than 32 characters, the system automatically uses the first 32 characters as the password.
Super Password Loss
The super password enables you to switch between four super levels. If you forget the super password, you will be unable to perform some higher privilege operations.
Follow these steps to bypass the super password:
1) Select 8 from the BootWare main menu.
===========================<EXTEND-BOOTWARE MENU>===========================
|<1> Boot System |
|<2> Enter Serial SubMenu |
|<3> Enter Ethernet SubMenu |
|<4> File Control |
|<5> Modify BootWare Password |
|<6> Skip Current System Configuration |
|<7> BootWare Operation Menu |
|<8> Clear Super Password |
|<9> Storage Device Operation |
|<0> Reboot |
============================================================================
Enter your choice(0-9):8
Clearing super password succeeded if the following output displays:
Clear Application Password Success!
![]()
l Exit the menu and reboot the access controller. You will directly enter system view after the access controller restarts.
l This setting works only once. When the access controller is restarted for a second time, the super password is restored.
This chapter describes how to troubleshoot H3C WA series WLAN access points problems. If you cannot solve a system problem, contact the H3C technical support staff.
l Email address: service@h3c.com
l Website: http://www.h3c.com/
Symptom 1
When the AP is powered on, no information is output on the console port although the serial port of the PC is connected to the RJ-45 port of the AP.
Analysis
l If the serial port of the PC is connected to the network port of the AP, no information is output.
l If the serial port settings are not correct, the serial port works abnormally.
Solution:
l Check whether the serial port of the PC is connected to the network port of the AP. If yes, connect the serial port to the port with silkscreen CONSOLE on the AP panel.
l Check the serial port settings of the PC. The correct port settings should be: 9600 bps baud rate, no parity check, and 8 data bits.
Symptom 2
When the AP is powered on, it cannot be connected to the network.
Analysis
l If the network cable is connected to the console port of the AP, the AP cannot be connected to the network.
l If the length of the network cable exceeds the specifications (for example, 100 m, or 328.08 ft.), the AP may not be able to connect to the network.
l If the network cable is neither a straight-through nor a cross-over cable, the AP may not be able to connect to the network.
Solution:
l If the network cable is connected to the console port of the AP, connect it to the network port by referencing the Installation Guide of the AP.
l Replace the network cable with one that meets the specifications.
l Replace the network cable with a standard network cable.
Symptom 3
When a power adapter and a PoE-MH are used to supply power to the AP through the network port, the AP cannot be powered on.
Analysis
Except the power interface for the power adapter, the PoE-MH has two RJ-45 ports, with one (# 1) at the same side as the power interface, and the other (# 2) on the other side. The network cable for power supply should be plugged into RJ-45 # 2. If it is plugged into RJ-45 # 1, power cannot be supplied to the AP.
Solution:
Plug the network cable for power supply into the correct port of the PoE-MH.
Symptom 4
The optical interface of the AP cannot be connected to the network, and the output is abnormal on the serial port.
Analysis
If you insert an optical transceiver with its upside down, short circuit of clock signals will occur, and the system will work abnormally.
Solution:
Restart the AP and make sure that the optical transceiver is plugged into the AP in a right direction.
Symptom 5
The AP cannot be connected when the basic configurations of the AP are completed.
Analysis
Check that:
l The radio on the AP is not enabled.
l The channel and country code settings are incorrect.
l The service template is not enabled.
Solution:
l Enable the radio.
l Use the country code of your own country or region.
l Enable the service template.
Symptom 6
The AP signal is weak when a client is associated with the AP.
Analysis
Check that:
l The value of the max-power is too small.
l No antenna is installed, or the antenna is not connected well.
l The 2.4 GHz antenna is installed where the 5 GHz antenna should be installed.
l The settings of the internal and external antennae are incorrect.
Solution:
l Set the max-power to the largest.
l Install an antenna, and check whether the antenna is well connected.
l Correctly installing the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz antennae.
l Correctly configure the internal and external antennae.
About the H3C WA Documentation Set 1-3
Audience 1-1
Automatically Managing and Upgrading the Applications Through an AC or a US 7-25
B
BootWare Menus 7-2
C
Configuring Basic Functions for an AP Operating in Fat Mode 6-1
Configuring Basic Functions for an AP Operating in Fit Mode 6-1
Conventions 1-2
D
Dealing with Password Loss 7-31
Document Organization 1-1
Documentation Feedback 1-4
E
Examining the Installation Site 3-2
F
Factory Default Configuration 7-7
Fit/Fat Working Mode Switching 7-8
I
Installation Preparations 3-1
Introduction 7-1
L
Logging In to an AP 5-2
M
Maintaining Application and Configuration Files 7-28
O
Obtaining Documentation 1-3
P
Powering on the AP and Connecting It to a Network 5-1
Preparing Installation Tools 3-1
R
Related Documentation 1-2
U
Upgrading an Application Through the Web Interface 7-23
Upgrading an Application Using FTP at the CLI 7-18
Upgrading Applications Through TFTP at the CLI 7-15
Upgrading Applications Through the Serial Port 7-11
Upgrading the Applications Through FTP at the CLI 7-18

