| Title | Size | Downloads |
|---|---|---|
| H3C S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07 Release Notes.pdf | 1.84 MB | |
| H3C S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes) .pdf | 1.46 MB | |
| S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07-MD5.rar | 733 bytes | |
| S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07.zip | 805.64 MB |
H3C S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07 Release Notes |
|
|
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. The information in this document is subject to change without notice. |
|
Contents
Hardware and software compatibility matrix· 6
Upgrade restrictions and guidelines· 8
Software feature and command updates· 9
Operation changes in R6652P07~R6628P40· 9
Operation changes in R6628P35· 9
Operation changes in R6628P30· 9
Operation changes in R6615P08· 10
Operation changes in R6615P07· 10
Operation changes in R6615P05· 10
Operation changes in R6615P03· 10
Operation changes in R6515P06· 10
Operation changes in R6510P02· 10
Operation changes in R6510· 10
Operation changes in F6510· 10
Operation changes in F6509L01· 10
Operation changes in F6508· 10
Operation changes in R6308· 11
Operation changes in F6306· 11
Operation changes in F6305· 11
Operation changes in F1502· 11
Operation changes in R1113· 11
Operation changes in R1112· 11
Operation changes in R1111· 11
Operation changes in R1110P06· 11
Operation changes in R1110P05· 11
Operation changes in R1110· 11
Operation changes in E1109· 11
Operation changes in E1108· 12
Registering and installing licenses· 13
Obtaining license server software and documentation· 13
Obtaining license server software and documentation· 14
Open problems and workarounds· 14
Resolved problems in R6652P07· 14
Resolved problems in R6652P06· 16
Resolved problems in R6652P05· 16
Resolved problems in R6652P02· 19
Resolved problems in R6628P40· 21
Resolved problems in R6628P35· 26
Resolved problems in R6628P30· 29
Resolved problems in R6615P08· 31
Resolved problems in R6615P07· 34
Resolved problems in R6615P05· 36
Resolved problems in R6615P03· 37
Resolved problems in R6515P06· 44
Resolved problems in R6510P02· 50
Resolved problems in R6510· 51
Resolved problems in F6510· 51
Resolved problems in F6509L01· 54
Resolved problems in F6508· 55
Resolved problems in R6308· 61
Resolved problems in F6306· 63
Resolved problems in F6305· 65
Resolved problems in F1502· 67
Resolved problems in R1113· 68
Resolved problems in R1112· 69
Resolved problems in R1111· 71
Resolved problems in R1110P06· 73
Resolved problems in R1110P05· 74
Resolved problems in R1110· 74
Resolved problems in E1109· 75
Resolved problems in E1108· 77
Appendix B Fixed security vulnerabilities· 82
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6652P05· 82
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6652P02· 84
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6628P35· 88
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6628P30· 88
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6615P08· 89
Appendix C Upgrading software· 90
System software file types· 90
Downloading software images to the master switch· 93
Upgrading from the Boot menu· 97
Accessing the basic Boot menu· 99
Accessing the extended Boot menu· 100
Upgrading Comware images from the Boot menu· 101
Upgrading Boot ROM from the Boot menu· 109
Managing files from the Boot menu· 116
List of tables
Table 2 Hardware and software compatibility matrix· 6
Table 3 ISSU version compatibility matrix· 8
Table 6 Minimum free storage space requirements· 97
Table 8 Basic Boot ROM menu options· 99
Table 9 BASIC ASSISTANT menu options· 100
Table 10 Extended Boot ROM menu options· 100
Table 11 EXTENDED ASSISTANT menu options· 101
Table 12 TFTP parameter description· 102
Table 13 FTP parameter description· 104
Table 14 TFTP parameter description· 110
Table 15 FTP parameter description· 111
Introduction
This document describes the features, restrictions and guidelines, open problems, and workarounds for version S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07. Before you use this version on a live network, back up the configuration and test the version to avoid software upgrade affecting your live network.
Use this document in conjunction with S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes) and the documents listed in "Troubleshooting resources ."
Version information
Version number
H3C Comware Software, Version 7.1.070, Release 6652P07
| NOTE: To identify the version number (see Note①), execute the display version command in any view. |
Version history
| IMPORTANT: The software feature changes listed in the version history table for each version are not complete. To obtain complete information about all software feature changes in each version, see the Software Feature Changes document for this release notes. |
Version number | Last version | Release date | Release type | Remarks |
R6652P07 | R6652P07 | 2024-06-28 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6652P07 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6652P06 | R6652P05 | 2024-04-30 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6652P06 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6652P05 | R6652P02 | 2024-03-31 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6652P05 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6652P02 | R6628P40 | 2023-09-25 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6652P02 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6628P40 | R6628P30 | 2023-07-15 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6628P40 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6628P35 | R6628P30 | 2023-04-30 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6628P35 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6628P30 | R6615P08 | 2023-01-13 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6628P30 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6615P08 | R6615P07 | 2022-06-10 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6615P08 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6615P07 | R6615P05 | 2022-06-09 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6615P07 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6615P05 | R6615P03 | 2022-02-25 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6615P05 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6615P03 | R6515P06 | 2022-01-31 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6615P03 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6515P06 | R6510 | 2020-12-31 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6515P06 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6510P02 | R6510 | 2020-11-13 | Release version | This version fixed bugs |
R6510 | F6510 | 2020-07-13 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-R6510 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
F6510 | F6509L01 | 2020-05-15 | Feature version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. New feature: · Configuring the device as a TFTP server · Configuring Layer 3 forwarding on Layer 2 Ethernet interfaces · Enabling password change prompt logging · Enabling mandatory weak password change Modified feature: · Setting the password for local password authentication · Configuring a sensor path |
F6509L01 | F6508 | 2020-04-21 | Feature version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. · Restful server-assisted MAC authentication user recovery · EPA |
F6508 | R6308 | 2020-03-16 | Feature version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes. · For more information about new features, modified features, and deleted features, see H3C S6520XI-CMW710-F6508 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes). |
R6308 | F6306 | 2019-10-25 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes and the company name change. New features: · Layer 3—IP services features · ACL and QoS features · EVPN features Modified feature: · Displaying summary and detailed information about IPv6 TCP connections · Enabling ND logging for user online and offline events · Specifying the link-local addresses of BGP peers · gRPC service |
F6306 | F6305 | 2019-07-30 | Feature version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes and the company name change. |
F6305 | F1502 | 2019-06-27 | Feature version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes and the company name change. |
F1502 | R1113 | 2019-03-22 | Feature version | None. |
R1113 | R1112 | 2019-01-31 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes and the company name change. Modified feature: · Configuring a frame match criterion for an Ethernet service instance. |
R1112 | R1111 | 2018-12-21 | Release version | This version fixed bugs. |
R1111 | R1110P06 | 2018-11-22 | Release version | This version fixed bugs. |
R1110P06 | R1110P05 | 2018-09-17 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes and the company name change. Modified feature: · Displaying online 802.1X user information · Displaying online MAC authentication user information |
R1110P05 | R1110 | 2018-08-29 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes and the company name change. New feature: · Associating a dynamically created Ethernet service instance with a VSI · VCF Fabric · Enabling ARP snooping in VXLANs · Configuring ND snooping in a VXLAN Modified feature: · Displaying IPv4 source guard bindings · Displaying IPv6 source guard bindings Removed feature: · Enabling the device to generate dynamic IPv4SG bindings based on ARP flood suppression entries |
R1110 | E1109 | 2018-08-15 | Release version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes and the company name change. New feature: · Configuring ND attack detection for a VSI Modified feature:: · Device reboot by using the reboot command · Loading the BootWare image in a file to the Normal area of BootWare · Displaying electronic label information for the device Removed feature: · Enabling dropping IPv6 packets that use IPv4-compatible IPv6 addresses |
E1109 | E1108 | 2018-05-04 | ESS version | This version fixed bugs and introduced feature changes and the company name change. New feature: · Setting the SoO extended community attribute for BGP routes · Configuring BGP RPKI Modified feature: · MAC authentication offline detection attribute assignment through RADIUS subattribute 210 · ARP scanning · Route-type match criterion · Route redistribution for OSPF · Route redistribution for IS-IS · Route redistribution for OSPFv3 · Creating a summary route in the BGP routing table · Enabling DLDP on a port |
E1108 | First release | 2017-11-28 | ESS version | None |
Hardware and software compatibility matrix
| CAUTION: To avoid an upgrade failure, use Table 2 to verify the hardware and software compatibility before performing an upgrade. |
Table 2 Hardware and software compatibility matrix
Item | Specifications |
Product family | H3C S6520X-EI/HI series |
Hardware platform | S6520X-30QC-EI S6520X-30QC-HI S6520X-54QC-EI S6520X-54QC-HI S6520X-30HC-EI S6520X-30HC-HI S6520X-54HC-EI S6520X-54HC-HI |
Memory | 2G |
Flash | 1G |
Boot ROM version | Version 117 or higher (Note: Execute the display version command in any view to view the version information. Please see Note②) |
Host software | S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07.ipe (See the MD5 file.) |
iMC Version | iMC ACLM 7.3 (E0705P12) iMC DM 7.3 (E0705P12) iMC PLAT 7.3 (E0705P12) iMC QoSM 7.3(E0505P01) iMC EIA 7.3 (E0611P13) iMC NTA 7.3(E0707L06) iMC SHM 7.3 (E0707L06) iMC EAD 7.3 (E0611P10) iMC VLAN 7.3 (E0705P12) |
iNode Version | iNode 7.3 (E0585) |
WLAN feature image version | S6520X-CMW710-UWW-R5456P05.bin Compatible Aps reference to H3C UWW-CMW710-R5456P05 Release Notes. |
H3C Comware Software, Version 7.1.070, Release 6615P08 ------- Note①
Copyright © 2004-2020 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
H3C S6520X-30HC-EI uptime is 0 weeks, 0 days, 0 hours, 5 minutes
Last reboot reason : User reboot
Boot image: flash:/s6520x-cmw710-boot-r6615p08.bin
Boot image version: 7.1.070, Release 6615P08
Compiled Jun 03 2020 11:00:00
System image: flash:/s6520x-cmw710-system-r6615p08.bin
System image version: 7.1.070, Release 6615P08
Compiled Jun 03 2020 11:00:00
Feature image(s) list:
flash:/s6520x-cmw710-freeradius-r6615p08.bin, version: 7.1.070, Release 6615P08
Compiled Jun 03 2020 11:00:00
flash:/s6520x-cmw710-escan-r6615p08.bin, version: 7.1.070, Release 6615P08
Compiled Jun 03 2020 11:00:00
Slot 1:
Uptime is 0 weeks,0 days,0 hours,5 minutes
S6520X-30HC-EI with 2 Processors
BOARD TYPE: S6520X-30HC-EI
DRAM: 2048M bytes
FLASH: 1024M bytes
PCB 1 Version: VER.A
Bootrom Version: 117 ------Note②
CPLD 1 Version: 001
CPLD 2 Version: 001
Release Version: H3C S6520X-30HC-EI-6615P08
Patch Version : None
Reboot Cause : UserReboot
[SubSlot 0] 24SFP Plus + 2QSFP28
ISSU upgrade type matrix
ISSU provides compatible upgrade and incompatible upgrade, depending on the compatibility between software versions. Table 3 provides the approved ISSU upgrade types only between the current version and the history versions within the past 18 months. This matrix does not include history versions that are 18 months earlier than the current version, for which, no ISSU upgrade verification was performed.
For more information about ISSU, see the fundamentals configuration guide for the device.
Table 3 ISSU version compatibility matrix
Current version | History version | Compatibility |
S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07 | S6520X-CMW710-R6652P06 | Compatible |
S6520X-CMW710-R6652P05 | Compatible |
Upgrade advice
As a best practice, upgrade to this version as long as possible.
Upgrade restrictions and guidelines
Before performing a software upgrade, it is important to refer to the Software Feature Changes document for any feature changes in the new version. Also check the most recent version of the related documents (see "Related documentation") available on the H3C website for more information about feature configuration and commands.
Hardware feature updates
R6652P07
Added support for the QSFP-40G-LX4-WDM1300 transceiver module.
R6652P06~R1110
None.
E1109
S6520X-30HC-EI, S6520X-30HC-HI, S6520X-54HC-EI, S6520X-54HC-HI, LSWM2ZSP8P, and LSWM2ZQP2P are supported.
E1108
First release.
Software feature and command updates
For more information about the software feature and command update history, see H3C S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes) and H3C WLAN Feature Package-CMW710-R5456P05 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes).
MIB updates
Item | MIB file | Module | Description |
S6520X-CMW710-R6652P07~S6520X-CMW710-E1109 | |||
New | None | None | None |
Modified | None | None | None |
S6520X-CMW710-E1108 | |||
New | First release | First release | First release |
Modified | First release | First release | First release |
Operation changes
Operation changes in R6652P07~R6628P40
None.
Operation changes in R6628P35
Changed the default of the port-security m-lag load-sharing-mode command from distributed local to centralized.
The default value of the Restore delay field in the display m-lag system command output changes from 30s to 300s.
Operation changes in R6628P30
The default setting of the stp port-log command is changed as follows:
¡ If the device starts with the initial configuration, the default setting of this command applies. Output of port state transition information is disabled.
¡ If the device starts with the factory defaults, the factory default setting of this command applies. Output of port state transition information is enabled.
Operation changes in R6615P08
The maximum MTU was increased from 1560 bytes to 9000 bytes for Layer 3 aggregate interfaces and their subinterfaces.
Operation changes in R6615P07
None.
Operation changes in R6615P05
None.
Operation changes in R6615P03
None.
Operation changes in R6515P06
None.
Operation changes in R6510P02
As from this version, the device will output the following information when the MAC learning limit is configured on an interface and the number of MAC address entries learned on the interface has reached the limit:
%Mar 2 21:36:03:196 2013 PE2 MAC/5/MAC_TABLE_FULL_PORT: The number of MAC address entries exceeded the maximum number 2 for interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4.
Operation changes in R6510
None.
Operation changes in F6510
None.
Operation changes in F6509L01
None.
Operation changes in F6508
None.
Operation changes in R6308
None.
Operation changes in F6306
None.
Operation changes in F6305
None.
Operation changes in F1502
None.
Operation changes in R1113
None.
Operation changes in R1112
None.
Operation changes in R1111
None.
Operation changes in R1110P06
None.
Operation changes in R1110P05
None.
Operation changes in R1110
None.
Operation changes in E1109
None.
Operation changes in E1108
First release.
Restrictions and cautions
Before performing a software upgrade, it is important to refer to the Software Feature Changes document for any feature changes in the new version. Also check the most recent version of the related documents (see "Related documentation") available on the H3C website for more information about feature configuration and commands.
When you use this version of software, make sure you fully understand the restrictions and cautions described in this section.
Restrictions
Hardware
None
Software
VLAN configuration priority restriction
If both MAC-based VLAN and IP subnet-based VLAN are configured on an interface, MAC-based VLAN configuration takes effect.
Restrictions for password settings
The new version enforces a stricter password control policy, which will examine whether the passwords meet the following requirements:
¡ Password composition restriction.
¡ Minimum password length requirement.
¡ The password cannot contain the username or the reverse letters of the username.
When you enter your password to log in, you are prompted to change the password that does not meet the above requirements.
Configuring Networking
Restrictions for aggregate CAR
A QoS policy that contains an aggregate CAR action cannot be applied to outgoing packets on an interface.
Cautions
Hardware
The data buffer of the interface configuration priority Cautions
· By default, the Burst feature is disabled. An interface can use up to 33% of the shared buffer, and each queue on the interface can use up to 70% of the data buffer of the interface.
· When the Burst feature is enabled, an interface can use up to 90% of the shared buffer, and each queue on the interface can use up to 70% of the data buffer of the interface.
Software
Rate of ARP packets delivered to the CPU
The maximum rate of ARP packets delivered to the CPU was changed from 500 pps to 800 pps to improve the ARP processing performance.
Configuring Networking
Compatible Aps reference to H3C UWW-CMW710-R5456P05 Release Notes.
Licensing
About licensing
H3C offers licensing options for you to deploy features and expand resource capacity on an as needed basis. To use license-based features, purchase licenses from H3C and install the licenses. For more information about the license-based features and licenses available for them, see H3C Switches License Matrixes.
Registering and installing licenses
To register and transfer licenses, access H3C license services at http://www.h3c.com/en/License.
For information about registering licenses, installing activation files, and transferring licenses, see H3C Switches and Routers Licensing Guide.
Some switches support the license for the unified wired and wireless access controller feature. You can purchase licenses to add the number of APs to be managed. For more information, see H3C Comware 7 or 9 Wireless Products Licensing Guide.
Obtaining license server software and documentation
To perform remote licensing, first download and install the H3C license server software.
· To obtain the H3C license server software package, click
H3C license server software package
· To obtain H3C license server documentation, click
H3C license server documentation
Obtaining license server software and documentation
To perform remote licensing, first download and install the H3C license server software.
· To obtain the H3C license server software package, click
H3C license server software package
· To obtain H3C license server documentation, click
H3C license server documentation
Open problems and workarounds
202311210102
· Symptom: On an M-LAG network, STP convergence might be slow.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you use the m-lag standalone enable command to enable the M-LAG standalone mode and then power-cycle the primary M-LAG member device.
· Workaround: Set the delay that the device must wait before changing to M-LAG standalone mode.
List of resolved problems
Resolved problems in R6652P07
202402051337
· Symptom: IRF fabric setup fails.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you perform the following operations:
¡ Use 100G interfaces on the related devices as IRF physical ports.
¡ Configure the devices as an IRF fabric through NETCONF on the controller side.
202403180668
· Symptom: An M-LAG system records STP dispute logs, leading to traffic interruption. The symptom occurs because of a logic mistake in processing a specific situation.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the reliability settings are different between the old and the new software versions when the software is upgraded, especially in STP protocol processing.
202406150478
· Symptom: MAC address authentication fails.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when users perform MAC authentication after both EAD assistant and MAC authentication are configured.
202406030333
· Symptom: After a period of time, the server automatically switches to active state.
· Condition: This symptom might occur after you manually set the server to block state when the server is unreachable, and authentication or accounting packets have been sent and not yet timed out.
202406150501
· Symptom: H.323 packets are looped between devices after H.323-based SQA is enabled.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you enable H.323-based SQA on two or more devices in the same VLAN.
202406071539
· Symptom: After service packets are decapsulated in a tunnel, the service packets are mistakenly matched to a private network, where the service packets are incorrectly processed. As a result, the VXLAN tunnel traffic is interrupted and the function is abnormal.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ Port A matches the ePort index assigned by VXLAN tunnel decapsulation (the lower 12 bits of the ePort index matches the physical port number of port A). For example, the ePort index is 12292, which is 0x3004 in hexadecimal.
¡ The lower 12 bits are 004 and correspond to physical port number 4 of port A. Port A is bound to a private network, and the network where the actual VXLAN service resides is different from this private network.
202406110434
· Symptom: The device failed to obtain the fan speed information.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you obtain fan status information via IMC
202404290270
· Symptom: In a BIDIR-PIM network, the RP fails to forward traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a loopback interface acts as the RP and the output interface is a Layer 3 interface.
202405310239
· Symptom: Only the ping operation initiated by the peer end can succeed. The ping operation initiated by the local end fails.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an interface with physical index 0 on the device is used to form the IRF fabric, a manual VXLAN tunnel is established with the peer end, and no ARP entries exist for IP address on the same subnet.
202405131121
· Symptom: No information might be displayed in the output from the display poe command. In addition, when you execute the poe enable command, the system prompts that the execution failed.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device is operating.
202406052409
· Symptom: The count for the IPv4 route resources is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur in the following situation:
¡ In an MPLS L3VPN, the local device establishes multiple peers with multiple devices at the remote end.
¡ When the local device's eport hardware resources are insufficient, the peer devices perform route migration for the same prefix.
Resolved problems in R6652P06
202404171222
· Symptom: After MAC address learning is disabled on a port, the port still learns MAC addresses.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you disable MAC address learning after configuring MAC authentication.
202404101064
· Symptom: When a BFD session for BGP is created, the ping delay is long or packet loss occurs.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a large number of BFD sessions for BGP have been created and BFD is enabled and disabled repeatedly.
202403270216
· Symptom: A tunnel cannot forward traffic properly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure a PBR policy, configure the outgoing interface as a tunnel, delete that tunnel, and then re-create that tunnel.
202404101092
· Symptom: A large number of ICMP destination unreachable messages are sent to the CPU.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a Layer 3 aggregate interface is associated with a VPN instance and the index of the Layer 3 aggregate interface the same as the index of the Layer 3 Ethernet interface that receive ICMP destination unreachable messages.
202404160893
· Symptom: A packet filter does not take effect in the inbound direction of a VLAN interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a PBR policy is applied to the VLAN interface and the ACL used in the PBR policy contains a rule with the established keyword specified.
Resolved problems in R6652P05
202403040340
· Symptom: Packet loss continues for more than 60 seconds after a master/subordinate switchover is performed on an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if multicast traffic is transmitted over the RPT path and the output interface of the optimal route is on the master device.
202401291764
· Symptom: An authenticated user is online simultaneously on both M-LAG member devices.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed on an M-LAG network:
A user first comes online through authentication on a single-homing interface of M-LAG 1.
The user comes online through authentication on a single-homing interface of M-LAG 2 and triggers a migration.
202403060066
· Symptom: BFD flapping occurs.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the deny-mode ACL rule used to match IPv4 packets configured on VLAN-interface 200 matches BFD packets by mistake, resulting in BFD packet loss and BFD flapping.
202402291384
· Symptom: Tunnel traffic received on a non-aggregate interface matches an ACL configured for an aggregate interface by mistake.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the ACL configured on an aggregate interface incorrectly matches the specific traffic characteristics. When an extension port is allocated to tunnel traffic, the lowest 8 bits coincide with the SRC TRUNK (source port aggregation) match criterion defined in the aggregate interface ACL.
202402040334
· Symptom: The MAC address is not deleted after a static AC on an interface is deleted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if 802.1x authentication is performed before the static AC is deleted.
202401090475
· Symptom: The keepalive link flaps due to timeout.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a large number of ARP packets are sent to the CPU.
202401230378
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, the number of available ARP resources is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the ARP packets move between the member leaf devices repeatedly.
202312041570
· Symptom: The packets are dropped by the device cannot be forwarded normally.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device has received packets with the last three bytes of the source MAC addresses set to 0.
· Impact: The packets with the last three bytes of the source MAC addresses set to 0.
· Workaround: None.
· Severity: Medium
202312040067
· Symptom: The ping operation fails.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a Layer 3 subinterface is configured as the tunnel outgoing interface and connected to a spine device and the ping command is executed.
202307130972
· Symptom: After the m-lag extra-vlan command is executed, the M-LAG member devices cannot synchronize ARP or ND entries for the extra VLANs through the peer-link interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if some M-LAG interfaces are not assigned to the extra VLANs, and the device is rebooted or the peer-link interface flaps.
202311150214
· Symptom: On an M-LAG network, the peer link cannot transmit traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed on an M-LAG network:
a. Enable automatic setup of a VXLAN tunnel between M-LAG member devices.
b. Shut down the M-LAG interface on one member device.
202307181156
· Symptom: In an EVPN M-LAG network, the member devices might not advertise BGP routes, and Layer 3 traffic cannot be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if BGP EVPN sessions are set up in an EVPN M-LAG network.
202310090404
· Symptom: An OSPF route anomaly occurs.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you shut down the BFD MAD detection interfaces on IRF devices by shutting down the downlink interface and then the uplink interface.
202307051264
· Symptom: The device does not display logs for adding MAC address entries and displays logs only for deleting MAC address entries.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure port security settings on a port and connect the port to the peer end.
202310240312
· Symptom: On an EVPN DRNI system with a tunnel peer link, the peer-link tunnel goes up slowly or even cannot go up.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if default VXLAN decapsulation is enabled for the IP address of loopback 0 and the IP address is the source IP addresses of non-peer-link VXLAN tunnels.
202310240098
· Symptom: After patch installation and device restart, slow device startup and the EVENT_TIMEOUT log might occur.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if DRNI and monitor link are configured together and the device reboots after installation of a patch with the drnid process included.
202308091835
· Symptom: The xmlcfgd process has exceptions in the next installation of a patch after the patch is loaded, because a subprocess has residues.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a patch is loaded on the controller connected to the device.
202309260374
· Symptom: The ovsdb-server process occasionally terminates abnormally on the device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when the controller deploys the configuration to the device.
202308291580
· Symptom: Packet loss occurs during the bulk addition or deletion of M-LAG interfaces on an EVPN M-LAG system.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if singlehoming AC-attached interfaces exist on the EVPN M-LAG system, and bulk addition or deletion of M-LAG interfaces is performed during traffic transmission between remote leaf devices and local ACs.
202309182105
· Symptom: The switch sends 802.1X authentication packets and accounting packets to different RADIUS servers because the state of the port security process is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a master/subordinate switchover is performed on an IRF fabric.
Resolved problems in R6652P02
202309090594
· Symptom: Residual dynamic ACL entries exist on subordinate devices in an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The IRF fabric has aggregate interfaces that contain member ports from multiple member devices.
¡ MAC authentication users are assigned authorization VSIs after they pass MAC authentication and come online.
¡ The MAC authentication users are frequently moving among the aggregate interfaces in different VLANs.
202309220595
· Symptom: If you configure the bfd min-transmit-interval 1000 command for hardware BFD, but the actual packet sending rate on the device interface is inconsistent with the configuration, BFD session establishment fails.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure the bfd min-transmit-interval 1000 command for hardware BFD.
202309121745
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, multicast forwarding is abnormal after a master/subordinate switchover.
· This symptom occurs after a master/subordinate switchover if you have configured Layer 3 interfaces before setting up the IRF fabric.
202308310672
· Symptom: The device reboots abnormally.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a single port on an IRF member device is added to an aggregation group when a static AC has been specified for the single port.
202308292319
· Symptom: Authentication MAC information and some ACL information remain.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if VXLAN static ACs are configured, normal ports perform URL authentication on users, and the users are logged off.
202308120522
· Symptom: The device reboots abnormally.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a user that comes online via a cross-card aggregated interface on an IRF device repeatedly manually create and delete ACs.
202308241645
· Symptom: Dynamic MAC addresses learned on a Layer 2 aggregate interface do not age out.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the member ID of the device is not 1.
202308111721
· Symptom: A core dump file is generated after the portsecd process repeatedly restarts.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the portsecd process repeatedly restarts when the following conditions exist:
¡ The device is an IRF fabric.
¡ Temporary MAC authentication users come online on a port operating in mac-else-userlogin-secure-ext port security mode.
202309040482
· Symptom: Traffic is forwarded out from an incorrect egress port.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the port is first added to the VLAN of a VLAN interface with a MAC address and then added to an aggregation group in this VLAN.
202308161652
· Symptom: Failed to synchronize the configuration from the controller to the switch during software upgrade, and an unsupported command (dci switch-delay) exists on the switch after the synchronization.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the switch does not support Layer 3 multicast in DCI scenarios.
202308250625
· Symptom: After a default route is redistributed into an OSPF area, other devices do not learn the type-5 default route.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The routing loop detection feature is disabled for the private OSPF process by executing the vpn-instance-capability simple command.
¡ The OSPF process is not enabled to redistribute routes from other routing protocols. (The import-route command is not executed.)
¡ No NSSA area is configured. (The nssa command is not executed.)
¡ The whole device is restarted and starts up with a binary configuration file.
202308160716
· Symptom: A user obtains an authorization ACL after it passes authentication and comes online. However, the port ranges in the ACL rules cannot take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the ACL number is not 2304 and the device is operating in switch mode.
202308111636
· Symptom: Service failure causes packet forwarding failure.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when the device receives a large number of HTTP or HTTPS attack defense packets destined for the device.
202305080149
· Symptom: On an EVPN M-LAG network, packet loss occurs when a device single-homed to a leaf device pings other devices.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a device single-homed to a leaf device broadcasts the received RARP packets on an EVPN+M-LAG network. As a result, ARP entries and ARP suppression entries become incorrect on other devices.
202306240066
· Symptom: ARP entries are learned on the IPP incorrectly. As a result, remote IP addresses on the same subnet might fail to be accessed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if proxy ARP is configured for the DRNI dual-active VLAN gateways or VRRP and periodic automatic ARP scanning is enabled by using the arp scan auto enable command.
202306290442
· Symptom: CAR rate limit failed to be deployed.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you execute the authorization-attribute command in ISP domain view with the car parameters specified, but the CAR rate limit settings do not meet the granularity range requirements.
Resolved problems in R6628P40
202305151137
· Symptom: The device reboots abnormally with a low probability.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you execute the display diagnostic-information command to display or save running status data after you remove and install subcards.
202306270487
· Symptom: A packet filter cannot drop the TCP packets with port 639.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when you configure a packet filter to drop TCP packets with port 639.
202305251379
· Symptom: The CPU usage is high on the leaf devices in an EVPN network.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ARP flood suppression works in response mode and the devices attached to the leaf devices migrate frequently, which causes IP address conflicts.
202305290972
· Symptom: After a service card is restarted or removed, IKE negotiation fails, resulting in interruption of the IPsec service.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device has multiple MPUs and a primary/backup switchover occurs.
202306301119
· Symptom: On an RRPP ring, multicast traffic fails to be forwarded after a link switchover is performed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you have enabled dropping unknown multicast data packets globally.
202305250569
· Symptom: Residual IPv6SG bindings exist after you clear ND snooping entries in a VLAN.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you configure the device to create both ND snooping entries and IPv6SG bindings for a VLAN. An endpoint migrates frequently within the VLAN and sends NS packets to the device.
202306130155
· Symptom: After a user goes offline, its IPv6 address binding entries are not deleted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ND snooping is configured for a VSI and a large number of endpoints migrate between ACs of the VSI frequently and send ND packets.
202305251218
· Symptom: The device outputs free memory early-warning notifications every hour if you edit the configured free-memory thresholds by adding the early-warning threshold and sufficient-memory threshold after a free-memory alarm has been triggered.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a free-memory alarm has been triggered without the early-warning threshold and the sufficient-memory threshold configured.
202306301160
· Symptom: After a Layer 3 aggregate interface bound to a VPN instance is deleted, relevant ACL resources remain.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you bind a Layer 3 aggregate interface to a VPN instance, and then delete the Layer 3 aggregate interface directly.
202305251252
· Symptom: A user fails HWTACACS authorization and accounting.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Use the ip host or ipv6 host command to configure the host name of an HWTACACS server.
b. In HWTACACS scheme view, specify the HWTACACS server by its host name and use it as the authentication, authorization, and accounting servers.
202306130886
· Symptom: The SNMP collected traffic statistics is not consistent with the actual statistics.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the inbound or outbound accumulated traffic statistics on the network management port exceeds 4294967295.
202306150365
· Symptom: The device cannot ping the PCs attached to access ports, and the PCs attached to trunk ports can be pinged.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ports join an aggregation group, a VPN instance is bound to the related Layer 3 aggregate interface, and ACL configuration is issued to the ports.
202305251257
· Symptom: An M-LAG peer-link interface cannot forward packets of 1859 bytes or larger.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an M-LAG peer-link interface forwards traffic.
202306250055
· Symptom: A VRRP network cannot be established.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the intermediate device is not configured with VRRP and is enabled with dropping unknown multicast data packets for a VLAN.
202306250483
· Symptom: You cannot use SSH or Telnet to log in to the local device from another directly connected device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following Web authentication-free subnets exist on the local device:
¡ Web authentication-free subnet that contains the IP address for SSH or Telnet login.
¡ Web authentication-free subnet that has a mask shorter than the mask of the IP address for SSH or Telnet login.
202306061815
· Symptom: The switch generates a core file for the PIM module.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the next hop of the optimal route to the source in an SSM multicast forwarding entry is a secondary IP address and route flapping occurs.
202305181213
· Symptom: The switch reboots due to KernelAbnormalReboot.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when multicast settings are configured on an IRF fabric.
202305291037
· Symptom: An ucmd exception occurs when you enter a command.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when HWTACACS command accounting is configured and the server changes from unreachable to reachable.
202306122053
· Symptom: When all online users that are assigned the same authorization ACL go offline, the device fails to delete the authorization ACL information. Residual authorization ACL information exists on the device. As a result, the ACL resources are insufficient.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Assign the authorization ACL to multiple BYOD online users in the same VSI.
b. Log off all the users. The first online user assigned the authorization ACL is not the last one to go offline.
202305290786
· Symptom: When conversational learning is enabled for forwarding entries of an AC, the device cannot issue AC forwarding entries to the hardware upon receiving traffic on the AC.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the AC is continuously receiving known unicast packets when you enable conversational learning for forwarding entries of the AC.
202306201965
· Symptom: A MAC authenticated user cannot obtain an IP address after it is assigned to the BYOD authorization VSI.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ AD-Campus 6.3 solution.
¡ IRF and EVPN VXLAN network.
¡ MAC-based traffic match mode is disabled for dynamic Ethernet service instances on the interface on which the user is authenticated. This mode is configured by using the mac-based ac command.
¡ The user must pass MAC portal authentication on the leaf device, and it has passed MAC authentication.
202305300747
· Symptom: Known unicast traffic is not isolated between VXLAN tunnels of different VXLANs.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if packets are forwarded between two VXLAN tunnel interfaces.
202305251496
· Symptom: The undo telnet server enable command cannot take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you execute this command when the device acts as the Telnet server and the third-party Telnet client does not support option negotiation.
202307010424
· Symptom: If the physical interface on which a PW resides receives more than 500 DHCP Discover messages per second, services (such as OSPF) running on that interface will be interrupted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
a. The device is on the MPLS L2VPN network and is enabled with the DHCP service.
b. The PW interface receives more than 500 DHCP Discover messages per second.
202305290977
· Symptom: NAT port blocks for users run out easily, which causes insufficient port blocks and affects user services.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when you configure DNS disabled with ALG in a NAT scenario. Five-tuple entries are generated and the aging timer for the entries is prolonged.
202305290958
· Symptom: A user fails HWTACACS authentication and cannot log in to the Web interface of the device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if HWTACACS authentication is configured for login and the user attempts to log in to the Web interface of the device.
202305290894
· Symptom: A SmartMC member repeatedly prints the following login failure log after it reboots: Feb 24 14:41:31:3042023 H3C NETCONF/6/SOAP_XML_LOGIN: admin from 127.0.0.1 loginfailed
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you perform the following operations on the commander:
a. Modify the password for the default user (admin) on members.
b. Save the member configuration and reboot the command.
202305290914
· Symptom: In a DR system, the outgoing interface for traffic is incorrect after ND entries migrate.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a DR member device reboots and synchronizes ND entries with the DR peer, ND entries migrate on the DR member device, and the outgoing interface for traffic changes.
202305260074
· Symptom: The output from the display lldp neighbor-information list command is displayed in garbled characters when LLDP is enabled on the device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if LLDP is enabled on the device and you execute display lldp neighbor-information list to display brief LLDP information that all LLDP agents received from the neighboring devices in a list.
202305251384
· Symptom: Command execution fails. The CLI gets stuck.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you execute the default command, MAC authentication commands, or port security commands on a port during optimized automated deployment of the AD-Campus 6.3 solution.
202305251188
· Symptom: Some DDNS features are unavailable.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when you send packets to the DDNS server in which the Host field is an IP address instead of its corresponding domain name.
202305251147
· Symptom: The IKED process on the MPU experienced an exception, which triggered the device to reboot abnormally.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if IPsec and DPD are deployed, the device acts as the headquarters device, has a large number of IKE packets to handle, and has run for a long time.
202305251580
· Symptom: The output from the display resource-monitor command shows that the VSI resource specification is 2K, which does not match the specification list.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you execute the display resource-monitor command to view VSI resource information.
202305260606
· Symptom: IRF physical interfaces on the device cannot come up after the device reboots. As a result, the device cannot form an IRF fabric with other devices.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you use 100-GE/40-GE ports as IRF physical interfaces.
202305130310
· Symptom: The following CAR-exceeded packet loss log is mistakenly reported:
¡ %Apr 18 04:49:15:237 2023 zubojieru-sw DRVPLAT/4/SOFTCAR DROP: -Slot=2;
¡ PktType=UNKNOWN_IPV4MCiptAKNOWN_IPV4MC , SrcMAC=642f-c7aa-d401, Dropped at Stage=0, StageCnt=0, TotalCnt=1.
· Condition: This symptom occurs after the switch receives an unknown multicast packet and creates a drop-unknown entry.
202305051250
· Symptom: A port on an LSWM2XMGT8P interface module fails to come up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a port on an LSWM2XMGT8P interface module connects to a non-10G port.
202305200041
· Symptom: The ACL resources are insufficient because the ACL resource occupation mode of voice VLAN is still the port mode after it is configured as the global mode.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if IP phones are automatically discovered through LLDP.
202305230595
· Symptom: A device cannot access the local device by using SSH through an aggregate interface. However, that device can ping the local device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed on the local device:
a. Configure remote Web authentication.
b. Use the web-auth free-ip command to specify Web authentication-free subnets.
c. Enable Web authentication on the aggregate interface and an Ethernet interface.
d. Remove the Web authentication-free subnets.
e. Reconfigure the Web authentication-free subnets.
202306070855
· Symptom: Packets carry incorrect source MAC addresses after being forwarded by an EVPN M-LAG system.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if packets received on a tunnel interface are forwarded at Layer 3 over the peer-link to a singlehomed M-LAG interface on the M-LAG peer.
Resolved problems in R6628P35
202303280502
· Symptom: The display interface brief command displays a nonexistent management port (MGE0/0/2) when it is executed on an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when you execute the display interface brief command on an IRF fabric.
202303130130
· Symptom: Traffic coming into an AC interface is sent out of that AC interface, forming a loop.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when the AC interface receives traffic whose source MAC address is the same as its destination MAC address.
202303101546
· Symptom: After obtaining an IPv6 address through DHCPv6, the device fails to add the default route to its routing table.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a device uses DHCPv6 for IPv6 address acquisition.
202303280505
· Symptom: The device cannot communicate with the directly connected peer device through IPv6, and the packet loss ratio approaches 100%.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a large number of unknown multicast packets exist between the devices and therefore ICMPv6 packets are abnormally dropped.
202303101686
· Symptom: Enable the DHCP snooping entry auto backup feature, and back up the DHCP snooping entries for one time. When you use the dhcp snooping binding database update now command to manually save DHCP snooping entries to the backup file again, the backup fails. In this case, the Status field displays writing in the command output from the display dhcp snooping binding database command.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the TFTP server does not support the protocol length feature.
202303031164
· Symptom: After a SmartMC member device restarts, the device keeps reporting log messages for local login failures. The log content is "Feb 24 14:41:31:3042023 H3C NETCONF/6/SOAP_XML_LOGIN: admin from 127.0.0.1 loginfailed."
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you use smartmc tc password on the commander to edit the password of default user admin for members, save member configurations, and then restart members.
202303101381
· Symptom: The IRF fabric reboots because the memory is exhausted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a master/subordinate switchover is performed or a DHCP client requests multiple addresses from the IRF fabric acting as a DHCP relay.
202304101304
· Symptom: An AP attached to an M-LAG system cannot obtain an IP address.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the M-LAG member devices act as management gateways and ARP snooping is enabled on them.
202303141487
· Symptom: The DHCP process exits unexpectedly and then recovers after DHCP relay entries are aged out.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The switch acts as a DHCP relay.
¡ A DHCP client obtains two IP addresses on an interface and then obtained one of the two addresses on anther interface.
¡ The DHCP relay entries are aged out.
202303240777
· Symptom: When the device is automatically deployed, some ports fail to be assigned to an aggregation group.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device is automatically deployed and multiple ports are assigned to the same aggregation group.
202303220706
· Symptom: When the RADIUS authentication server for 802.1X authentication is unreachable, users cannot bypass authentication through the none authentication method.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the RADIUS authentication server is unreachable and the none authentication method is used.
· Workaround: Execute the dot1x critical eapol command.
202303100258
· Symptom: A server attached to an EVPN M-LAG system cannot ping an external network.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an M-LAG interface with the lacp edge-port setting configured flaps repeatedly.
202302270531
· Symptom: After an IRF fabric splits, the subordinate device cannot detect loops.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an IRF fabric splits.
202303030899
· Symptom: BGP sessions flap.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device receives a large number of packets that do not match any routes.
202302201089
· Symptom: The device does not support collecting packet statistics on Layer 3 aggregate subinterfaces.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the traffic-statistic enable command is executed on Layer 3 aggregate subinterfaces.
202302170758
· Symptom: Track is associated with EAA. When the state of a track entry changes from negative to positive, the monitoring policy action is not executed.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a track monitoring event is associated with multiple track entries and one of the track entries changes from not ready state to positive state.
202303090021
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, traffic received on a Layer 3 aggregate interface cannot be forwarded between the IRF member devices.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a Layer 3 aggregation group is created before IRF physical interfaces are bound to IRF ports.
202302240358
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly because of a kernel exception.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the display diagnostic-information command is executed.
202301092178
· Symptom: When a TFTP server is used to save auto backup DHCP snooping entries, only one entry can be stored.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a TFTP server is used to save auto backup DHCP snooping entries.
202302160003
· Symptom: Static EVPN MAC address entries synchronized from the remote VTEP to the local VTEP are deleted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if only static EVPN MAC address entries are synchronized from the remote VTEP to the local VTEP. The synchronized EVPN MAC address entries are deleted after an aging period.
202302101133
· Symptom: When a VXLAN tunnel is used as a peer link on an EVPN M-LAG network, the broadcast packets received on the peer link are incorrectly forwarded to the local M-LAG interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if broadcast packets are received on the peer link.
202302101493
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, the SNMP server does not receive link-down alarms from IRF physical interfaces.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a service interface of the subordinate IRF member device is connected to the SNMP server and the IRF physical interfaces go down.
202212300039
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if MQC configuration matches both IPv4/IPv6 packets and packets with multiple outer VLAN tags.
202302021438
· Symptom: The switch prints an error message when a DHCPv6 client requests an IPv6 prefix from the DHCPv6 server through the switch.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the switch acts as a DHCP snooping device and you have executed the ipv6 dhcp snooping pd binding record and ipv6 verify source ip-address mac-address commands on the switch.
202303090071
· Symptom: Alarm log messages show that available AC resources exist when underlying hardware resources are exhausted.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if AC resources are exhausted by a large amount of configuration.
Resolved problems in R6628P30
202212240006
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly or fails to set up NAT sessions.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the display nat session command is executed during execution of the nat static outbound command.
202301110093
· Symptom: On an M-LAG system, ARP entries and MAC address entries are incorrect, and the peer link cannot be used to forward traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the M-LAG system is automatically deployed by using devices that start up with initial configuration.
202301111261
· Symptom: On an EVPN VXLAN M-LAG system formed by two leaf devices, reboot of one M-LAG member device results in reboot of the other M-LAG member device. The M-LAG system resumes operation after multiple automatic reboots.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if 1500 MAC authentication users access the network through ARP learning and the primary member device is rebooted.
202212300039
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if MQC configuration matches both IPv4/IPv6 packets and packets with multiple outer VLAN tags.
202301060304
· Symptom: A delay exists when MAC authentication users access the network.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if MAC authentication users go offline after successful authentication and MAC authentication is triggered again.
202212081055
· Symptom: The device cannot come online because the ipv6 address dhcp-alloc command on VLAN interface 1 is lost.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the automatic configuration process ends or you manually terminate the automatic configuration process during an IPv6 automatic deployment.
202212080022
· Symptom: The device reboots when a large number of MAC authentication users come online and go offline on an aggregate interface and ACLs and URLs are authorized to the users.
· Condition: This symptom occurs might if a large number of MAC authentication users come online and go offline on an aggregate interface and ACLs and URLs are authorized to the users.
202208301357
· Symptom: An endpoint cannot pass Web authentication in an M-LAG system.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The distributed even-/odd-MAC mode is configured for authentication load sharing.
¡ The MAC address of the endpoint is an odd MAC address.
¡ The authentication packets are sent to the M-LAG member device in distributed even-MAC mode.
202211280698
· Symptom: When a route server reflects an EBGP route, it mistakenly modifies the router MAC address in the route as its own router MAC address.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you have executed both the peer route-server-client and peer router-mac-local dci commands on the route server.
202211240773
· Symptom: A clients reports two different XPATH messages, and another client reports no messages.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure gNMI subscriptions and concurrent sessions exist.
202301040135
· Symptom: The subscribed IP-SGT information is deleted one hour after the WebSocket connection between the device and the controller is disconnected.
· Condition: This symptom occurs after the WebSocket connection between the device and the controller is disconnected.
202301040134
· Symptom: An error occurs during device startup.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device starts up.
202301040841
· Symptom: After you execute the display mad verbose command on an IRF member device, the command output displays both VLAN interfaces and excluded ports while only VLAN interfaces should be displayed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an IRF fabric is split and then established.
202207050531
· Symptom: After you delete an interface, the resources allocated to the interface cannot be released. As a result, the system cannot allocate these resources to other functions.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you delete the source interface specified for VXLAN default decapsulation.
202212280017
· Symptom: In an EVPN multicast network, the multicast traffic is mistakenly forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device forwards multicast traffic.
202212280016
· Symptom: A QoS policy on an M-LAG member device fails to match with the packets sent from the peer.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an M-LAG member device configured with a QoS policy receives packets from the peer through the peer link in an M-LAG system.
202301051651
· Symptom: Failed to restore the default settings for a Smartrate-Ethernet interface by executing the default command.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you have executed the stp instance 0 port priority 16 command on a Smartrate-Ethernet interface.
202301040139
· Symptom: In an M-LAG system, the interfaces in M-LAG MAD DOWN state fail to restore to normal after an M-LAG member device restarts.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the member port rates of the peer link interface are inconsistent.
202212220265
· Symptom: The device fails to issue the m-lag extra-vlan command through NETCONF for the first time.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device issues the m-lag extra-vlan command through NETCONF for the first time after device startup.
202212281015
· Symptom: In a VXLAN network configured with M-LAG, the device acting as a leaf node drops multicast packets from the spine.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when the leaf node receives multicast packets from the spine in a VXLAN network configured with M-LAG.
202212260304
· Symptom: The OSPF neighbors and PIM neighbors flap.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device receives a large number of multicast packets with TTL 1.
202212191223
· Symptom: On an MPLS network, the VSI TTI configuration is not cleared after you configure AC settings and then restore the device to empty configuration.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure AC on the device and then restore the empty configuration for the device.
202212060168
· Symptom: No output is displayed upon execution of the display kernel reboot command.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when you execute the display kernel reboot command to view information about device reboot events.
202211181050
· Symptom: In an M-LAG network, online 802.1X user go offline and new users cannot come online after one member device (leaf device) is upgraded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you form an M-LAG network by using two leaf devices and upgrade one leaf device
202212200312
· Symptom: 40-GE IRF physical interfaces might fail to come up with a low probability.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if 40-GE cables are used to set up an IRF fabric and one IRF member device is rebooted.
Resolved problems in R6615P08
202207111528
· Symptom: No commands can be entered after the dmesg command is executed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you enter the dmesg command in kdb view after the device is power cycled.
202208051014
· Symptom: In a VPLS network, the packets of a PW have inner encapsulation errors.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you flap the PW-side interface repeatedly.
202208040950
· Symptom: VPLS packets fail to be forwarded in an MPLS network with P devices.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the outgoing label on the public network PE is the same as the incoming label on the P device.
202207220046
· Symptom: Endpoints fail to be obtain IP addresses from the IRF fabric acting as a DHCP server.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the IRF fabric connects to the AC interface and experiences a master/subordinate switchover.
202206020061
· Symptom: Cross-subnet packets cannot be forwarded in hardware.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the peer device is enabled with source MAC check.
202208041205
· Symptom: The HardwareRev information about a subcard read through NETCONF is wrong.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you read the HardwareRev information about a subcard through NETCONF.
202206161204
· Symptom: A user fails to obtain an IP address and fails to come online after the user.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ Policy check is enabled on the server.
¡ The user comes online from the isolation security group and passes security checks.
¡ The user is switched to the service security group.
202206210576
· Symptom: The configuration fails to take effect because the free memory is insufficient.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a physical interface goes down and comes up frequently.
202206250439
· Symptom: The VPN instance associated with interface does not take effect after the device reboots
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you associate the same VPN instance with a Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface and a VLAN interface that have the same interface number.
202202150772
· Symptom: IRF physical interfaces cannot come up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a 100-Gbps expansion interface card is installed in the device, interfaces on subcards are installed with 40-Gbps transceiver modules or cables, and these interfaces can configured as IRF physical interfaces.
202112271474
· Symptom: Member devices in a VXLAN DR system might reboot unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a certain script is executed.
202109060975
· Symptom: PIM DM is disabled on a VLAN interface, Layer 2 multicast entries are not established on the subordinate IRF member device, and multicast traffic is broadcast within the VLAN.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if both Layer 2 multicast and Layer 3 multicast are configured for the same VLAN, traffic is received on the subordinate IRF member device, and IGMP snooping is configured for the VLAN on an IRF fabric.
202205270372
· Symptom: Outgoing packets carry an incorrect source MAC address.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations have been performed:
¡ Configure a MAC address on a VLAN interface.
¡ Delete the VLAN interface and re-create it.
202205240571
· Symptom: Threads of OSPFv3 access invalid pointers and are hanged, the core is abnormal, and routes are not updated.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Configure a VPN instance that has no OSPFv3 instances.
b. Associate the VPN instance with an interface and execute the ipv6 address command on the interface.
c. Execute OSPFv3 preconfigured commands but not OSPFv3 enable commands. The ospfv3 1 area 0 command is an example of OSPFv3 enable commands. OSPFv3 preconfigured commands refer to commands other than enable commands, such as ospfv3 timer hello, ospfv3 network-type, and ospfv3 cost.
d. Remove the VPN instance-interface association or delete the VPN instance.
202204110848
· Symptom: Source ports in a local mirroring group fail to be configured after the source ports in another local mirroring group are configured.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
¡ Configure the monitor port as the same port for seven local mirroring groups.
¡ Configure the source ports for the seventh local mirroring group.
¡ Configure the source ports for another local mirroring group among the remaining local mirroring groups.
202110261296
· Symptom: In an inter-VPN forwarding scenario, multicast traffic cannot be forwarded to the public network.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a member port is repeatedly added to and removed from the aggregate interface for the tunnel and the private route flaps.
202112310599
· Symptom: The device issues Layer 3 IPv4 multicast entries successfully and might fail to issue some Layer 3 IPv6 multicast entries, which causes multicast forwarding errors.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device issues 3000 IPv4 IPMC multicast entries and then 250 IPv6 IPMC multicast entries and the number of multicast entries reaches the upper limit.
Resolved problems in R6615P07
202110191417
· Symptom: Once removed from a monitoring group, an interface cannot be assigned to monitoring groups again.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if traffic is mirrored to a monitoring group through local mirroring and flow mirroring.
202112250446
· Symptom: EVPN and Layer 2 multicast are configured on the device, and the igmp-snooping drop-unknown setting does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a VXLAN ID is deleted and recreated on a VSI.
202111260029
· Symptom: MAC address entries created for MAC authentication users are not deleted after MAC authentication is disabled on DR interfaces.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if MAC authentication is disabled on DR interfaces of a DR system that uses an Ethernet aggregate link as the IPL.
202112081609
· Symptom: On an EVPN DR system, a BGP task is abnormal and creates a core file.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the DR system receives ARP packets and 1000 attached hosts migrate from the DR system.
202112081745
· Symptom: The device generates blackhole MAC address entries and does not forward certain traffic.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if incoming traffic matches a MAC-based VLAN and an IP subnet-based VLAN simultaneously on the same interface.
202112131788
· Symptom: EVPN is enabled to forward Layer 2 multicast traffic. After a VXLAN ID is deleted and then created again, the drop-unknown setting does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a VXLAN ID is deleted and created again with the drop-unknown setting being intact.
202112280428
· Symptom: MAC address entries are not deleted completely, and the type of the MAC address entries is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following events occur on a DR system formed by two devices with different capabilities:
a. The traffic load reaches the limit of the device with higher capabilities.
b. The reset l2vpn mac command is executed.
202112280864
· Symptom: MAC address learning is disabled globally when the device is receiving dense traffic, but dynamic MAC address entries are not deleted.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if MAC address learning is disabled globally when the device is receiving dense traffic.
202112281596
· Symptom: An EVPN DR system uses an Ethernet aggregate link as the IPL. After an AC is deleted and recreated, the AC does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following events occur:
a. The maximum number of ACs is reached.
b. A static AC is deleted and recreated on a non-DR interface or DR interface.
202201040231
· Symptom: The device fails to forward some multiple packets.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if BIDIR-PIM is enabled and RPs are configured in BIDIR-PIM domains.
202112291070
· Symptom: Users fail authentication after the attached IRF fabric reboots.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an IRF master/subordinate switchover occurs when the interface used for authentication is down and users are online.
202112291428
· Symptom: A non-existent VLAN is created on the primary DR device in type 2 configuration consistency check.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following operations are performed:
a. Two devices are booted with initial configuration, and they are configured to set up a DR system.
b. The keepalive link comes up.
c. An IPP is configured on the primary and secondary devices in sequence.
202112301425
· Symptom: On an EVPN DR system, synchronized MAC addresses are issued to incorrect ACs, and this issue cannot be recovered.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if ACs match single-tagged packets and the following operations are performed:
a. ACs matching the same VLAN are mapped to different VSIs.
b. The ACs are deleted.
c. The ACs are recreated to match the same VLAN and mapped to the same VSI.
·
202201041255
· Symptom: Broadcast/multicast storm suppression does not take effect on a 100G interface. Broadcast/multicast/unknown unicast storm suppression cannot be disabled on a 100G interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you enable broadcast/multicast/unknown unicast storm suppression on a 100G interface and then disable broadcast/multicast/unknown unicast storm suppression on the 100G interface.
202205111296
· Symptom: A VSI interface in down state can still act as a gateway interface to forward traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the shutdown command is executed on a VSI interface configured as the VXLAN gateway interface.
202205111299
· Symptom: When a PoE interface fails to supply power, the traps cannot correctly report the failure.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the maximum power configured on the PoE interface cannot meet the power requirements of the attached PDs.
202205111292
· Symptom: Within 5 minutes after the VCF fabric is automatically deployed. the devices try to obtain the device list file.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if legacy automated deployment is performed for the devices and the device list is not configured.
202205111301
· Symptom: After the VCF fabric is automatically deployed, the original PVID settings of interfaces are lost.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a device is automatically deployed as an access device, the interfaces have original PVID settings, the interfaces are connected to APs, and then the APs are removed.
202203300334
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an AC is associated with a VSI on the device.
202201200603
· Symptom: When loop detection is configured on a VSI and ARP packets are injected to a blocked AC, the AC can still respond with ARP replies normally.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ARP proxy is configured on the VSI.
202108170529
· Symptom: The MAC address entries for MAC authentication users and 802.1x users are not deleted after they go offline.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if MAC authentication users and 802.1x users move between member devices on an IRF fabric.
202203211300
· Symptom: After a transceiver module is installed into a port, the device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
a. A DR system has peer links.
b. Configure an AC on the DR interface (an aggregate interface).
c. On a single-homed interface, configure an AC with the same service instance.
Resolved problems in R6615P05
202202160159
· Symptom: Errors occur in issuing flow IDs to the driver after BYOD users come online.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if BYOD users come online on a single interface.
202202150963
· Symptom: ACLs issued for VXLAN ACs are not deleted after the ACLs age out.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ Conversational learning is enabled for forwarding entries when ACs are mapped to VSIs.
¡ ACs receive traffic, and then the traffic stops.
202202080204
· Symptom: An interface with static ACs configured cannot ping the controller.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an aggregate interface with static ACs configured flaps and conversational learning is enabled for forwarding entries on the static ACs.
202201050390
· Symptom: Synchronized MAC address entries do not age out on a distributed EVPN gateway.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if MAC addresses move between two DR interfaces.
202202080199
· Symptom: The active MPU and driver do not have AC data.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if ACs with conversational learning enabled are deleted and then ACs with conversational learning disabled are created.
202202080205
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if conversational learning is enabled for ACs and then the interface where the ACs reside flaps.
202112270862
· Symptom: AC resources for a VSI might not be deleted completely when an authentication user logs off and then logs on again.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if user MAC addresses move between interfaces and a large number of authentication users exist.
Resolved problems in R6615P03
202012181363
· Symptom: The interface-up events of 100-GE interfaces on the front panel might not be sent.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exists:
¡ 100-GE interfaces on the front panel are connected with 100-G cables.
¡ A broadcast storm occurs.
¡ One of the interfaces is shut down by using the shutdown command.
202012171705
· Symptom: When an NMS is used to read the value of the hh3cEntityExtErrorStatus MIB variable for sensor 3 on a device that has two slots, the system returns a value "not supported".
· Condition: This symptom occurs on a device that has two slots
202012171693
· Symptom: Some endpoints cannot obtain IP addresses.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. The device acts as the WLAN gateway and provides DHCP relay and portal authentication services.
b. The endpoints send DHCP requests towards the device.
202012031187
· Symptom: The BFD MAD session of an IRF fabric comes up and then goes down after the IRF fabric splits.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when BFD MAD is used to detect IRF split.
202012030458
· Symptom: SSH users cannot log in.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a large number of SSH users concurrently log in to or log out of the device and meanwhile, AAA settings are added or deleted on the device.
202010130105
· Symptom: Unknown unicast storm suppression does not take effect if broadcast storm suppression and unknown unicast storm suppression are both configured on an interface of an LSWM2XMGT8P interface module.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if broadcast storm suppression and unknown unicast storm suppression are both configured on an interface of an LSWM2XMGT8P interface module.
202009251219
· Symptom: A serial port does not respond to commands when the device is operating in VXLAN mode.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if routes are added or deleted after the device load digware.
202009120515
· Symptom: An IRF fabric unexpectedly outputs error messages.
· Condition: This symptom might occur after a master/subordinate switchover or after a cable is removed and then inserted.
202005251254
· Symptom: The portsecd process is stuck and it cannot process other services after the device reboots.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device reboots when the following conditions exist:
¡ The IMC server does not support the RESTful server-assisted MAC authentication user recovery feature.
¡ The RESTful server-assisted MAC authentication user recovery feature is enabled on the device.
202005130044
· Symptom: The entPhysicalDescr MIB node information for an interface card still exists after the interface card is removed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you display MIB node information after an interface card is removed.
202004160007
· Symptom: When RESTful server-assisted MAC authentication user recovery is configured on an S6520X IRF fabric, some of authenticated dumb terminals cannot reauthenticate to come online after the entire IRF fabric reboots.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist on the S6520X IRF fabric:
¡ The IRF fabric is a leaf device.
¡ A large number of MAC authenticated dumb terminals have been online on the IRF fabric before it reboots.
202112020369
· Symptom: The gRPC server does not generate messages for the LLDP events that occur on the device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the gRPC dial-in mode is enabled for gRPC clients to subscribe to LLDP events on the device.
202112020418
· Symptom: gPRC cannot collect LLDP information.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if sensor paths are configured for gRPC.
202112100200
· Symptom: The memory usage of DBM keeps increasing.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if DHCP users come online after DHCP snooping is enabled.
202112300693
· Symptom: The device generates the following log message:
¡ %Sep 16 09:20:04:133 2021 QX-S5324GT-4X1CLIPC/4/LIPC_STCP_CHECK: -Slot=1; Data
¡ stays in the receive buffer for an overlong time. Owner=ifmgr, VRF=0, local add
¡ ress/port=8/23721, remoteaddress/port=48/14610.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device is in an IRF fabric under stress tests.
202112031013
· Symptom: The device cannot forward multicast traffic through interfaces on the module that receives the traffic.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the module provides member ports for a multislot aggregate interface and the received multicast traffic is forwarded out of other member ports of the aggregate interface.
202112070565
· Symptom: gRPC cannot be enabled, and core files are created as a result.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the grpc enable command is executed.
202112110581
· Symptom: The device drops the ARP packets synchronized by iBGP, and iBGP flapping occurs as a result.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device receives heavy ARP traffic.
202111011647
· Symptom: RADIUS packet source IP configuration does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the source IP address of RADIUS packets is configured in system view while the specified IP address is not configured in the RADIUS scheme.
202112151668
· Symptom: The display drni consistency type1 global command does not display the configuration consistency check result for STP.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if spanning tree is enabled before DRNI is configured.
202112021613
· Symptom: In an MVXLAN network, a spine device forwards only half of the traffic demanded by multicast receivers.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the spine device receives multicast traffic from a multislot aggregate interface.
202112200471
· Symptom: The ssl renegotiation disable command does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the ssl renegotiation disable command is executed.
202112061020
· Symptom: If MAC resources are insufficient, an error occurs when a MAC address is assigned to a Layer 3 interface. When the interface is assigned a MAC address again, the device outputs an incorrect message.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a MAC address is assigned to a Layer 3 interface when MAC resources are insufficient.
202112211353
· Symptom: A DR system is formed by two EVPN VXLAN-configured devices. When a DR member device forwards packets received from a VXLAN tunnel interface out of a DR interface, incorrect VLAN tags are added to the packets.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the l2vpn drni peer-link ac-match-rule vxlan-mapping command is executed on the DR member devices.
202201040031
· Symptom: An IRF member device that performs user authentication reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following operations are performed:
a. Send traffic sourced from 100 different MAC addresses to a subordinate device for MAC authentication.
b. Execute the undo mac-address vlan x command on the master device to delete the MAC address entries of the VLAN where the source MAC addresses belong.
c. Repeatedly restart the peer interface connected to the interface with MAC authentication enabled.
202112131083
· Symptom: A PBR policy cannot match packets on a VSI interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a PBR policy is applied to a VSI interface.
202112110479
· Symptom: In an EVPN VXLAN network, a leaf device cannot ping a spine device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ A microsegment that does not contain members is bound to an interface with ACs configured on the leaf device.
¡ The microsegment uses a PBR policy as a GBP, and the output interface is null.
202112020366
· Symptom: The device fails to forward Layer 2 packets destined for a VRRP virtual MAC address.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a VRRP virtual MAC address is not deleted after VRRP configuration is deleted.
202112020088
· Symptom: MLD snooping entries are synchronized to an IPP.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ Layer 3 multicast is configured on a DR system.
¡ MLD snooping is enabled on one of the DR member devices.
202112020336
· Symptom: An IRF fabric does not issue microsegments to users immediately after it reboots. The microsegments are issued after users come online again.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a master/subordinate switchover occurs when local users are online.
202112220251
· Symptom: Multicast cannot be enabled on a Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if multicast is enabled on a Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface.
202112220439
· Symptom: Multicast traffic forwarding is abnormal in BIDIR-PIM mode.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if BIDIR-PIM is enabled on interfaces after the device issues PIM SSM entries.
202112081824
· Symptom: The device creates MAC address entries for the PVID configured for QinQ on an interface with both QinQ and many-to-one VLAN mapping configured.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if both QinQ and many-to-one VLAN mapping are configured on an interface.
202112081736
· Symptom: The device drops the broadcast packets received on an interface with both QinQ and VLAN mapping configured.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the broadcast packets match only the QinQ configuration.
202112270899
· Symptom: Memory leakage occurs.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the MAC address in an ARP entry changes constantly.
202112090315
· Symptom: A downlink aggregate interface on a leaf device has one selected member port and one unselected member port, and the unselected member port receives massive gratuitous ARP packets. As this condition persists, the network becomes abnormal.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The member ports of the downlink aggregate interface are attached to an IRF master device and an IRF subordinate device, respectively.
¡ The IRF member devices boot with initial configuration.
202112200322
· Symptom: An EVPN DR system forwards traffic incorrectly.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist;
¡ The l2vpn drni peer-link ac-match-rule vxlan-mapping command is executed on the DR member devices.
¡ One DR member device receives gratuitous ARP packets and forwards them over the IPL to the other DR member device.
202112022120
· Symptom: An error occurred in setting up link aggregations during automatic deployment of a VCF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if network cables are replaced when automatic deployment is paused.
202112020363
· Symptom: In an MPLS VPLS network, two endpoints cannot ping each other over their attached PEs.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the mpls ttl propagate vpn command is executed on the PEs.
202112090252
· Symptom: A primary/secondary device switchover occurs when a DR system is stable.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if all interfaces on the primary DR device are shut down and the interfaces are brought up when the device role changes to none.
202112020423
· Symptom: The dhcpc6d process is abnormal, which causes the device to reboot.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the DHCPv6 client feature is configured on the automatically deployed device.
202112220442
· Symptom: An EVPN gateway fails to forward Layer 3 unicast traffic.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the underlay network is an IPv6 network and VPN instances are associated with VSI interfaces.
202112270385
· Symptom: The display vxlan tunnel command does not output VXLAN tunnel information.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device is running a script.
202112271425
· Symptom: The DHCP client attached to a DR interface receives two identical DHCP ACK packets.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if EVPN, DRNI, and DHCP relay are configured in conjunction.
202111250623
· Symptom: An access device attached to an EVPN DR system cannot ping a remote IP address.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The DR member devices create frame match criteria based on VXLAN IDs for the dynamic ACs on the Ethernet aggregate link IPL.
¡ A DR interface on one DR member device is disconnected, and the uplink on the other DR member device is disconnected.
202112141808
· Symptom: An EVPN DR system receives the ARP packets that have been forwarded to a remote device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a DR member device forwards ARP packets over a tunnel.
202112171738
· Symptom: Users fail authentication after the device reboots.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if microsegment authentication is enabled and the running configuration is saved before the device is rebooted.
202112100527
· Symptom: On an EVPN DR system, MAC address entries synchronized from a DR peer are deleted.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a VSI has multiple route targets and the ARP and MAC information for an endpoint moves between a DR interface and a single-homed interface.
202112020434
· Symptom: The MAC address of an aggregate interface changes constantly, which causes 802.1X handshake failure and 802.1X user logoff.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an IRF master/subordinate switchover occurs after aggregate interfaces are configured.
202112022115
· Symptom: The device warns of resource insufficiency when the number of VSIs exceeds half of the upper limit.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the number of VSIs exceeds half the upper limit.
202110110734
· Symptom: IPSG bindings are not deleted completely.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device changes the output interface in an ARP snooping entry after receiving an RARP packet.
· Remarks: This problem is resolved when you install the patch. However, you must execute the process restart name ipcimd slot 1 command to delete the residual IPSG bindings. If the device does not have enough available memory, it might reboot during patch installation.
202111041425
· Symptom: A leaf device cannot reach the external networks.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device fails to forward tunneled packets based on ECMP routes with the same destination network and next hop.
202112020347
· Symptom: The device fails to forward traffic over an EVPN network.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if VSIs, VPN instances, and VSI interfaces are repeatedly deleted and created.
202111290655
· Symptom: The MAC-portal user who comes online first can access the external networks without BYOD authentication.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a BYOD user accesses an IRF subordinate device for authentication.
202108161213
· Symptom: The LLDP process restarts unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an aggregate interface and its member ports have descriptions configured and the lldpLocManAddrEntry MIB node is read.
· Workaround: Do not read the lldpLocManAddrEntry MIB node if an aggregate interface and its member ports have descriptions.
202112020345
· Symptom: In the output from the display power command, the status of a present power module might be absent.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the display power command is executed.
202112020081
· Symptom: Two 100G interfaces are connected to each other. After one interface is shut down, the other interface is still up.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if two 100G interfaces are connected to each other on an IRF fabric and one of the interfaces is shut down.
202112100319
· Symptom: NETCONF fails to obtain information from the DevicePortInfo node.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if NETCONF is used to read the DevicePortInfo node.
Resolved problems in R6515P06
202012150773
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the number of multicast receivers that join a multicast group exceeds the upper limit and the multicast receivers repeatedly perform 802.1X authentication to come online and then go offline.
202012180150
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs with a low probability if the following conditions exists:
¡ The setting of unknown unicast packet filtering causes an array out of bound exception.
¡ On a device with a slot number other than 1, Layer 3 interfaces are configured and the interfaces in up status are assigned to a VLAN by using the port access vlan command.
202012151121
· Symptom: On an AD-campus network, MLD packets are flooded .
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the flooding disable all all-direction command is executed in a VSI after IPv6 addresses are configured on interfaces or IPv6 related features are configured.
202012150852
· Symptom: On an AD-campus network, configuration on leaf nodes gets lost and the leaf nodes are unmanaged.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The devices are brought online by automated VCF fabric deployment.
¡ Spine nodes are upgraded and restarted after leaf nodes are upgraded and restarted.
202012150822
· Symptom: Packet forwarding delay exists on the device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a single-mode fiber is connected to the transceiver module on the device or the Rx signals are unstable.
202012150828
· Symptom: Storm control does not take effect when the device receives traffic that exceeds the threshold.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if storm control is configured on the device and the threshold is set in percentage.
202012150751
· Symptom: The MAD IP address configuration fails to be deployed to member devices in an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if BFD MAD is configured on the IRF fabric.
202012150833
· Symptom: A delay exists when the device displays logs.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you constantly display VSI information or MAC address entries for VSIs and then display logs on the device.
202012150840
· Symptom: Information about a MIB node with OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.11.1.3 obtained through NMS is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following condition exist:
¡ The device is configured to perform an NQA operation.
¡ NMS is used to obtain information about the MIB node with OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.8.3.1.11.1.3.
202012150849
· Symptom: The system generates a large number of core files when an EPS scanner module scans devices in the management network.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when an EPS scanner module scans devices in the management network.
202012150848
· Symptom: In an IRF fabric, multicast group members cannot receive multicast traffic when a master/subordinate switchover is performed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the members join the multicast group through the master device.
202009120190
· Symptom: On the Oasis platform, the topology recalculation function fails to work.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when the Recalculate button is clicked.
202006301536
· Symptom: The RA guard policy applied to a VLAN does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an RA guard policy is configured and applied to a VLAN.
202006301448
· Symptom: Packet filter fails to apply a Layer 2 ACL to the incoming traffic on a port when the table capacity mode is set to 5, the 2304 ingress ACL mode.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when the table capacity mode is set to 2304 ingress ACL mode by using the switch-mode 5 command.
202004271236
· Symptom: In a VXLAN network, the device cannot generate complete SIP session entries.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you view SIP session entries in a VXLAN network.
202010231016
· Symptom: Multicast data packets are lost.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a large number of receivers exist and some receivers leave the original multicast group and join another multicast group.
202008110678
· Symptom: When a 10-Gbps fiber port on the device is connected to a third-party DCI device, the peer port cannot come up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a 10-Gbps fiber port on the device is connected to a third-party DCI device.
202005091477
· Symptom: In a VXLAN network, a MAC address fails to be moved.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if only one or a small number of packets are sent after the MAC address moves to a new interface.
202004170866
· Symptom: The CPU usage is high.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if DRNI and port security are configured.
201803080642
· Symptom: When the device receives a large amount of Layer 3 traffic destined for an IP address of the device, IPv4 and IPv6 SSH/Telnet connections cannot be established.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if SSH/Telnet is enabled on the device and the device receives a large amount of Layer 3 traffic destined for an IP address of the device.
202004010169
· Symptom: Some multicast data packets get lost on a Layer 2 multicast network.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an IGMP snooping-enabled Layer 2 device is configured with more than 1530 simulated hosts for different multicast groups.
201901280489
· Symptom: A tier-2 PEX cannot come online.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist in an IRF 3.1 system:
a. The master device is a multichassis IRF fabric.
b. The tier-1 PEX is an IRF fabric.
c. The tier-2 PEX is an S5560X-EI switch.
d. The parent devices are rebooted to perform a master/subordinate switchover for the master device.
201808240515
· Symptom: The authentication server is configured to issue an authorization user profile that contains the inbound rate limit to MAC authentication users. The MAC authentication users can come online, but the inbound rate limit does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the authentication server is configured to issue an authorization user profile that contains the inbound rate limit to MAC authentication users.
202007010328
· Symptom: When MAC Information is enabled globally, the mac-address information enable added command setting does not take effect on interfaces.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if MAC Information is enabled both globally and on interfaces and the MAC learning limit is set on MAC Information-enabled interfaces.
202006290368
· Symptom: The DHCP snooping module does not synchronize its snooping entry information to the IP source guard module after a user comes online.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when DHCP snooping is enabled and a user comes online.
202006231151
· Symptom: OSPF sends trap messages. This implementation is not compliant with RFC.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when the OSPF device receives Type-5 LSAs containing larger router IDs than the local device and the same prefixes as existing Type-5 LSAs.
202006230467
· Symptom: Idle MAC authentication users are not logged off after MAC authentication offline detection is enabled.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if MAC authentication offline detection is enabled for users on an aggregate interface and the offline detect timer is set.
202006111432
· Symptom: The uplink port of a secondary VLAN cannot receive packets after the ports in another secondary VLAN are isolated.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations have been performed:
a. Add a downlink port to a secondary VLAN associated with a primary VLAN, and add another port to a secondary VLAN associated with another primary VLAN.
b. Configure port isolation at Layer 2 in each secondary VLAN.
c. Cancel port isolation at Layer 2 for one secondary VLAN.
202006101032
· Symptom: The device cannot assign users to the 802.1X Auth-Fail VSI on an interface after the users fail 802.1X authentication on the interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if EAD assistant is enabled on the device.
202005120257
· Symptom: In a VXLAN network with Layer 2 multicast configured, when an AC receives a PIM hello message, the local and remote multicast members each receive two PIM hello messages.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when an AC in a VXLAN network with Layer 2 multicast configured receives a PIM hello message.
202005120193
· Symptom: The license for unified wired and wireless access control on the device does not take effect after the device software version is upgraded to F6510.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when the following conditions are met:
a. The license for unified wired and wireless access control is installed on a device running F6510.
b. The software version is reverted to F6509L01.
c. The software version is upgraded to F6510.
202005110902
· Symptom: The EXP field in an MPLS packet was lost after the packet was label swapped.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if MPLS is configured and the device performs a label swap operation for MPLS packets.
202005110834
·
· Symptom: The switch does not support critical VLANs or critical VSIs for wireless access after loading the unified wired and wireless access control package.
· Condition: This symptom might occur after the switch loads the unified wired and wireless access control package.
202005060378
· Symptom: Port flapping occurs because the device cannot detect the transceiver module of the port.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you quickly remove and then insert the transceiver module for the port.
202004281103
· Symptom: When both MAC authentication and Web authentication are configured, the device cannot trigger Web authentication for a user after the user fails MAC authentication.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the user fails MAC authentication because the authentication domain does not exist.
202004231113
· Symptom: ACL resources are not sufficient for the system to deploy all IP source guard binding entries.
· Condition: This symptom occurs in the DHCPv6+SLAAC application scenario where IP source guard binding entries are to be deployed.
202004221424
· Symptom: It takes time for the DHCP and DHCPv6 clients to obtain IP addresses.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if many-to-one VLAN mappings are configured on the downlink interface of the device.
202004210011
· Symptom: A DHCPv6 client cannot obtain an IPv6 address.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if many-to-one VLAN mapping is configured on the downlink port connecting to the DHCPv6 client.
202004150339
· Symptom: On a DR system, one DR member device cannot ping a device that is attached to the other DR member device through a single-homed AC.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if IPv6 addresses of the same subnet are assigned to VLAN interfaces on the DR member devices.
202002180815
· Symptom: Dynamically learned MAC address entries are not removed from a downlink interface on a leaf device when MAC authentication is enabled on the downlink interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the MAC address entries have been learned on the downlink interface before MAC authentication is enabled and the leaf device belongs to an AD-Campus network.
202002170544
· Symptom: An interface on an LSWM2ZSP8P interface card might fail to come up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an LSWM2ZSP8P interface card is installed in the device and uses Hisense 25-G optical fibers.
201910310324
· Symptom: In an EVPN network, an IRF fabric VTEP receives duplicate packets from a multihomed site within 20 seconds after the IRF fabric starts up.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a master/subordinate switchover is performed when the IRF fabric is forwarding traffic to the multihomed site.
201910220598
· Symptom: The hash conflict entries are incorrectly recorded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if traffic is received at a low speed.
201910180019
· Symptom: When a guest user is configured on the device and a description is configured for the user, the guest user description fails to be modified through importing a configuration file.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ A guest user is configured on the device.
¡ A description is configured for the user.
¡ The guest user description is modified through importing a configuration file.
201907150221
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric configured with local port mirroring, the rate of mirrored packets is different from the rate of original packets.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if multirate cards are installed into the IRF fabric and the source port and the monitor port reside on different slots.
201907030509
· Symptom: On a multihomed EVPN VXLAN or EVPN VPLS network, the remote VTEP or PE is a two-chassis IRF fabric. After a master/subordinate switchover, the IRF fabric cannot forward known Layer 2 unicast traffic from an AC on the IRF subordinate device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ One port on each IRF member device connects to a tester, and both of the ports are added to a static aggregation group and the aggregate interface is used as the AC.
¡ After the master/subordinate switchover, the underlay link for Layer 3 EVPN intercommunication connects to the IRF master device.
201906141063
· Symptom: The IRF fabric splits.
· Condition: This symptom might occur after the master device is rebooted.
201901280485
· Symptom: A tier-1 cascade port flaps after a master/subordinate switchover is performed in the parent fabric.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if S10500 switches are used as parent devices and the parent fabric connects a large number of PEXs.
201901240569
· Symptom: The master device is restarted again during the restart process and the IRF fabric might split after the master device restarts.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ A large number of MAC authentication users and 802.1X users come online.
¡ A large number of global ACLs are configured.
Resolved problems in R6510P02
202010150768
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an ACL contains multiple port range rules and multiple class-behavior associations using the ACL are bulk issued.
202010160355
· Symptom: When you operate a device, the device gets stuck or its IRF fabric splits.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
A port that is not up on the device is connected to a Lenovo server of a specific model through a transceiver module.
The connected port on the server side continuously sends instable optical signals.
202009180912
· Symptom: Traffic sent out of a local AC interface carries two layers of VLAN tags.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if traffic is sent from an AC interface to another local AC interface and the AC interface is configured to match frames that are tagged with the specified outer 802.1Q VLAN tag.
202010281117
· Symptom: A VM cannot come online.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a switch is attached to the device as a VM and the device receives ARP packets from the VM.
202010150794
· Symptom: The CPU usage of the SOFT task is high.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a transceiver module is inserted into the device after the device is started.
202010220299
· Symptom: Pass-through RA packets cannot be transparently transmitted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device acts as an access device and receives pass-through RA packets.
202010281129
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly repeatedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the controller fails to deploy the automation configuration and the device cannot recognize the device.csv file in a VCF fabric network.
Resolved problems in R6510
201907220915
· Symptom: Memory leak might occur with a low probability to the DRMACD module.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device has been running with full load for a long period of time in a DRNI network.
201909300697
· Symptom: The HA batch backup process takes more than 10 minutes after an IRF fabric merge caused by shutting down and then bringing up the IRF physical interfaces on the master device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
a. The IRF fabric acts as a VTEP in an EVPN+ES network, and the master device has a lower priority than the subordinate device.
b. The IRF fabric processes a large number of multicast join messages and multicast data messages.
202006220117
· Symptom: After a DELL server is restarted, the switch's interface connected to the DELL server cannot come up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the DELL server is connected to the switch through a 10-Gbps fiber port, the fiber port comes up, and then the DELL server is restarted.
Resolved problems in F6510
202004130571
· Symptom: The secure MAC address entries on an interface are not aged as they should be and the entry hit flag bit in the driver is always 1.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you enable port security globally and configure the following features on the interface:
¡ Set the port security mode to autolearn.
¡ Convert sticky MAC addresses into dynamic secure MAC addresses.
¡ Configure inactivity aging for the secure MAC addresses.
202004141417
· Symptom: When a GRE tunnel source interface is flapping, the ecmpEnable bit of the interface's eport is incorrectly set. The ecmpEnable bit error causes traffic forwarding failure.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the GRE tunnel interface is used as the output interface of an IPv6 route.
202003201480
· Symptom: The mirrored packets cannot be sent out of the reflector port.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if Layer 2 remote port mirroring in reflector port mode is configured and a fiber port with a transceiver module or cable installed is configured as the reflector port.
·
202003170155
· Symptom: NetStream does not record any traffic statistics or export the statistics to the NetStream server.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you repeatedly execute the session-based netstream enable and undo session-based netstream enable command sequence.
202004131488
· Symptom: Forwarding errors occur on a VXLAN network.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a VM migrates to a VTEP with the ipv6 nd mode uni command executed.
202004210449
· Symptom: The Ethernet OAM remote loopback or bridging configuration does not take effect on an Ethernet interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if Ethernet OAM remote loopback or bridging is enabled after the Ethernet interface is switched from a Layer 3 port to a Layer 2 port.
202003270783
· Symptom: The device does not respond when you try to cancel the reflector port configuration.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if Layer 2 remote port mirroring in reflector port mode is configured and the reflector port configuration is cancelled when traffic exists on the reflector port.
202004031244
· Symptom: The DSCP value of mirrored packets is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure the source IP address, destination IP address, and DSCP value to be encapsulated in mirrored packets when configuring the action of mirroring traffic to an interface.
202003310402
· Symptom: The system fails to run either of the ipv6 nd detection enable and ipv6 nd suppression enable commands when underlying resources are insufficient.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when underlying resources are insufficient and either of the ipv6 nd detection enable and ipv6 nd suppression enable commands are executed.
202003300535
· Symptom: When an IRF physical interface is shut down by using the shutdown command on one member device, its peer IRF physical interface on the neighboring member device does not go down accordingly. Because of this issue, the IRF fabric is operating incorrectly.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the IRF physical interface is shut down in the following conditions:
¡ Two member devices use 100-GE ports as IRF physical interfaces, and loops exist on the IRF fabric.
¡ A broadcast storm has occurred after the member devices receive traffic with the same source MAC addresses.
202004080920
· Symptom: All packets are counted as error packets when TWAMP is used to measure two-way metrics.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an interface is assigned to an aggregation group but PTP is enabled neither globally nor on this interface.
202004081302
· Symptom: 6to4 tunnels and ISATAP tunnels cannot forward traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you create 6to4 tunnels and ISATAP tunnels after you delete a GRE tunnel.
202004080251
· Symptom: The DHCP clients cannot get online through the device downstream port where a many-to-one VLAN mapping is configured.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when a many-to-one VLAN mapping is configured on the downstream port of the device.
202004140379
· Symptom: Exception occurs in the stamgr process and a core file is produced after 802.1X users come online.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a large number of APs and clients come online.
202004011195
· Symptom: An S6520X-SG-XX IRF fabric splits after it receives traffic in multiple queues on the ingress port.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The traffic ingress and egress ports are distributed on two member devices.
¡ Rate limiting is configured in the outbound direction of the ingress port.
¡ WRED is configured to rate limit traffic of eight queues.
201901220680
· Symptom: The information center does not receive a notification about RADIUS server recovery after the RADIUS server recovers.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when SNMP notifications for RADIUS are enabled by using the snmp-agent trap enable radius command.
201905280859
· Symptom: After an IRF fabric splits, a member device of an IRF fabric can display the member device information of another IRF fabric, and the interface expansion module on the member device is unstable.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations have been performed:
a. Use three switches to form a daisy-chain IRF fabric through interfaces on interface expansion modules.
b. Remove and insert an interface expansion module to cause an IRF fabric split.
201908140722
· Symptom: The maximum shared-area ratio in the display buffer queue command output is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the display buffer queue command is executed after the burst mode enable command is executed.
202003121045
· Symptom: The message that "fail to add openflow arp entry" is displayed during the startup process of a subordinate device. After the subordinate device starts up, OpenFlow rolls back the ARP entry and the OpenFlow ARP entry is deleted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the outgoing interface (AC interface) of an ARP entry is on the subordinate device in a basic IPoE network and the subordinate device is rebooted after the ARP entry is successfully issued.
201812240120
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric formed by two or more S6520X-30QC-HI switches, the CLI responds slowly if a command requires inter-member switch communication.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an IRF fabric is formed by two or more S6520X-30QC-HI switches
201901220819
· Symptom: The IRF fabric cannot be accessed from the subordinate device, and the master device cannot forward packets correctly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations have been performed:
a. Use multiple switches to form a ring IRF fabric.
b. Shut down IRF physical interfaces on a member device and activate the IRF port configuration to convert the IRF fabric to a daisy-chain topology.
201908121021
· Symptom: Red packets are still dropped though an aggregate CAR action is configured to permit red packets to pass through.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an aggregate CAR action is configured to permit red packets to pass through.
202002170426
· Symptom: IPv6 multicast forwarding failed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the uplink interface of the device connecting to a client is a Layer 3 Ethernet interface and configured with IPv6 PIM in an IPv6 Layer 3 multicast network.
201909251035
· Symptom: The keepalive and IPL links flap.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the STP topology changes in a DRNI network that is forwarding traffic.
201812120778
· Symptom: In an S6520X-30QC-HI IRF fabric, the communication between the master device and the subordinate devices is rather slow.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the master device and the subordinate devices communicate with each other.
Resolved problems in F6509L01
201905160120
· Symptom: Traffic is interrupted for about 15 seconds when a member device in a DR system is rebooted.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a member device is rebooted in a DR system that acts as a gateway.
201910210749
· Symptom: After a master/subordinate switchover, an IRF fabric cannot be re-formed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs after a master/subordinate switchover.
201909160347
· Symptom: Packets match only the ACL in a PBR policy, but not IPSG bindings.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if both PBR and IP source guard are configured on an interface.
202003120622
· Symptom: The private VLANs cannot communicate with each other.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist on an IRF fabric:
¡ Configure a multi-device aggregate interface as a downlink interface.
¡ In each secondary VLAN, enable Layer 2 isolation for ports.
¡ Shut down and bring up the aggregate interface.
202003120319
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the authorization ACL is modified for online 802.1X users.
202003100892
· Symptom: The packet filtering configuration on a VLAN interface might change from taking effect globally to taking interface on an interface with a low probability.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a VLAN interface is configured with packet filtering and the device repeatedly rolls back the configuration.
202003120433
· Symptom: Ports are isolated at Layer 2 in another VLAN.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if Layer 2 isolation is configured for a secondary VLAN and ports in the secondary VLAN permit another VLAN.
201910310234
· Symptom: Transient multicast traffic loss occurs on the EVPN VTEPs at a multihomed site when the DFs for ACs change.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the DFs for ACs change at a multihomed site.
201902020121
· Symptom: In an IRF 3.1 system, the PE CSP connection between a PEX and the parent fabric flaps after a cascade member port of the master device in the parent fabric is shut down and then brought up.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the PEX connects to the parent fabric through two links.
Resolved problems in F6508
201909111019
· Symptom: Packets in the Layer 3 channel might be dropped, which causes Layer 3 forwarding failure.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the rate limit value is low for the Layer 3 channel in an IRF 3.1 system.
· Workaround: This problem has been resolved.
201910291091
· Symptom: An ACL fails to be issued in the driver and does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a subnet is configured in an object group and then an ACL referencing the object group is issued.
· Workaround: None.
201811160304
· Symptom: Traffic cannot be forwarded from the local end to the remote end.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ A 10-Gbps interface on an S6520X switch has a 10-Gbps transceiver module installed and is connected to the remote end through a single fiber.
¡ The local end acts as the transmitter, and the remote end acts as the receiver.
¡ Interfaces at both ends are forcibly brought up by using the port up-mode command.
· Workaround: None.
201812250331
· Symptom: In an EVPN network, the whole IRF fabric reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an IRF fabric formed by S6520X switches acts as a leaf device, and the undo vxlan ip-forwarding command is executed and VSIs and tunnels are configured on the IRF fabric.
· Workaround: None.
201910310312
· Symptom: In a multihoming EVPN network, the ARP packets received by a BDF from an AC is forwarded back to the ES through the DF.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ARP flood suppression is configured on a VSI.
· Workaround: None.
201910310420
· Symptom: After an ARP attack entry ages out, the corresponding blackhole MAC address entry cannot be deleted from the driver.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ An AC interface configured with a static AC matching untagged packets detects an ARP attack.
¡ The link type of the AC interface is switched between access and trunk with different PVIDs.
¡ After the attack stops, the generated ARP attack entry ages out.
201807270579
· Symptom: When you execute the issu run switchover command after upgrading a subordinate IRF member device, the system prompts that the operation failed and the software cannot be upgraded successfully.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ISSU for multichassis IRF fabrics is not supported.
201811120193
· Symptom: In an EVPN network, the MAC address entries displayed by using the display l2vpn mac-address and display evpn route mac local commands are inconsistent.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. An aggregate interface is configured with multiple ACs. The aggregate interface receives traffic continuously for a period of time. The ACs learn MAC address entries.
b. Use the display l2vpn mac-address and display evpn route mac local commands to display the learned MAC address entries.
201810160530
· Symptom: When the configured MAC learning limit is reached and the device is disabled from forwarding unknown frames after the MAC learning limit is reached, some unknown frames can still be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the MAC learning limit is configured and the device is disabled from forwarding unknown frames after the MAC learning limit is reached.
201812030539
· Symptom: When BFD MAD is configured, packets destined for UDP port 6784 or 4784 match a wrong ACL and thus are sent to the CPU.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the switch configured with BFD MAD receives packets with destination UDP port 6784 or 4784.
201906200802
· Symptom: Traffic cannot be forwarded correctly between member switches of an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the IRF fabric receives single-tagged packets after the TPID value in CVLAN tags is modified on it.
201812240093
· Symptom: WRR queuing does not take effect on an interface when used together with rate limiting.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the qos lr and qos wrr weight commands are used together on an interface:
201906260861
· Symptom: Two switches enabled with automatic configuration cannot form an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ IRF physical interfaces are configured on only one of the switches during automatic configuration.
¡ The switches send LLDP packets to each other.
201905110281
· Symptom: On an interface, a QoS policy is applied to the outbound direction to change the DSCP value of the outgoing packets, and port mirroring is configured to mirror the outgoing packets. The DSCP value of mirrored packets is not changed.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a QoS policy is applied to the outbound direction to change the DSCP value of the outgoing packets, and port mirroring is configured to mirror the outgoing packets on an interface.
201907180670
· Symptom: The management Ethernet interface of the switch is displayed incorrectly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the panel of the S6520X-54HC-HI or S6520X-54HC-EI switch is opened in IMC.
201907180912
· Symptom: The IRF links forward a large number of protocol packets.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if multiple devices form a ring-topology IRF fabric and the IRF physical interface bound to an IRF port on a member device is shut down.
201910120550
· Symptom: The traffic is not evenly load shared among Selected member ports of an aggregation group.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the default load sharing mode or destination port-based load sharing mode is used and the aggregate interface receives packets with varying destination port numbers.
201905310107
· Symptom: The status of IRF physical interfaces on a subordinate IRF member device is displayed incorrectly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if link flapping protection is configured on IRF physical interfaces on a subordinate IRF member device.
201909240598
· Symptom: When a DR member device role changes to None, the keepalive link cannot come up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the keepalive link is shut down and then brought up when the IPP is down in a DRNI network.
201910220923
· Symptom: A user cannot obtain an IP address after successfully passing MAC or 802.1X authentication and coming online.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when a user comes online after passing MAC or 802.1X authentication.
201910310404
· Symptom: A 100-GE interface might fail to come up after the using twenty-fivegige and using hundredgige commands are repeatedly executed in sequence.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following tasks are repeatedly performed in sequence:
a. Execute the using twenty-fivegige command on the 100-GE interface.
b. Execute the using hundredgige command on any of the 25-GE breakout interface.
201907300448
· Symptom: In a DRNI network, residual DR system MAC address entries exist on the peer DR member device after MAC address entries are deleted on the local DR member device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if MAC address entries are deleted after a large number of MAC address are learned.
201910310389
· Symptom: An access node in a VCF fabric fails to come online during automated VCF fabric deployment.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The switch is a leaf node attached to the access node by an aggregate link that is formed by two physical links.
¡ The access node sends DHCP requests in VLAN 1, and the leaf node does not forward the DHCP requests to the upstream spine node.
201910310344
· Symptom: The data link layer state of a shutdown 100-GE interface changes to up when the speed or duplex command is executed on the interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the speed or duplex command is executed on the shutdown 100-GE interface.
201910310162
· Symptom: Traffic forwarding errors occur on an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the IRF fabric adds outer VLAN tags to double-tagged packets based on a QoS policy.
201908120562
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, errors occur when traffic received on one IRF member switch is forwarded through another IRF member device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The TPID value in CVLAN tags is set to a value other than 0x8100 on an interface.
¡ The interface permits VLAN 1.
¡ The interface receives traffic with an outermost TPID value the same as the set one.
201906140873
· Symptom: The status of the authorization ACL for online MAC portal authentication users displayed on the device is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if multiple online MAC portal authentication users exist on an interface and a rule unsupported by the device is added to the authorization ACL of the users.
201905050083
· Symptom: During a radar ping, probe packets are discarded on the source device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the controller uses 0-0-1 as the source MAC address of probe packets.
201911070038
· Symptom: ARP broadcast storms occur and the DR keepalive link of a DR system flaps.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the destination and source IP addresses of DR keepalive packets are the IP addresses of VLAN interfaces and a Layer 2 loop exists between a DR member device and other devices.
201911060007
· Symptom: The actual packet rate is slightly lower than the rate limit in traffic policing settings.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if traffic policing is configured by using the MQC approach.
· Workaround: Set the rate limit to a value slightly greater than the expected value. For example, to limit the rate to 10 Mbps, set the rate limit to 11 Mbps.
201911050693
· Symptom: Packets on an aggregate interface are not distributed among Selected member ports of the aggregation group.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the aggregate interface is configured to distribute packets based on source MAC addresses and the aggregate interface receives packets from different MAC addresses.
201910310425
· Symptom: On a VXLAN network, a VXLAN IP gateway forwards an extra copy of packets to the VXLAN tunnel of a VXLAN.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The flooding disable all all-direction command is executed on the VSI of the IP gateway and then this configuration is removed.
¡ The VXLAN IP gateway receives ARP requests.
201910310423
· Symptom: In an IRF fabric, non-voice traffic is forwarded instead of being dropped after the voice VLAN security mode is disabled and then enabled.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Disable and then enable MAC address learning globally.
b. Disable and then enable the voice VLAN security mode.
201910310421
· Symptom: The switch incorrectly adds a layer of VLAN tag with VLAN ID 0 when forwarding double-tagged packets.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the switch forwards the packets out of an AC interface.
201910310416
· Symptom: In an IRF 3.1 system, PEXs learn MAC addresses into the incorrect VLAN from broadcast packets with different source MAC addresses.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ S6520X switches act as parent devices and S5560X/S5130S switches act as PEXs.
¡ Each PEX is connected to both parent devices.
201910310410
· Symptom: Some of the 25-GE breakout interfaces split from a 100-GE interface cannot come up after the switch is rebooted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the four 25-GE breakout interfaces are connected to four interfaces on an card on an S5560X switch.
201910310408
· Symptom: In an IRF fabric, the MAC address entries on the master and subordinate devices are inconsistent.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure a MAC address requiring authentication as a blackhole MAC address and then reboot the master device.
201910310407
· Symptom: A fiber port cannot be shut down after it is forcibly brought up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the fiber port is on an LSW2SP2PB card.
201910310406
· Symptom: In an IRF 3.1 system, the voice VLAN aging timer setting on PEXs does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if S6520X switches act as parent devices.
· Workaround: Do not add interfaces on PEXs to the voice VLAN.
201812110109
· Symptom: An IRF fabric splits, and a member device reboots after a VSI is disabled and enabled repeatedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ A large number of multicast VXLAN packets with different source MAC addresses exist, and these packets match the AC interface associated with the VSI.
¡ The AC interface associated with the VSI is an aggregate interface.
201812070359
· Symptom: When both WRR queuing and outbound rate limiting are configured on an interface, WRR queuing produces inaccurate scheduling results.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if both WRR queuing and outbound rate limiting are configured on an interface.
201812070356
· Symptom: When both SP queuing and outbound rate limiting are configured on an interface, SP queuing does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if both SP queuing and outbound rate limiting are configured on an interface.
201808140106
· Symptom: If an access port on a PEX in an IRF3.1 system is moved to another VLAN, the MAC address entry for the original VLAN is not deleted. As a result, traffic forwarding becomes abnormal.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an access port on a PEX in an IRF3.1 system is moved to another VLAN.
201801110964
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, errors occur when traffic with VLAN type 8011 received on one IRF member switch is forwarded through another IRF member device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The TPID value in CVLAN tags is set to a value other than 0x8100 on an interface.
¡ The interface permits VLAN 1.
¡ The interface receives traffic with an outermost TPID value the same as the set one.
Resolved problems in R6308
201906120349
· Symptom: In an IRF 3.1 system, it takes an online tier-1 PEX a long period of time to register its ports after its cascade ports are shut down and then brought up.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the cascade ports of a tier-1 PEX are shut down and then brought up.
201905220422
· Symptom: A two-chassis IRF fabric fails to reunite because of login failure.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The IRF fabric splits because the KDB process is too long.
¡ The member switch in Recovery state is rebooted for the IRF fabric to reunite.
201901280472
· Symptom: The aggregation member ports of an upstream port connecting a tier-2 PEX to a tier-1 PEX cannot receive LLDP packets and therefore cannot become Selected ports.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ S10500 switches are used as parent devices and the parent fabric connects a large number of PEXs.
¡ Tier-1 PEXs are IRF fabrics, and the aggregation member ports of the upstream port on a tier-1 PEX connect only to the master device in the parent fabric.
¡ The aggregation member ports of the upstream port on a tier-2 PEX connect to the master device and subordinate device in the tier-1 IRF fabric.
201901180341
· Symptom: In a VXLAN network, the physical interface where the AC resides processes packets incorrectly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure an outer VLAN ID match criterion for the physical interface and assign the physical interface to the specified outer VLAN ID.
201907100846
· Symptom: The BGP process fails and then restarts after the NMS performs an SNMP get-next operation to retrieve the value of a BGP node following the specified node.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the information about the specified node is not fully issued during the get-next operation.
201907050093
· Symptom: The device uses global PBR for packet forwarding, which causes the intercommunication between the underlay and overlay networks.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if no service chain is configured on the next hop tunnel interface in the global PBR or the next hop in the global PBR is a local Ethernet service instance.
201907100603
· Symptom: On a multihomed EVPN VXLAN or EVPN VPLS network, the remote VTEP or PE is a two-chassis IRF fabric. 20 seconds after the IRF fabric reboots from a master/subordinate switchover, redundant VTEPs receive two copies of known Layer 2 unicast traffic from an AC on the IRF subordinate device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ One port on each IRF member device connects to a tester, and both of the ports are added to a static aggregation group and the aggregate interface is used as the AC.
¡ After the master/subordinate switchover, the underlay link for Layer 3 EVPN intercommunication connects to the IRF master device.
201907180544
· Symptom: When the device uses the dial-out mode to push BGP instance information to the collector, the device can push only information about the default instance, and the pushed information is incomplete.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device uses the dial-out node to push BGP instance information to the collector.
201907180643
· Symptom: The gRPC port number cannot be modified through configuration rollback.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if gRPC is enabled.
201907180794
· Symptom: All broadcast or multicast packets are blocked and cannot be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the broadcast or multicast suppression threshold is set to 0.
201907190299
· Symptom: The default settings cannot be restored for an interface with the port up-mode command executed, and the interface is still up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Execute the port up-mode command on an interface without a transceiver module installed on an LSW2SP2PB or LSW2SP4PB interface card.
b. Execute the undo port up-mode or default command on the interface.
201907191023
· Symptom: After a 100-GE interface is split and then the breakout interfaces are combined, the 100-GE interface cannot come up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are repeated multiple times until the message containing DRV_PORT_802dot3AP_config_set err appears:
a. Split a 100-GE interface with a QSFP28 non-1-to-4 cable installed.
b. Combine the breakout interfaces.
201907181059
· Symptom: Some 25-GE breakout interfaces cannot come up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Split a 100-GE interface into four 25-GE breakout interfaces.
b. Save the configuration and reboot the device.
201907190685
· Symptom: A memory leak of 2K bytes occurs on the device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist when DRNI is configured:
¡ Traffic forwarded between DR member devices triggers MAC address synchronization, or MAC address synchronization is performed every 5 minutes.
¡ The MAC address entries for the specific VLAN fail to be found on the local device.
Resolved problems in F6306
201906261206
· Symptom: The switch reboots because of a dead loop when an OAP module is rebooted.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a user logs in to an OAP module and reboots it at the CLI.
201906260394
· Symptom: The switch is stuck in endless reboot loop after the management Ethernet interface is connected in an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when the management Ethernet interface is connected in an IRF fabric and the management Ethernet receives and sends packets.
201906181001
· Symptom: The displayed state of an interface is not its actual state.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following operations are performed:
a. Execute both the port up-mode and link-delay down commands on the down interface.
b. Execute the default or undo port up-mode command on the interface.
201906170848
· Symptom: Residual ACLs exist on the parent fabric of an IRF 3.1 system.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following operations are performed:
a. Configure voice VLANs on the parent fabric and PEXs in an IRF 3.1 system until ACL resources are exhausted.
b. Delete voice VLANs from some interfaces.
201904150122
· Symptom: On a self-looped switch, a loop disappears after a period of time.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following operations are performed:
a. Enable loop detection on Switch A, and disable loop detection and spanning tree on Switch B.
b. Connect two interfaces to each other on each switch, and connect Switch A to Switch B by using non-self-looped interfaces.
201904150318
· Symptom: An S6520X-54HC-HI switch reboots unexpectedly after certain operations are performed.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following operations are performed:
a. Connect a 100-GE fiber port of the switch to an LSWM2ZSP8P interface module through a breakout cable.
b. Split the 100-GE fiber port into four 25-GE breakout interfaces.
201903290821
· Symptom: Traffic cannot be forwarded correctly between member switches of an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the IRF fabric receives single-tagged packets after the TPID value in CVLAN tags is modified on it.
201901280478
· Symptom: The aggregation member ports of an upstream port connecting a tier-2 PEX to a tier-1 PEX cannot receive LLDP packets and therefore cannot become Selected ports.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ S10500 switches are used as parent devices and the parent fabric connects a large number of PEXs.
¡ Tier-1 PEXs are IRF fabrics, and the aggregation member ports of the upstream port on a tier-1 PEX connect to the master device and subordinate device in the parent fabric.
¡ The aggregation member ports of the upstream port on a tier-2 PEX connect to the master device and subordinate device in the tier-1 IRF fabric.
201811220408
· Symptom: VCFC failed to automatically deploy PBR configuration to the device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the automatically deployed PBR configuration contains ACLs with VPNs.
201812240203
· Symptom: On a card, an interface is configured with the qinq ethernet-type customer-tag command. When the interface receives packets with an SVLAN tag TPID identical to the CVLAN tag TPID specified by using the command, the switch cannot correctly forward the packets through another card.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an interface configured with the qinq ethernet-type customer-tag command receives packets with an SVLAN tag TPID identical to the CVLAN tag TPID specified by using this command.
Resolved problems in F6305
201903110648
· Symptom: When VPN instances are created and deleted repeatedly on an IRF fabric that provides the Layer 3 forwarding service and multicast forwarding service, the master reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if VPN instances are created and deleted repeatedly on an IRF fabric that provides the Layer 3 forwarding service and multicast forwarding service.
201812180528
· Symptom: The management Ethernet interface on the switch is up, but it is not up and cannot be operated on IMC.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the management Ethernet interface is operated through IMC.
201901290587
· Symptom: The jumboframe enable command does not take effect on a 100G interface on the front panel if certain operations are performed on that interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following operations are performed on a 100G interface on the front panel:
a. Connect it to a peer interface by using a 100G cable.
b. Execute the jumboframe enable command.
c. Shut down and then bring up the peer interface, or re-install the interface module where the peer interface resides.
201812190695
· Symptom: After Layer 3 aggregate subinterfaces are configured, the MAC address learning rate slows down on the main aggregate interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if subinterfaces are created on a Layer 3 aggregate interface, and that interface forwards traffic constantly.
201901190109
· Symptom: A port blocked by RRPP permits loop detection packets.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ Loop detection is enabled globally.
¡ Loop detection packets are transmitted on a per-VLAN basis, and the switch ignores the blocked state of the outgoing interface for loop detection packets.
201901240143
· Symptom: The IP addresses in the output from the debug qacl show slot x chip x verbose x acl-type x sip x command start with the lowest-order octet.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the debug qacl show slot x chip x verbose x acl-type x sip x command is executed.
201812240778
· Symptom: A 100G interface receives CRC error packets or jumbo frames constantly. When the traffic stops, the number of aborts packets on that interface becomes 0.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a 100G interface receives CRC error packets or jumbo frames constantly.
201903130614
· Symptom: Devices cannot ping each other if the qinq ethernet-type service-tag command is executed on the interfaces that interconnect them.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the qinq ethernet-type service-tag command is executed on the interfaces that interconnect two devices.
201903140140
· Symptom: The gRPC process restarts unexpectedly one day after the gRPC dial-out feature is configured.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the gRPC dial-out feature is configured with the gRPC server disabled.
201903210010
· Symptom: On the LSWM2ZQP2P module, an interface installed with a 40-G cable cannot come up.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if one of the following conditions exists:
¡ The interface is shut down and then brought up.
¡ The interface is connected to an interface on the front panel, and the cable is first installed in the front panel interface.
201903160011
· Symptom: An interface cannot learn MAC addresses after it is removed from a service loopback group.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an interface is removed from a service loopback group.
201903200176
· Symptom: A PBR policy that uses only the path ID as the service chain match criterion cannot match packets that have the path-index field.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the service chain match criterion is set to path ID for a PBR policy.
201903080517
· Symptom: The SYS LED does not indicate the result of configuration file loading.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the switch does not have a configuration file and loads a configuration file from a USB drive.
201903160176
· Symptom: An interface in a service loopback group cannot come up after its transceiver module is reinstalled.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the transceiver module is reinstalled for an interface in a service loopback group.
201812240048
· Symptom: A VXLAN VTEP cannot correctly forward IGMP packets.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
a. IGMP is enabled and the flooding disable command is executed on a VSI.
b. An AC of the VSI receives IGMP queries.
201905130487
· Symptom: The configuration on a port changes to the default configuration.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if no configuration file is specified for the port and an AP or IP phone is connected to the member.
201906120769
· Symptom: The switch obtains a different IP address through DHCP than the last time.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations have been performed:
a. Use the autoconfiguration process.
b. Delete the configuration and reboot the switch.
201904290057
· Symptom: A user cannot normally access web pages.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if multiple portal users are authenticated at the same time or multiple first packets of HTTP/HTTPS packets are forwarded.
Resolved problems in F1502
201805230145
· Symptom: An IRF fabric splits and the master member device is rebooted unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if heterogeneous IRF loops are formed in a specific network environment.
201812120294
· Symptom: Tunneled public network traffic received from a GRE tunnel cannot be forwarded after de-encapsulation if the incoming interface is a Layer 3 interface and the GRE tunnel uses private IP addresses for encapsulation.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a Layer 3 interface receives tunneled public network traffic forwarded through a GRE tunnel that uses private IP addresses for encapsulation.
201901290301
· Symptom: An IRF fabric cannot forward Layer 3 traffic correctly if it splits and then reunites.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the IRF bridge MAC address changes.
201805110166
· Symptom: The interfaces on the LSW2ZSP2P module cannot come up if configured with the port up-mode command.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the port up-mode command is executed on interfaces of the LSW2ZSP2P module.
201808230435
· Symptom: An interface enabled with SP queuing forwards low-priority traffic.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an interface enabled with SP queuing receives traffic with different priorities.
201901180848
· Symptom: In a VCF fabric deployed on a campus network, when an access node reboots, the aggregate interface connected to the access node is automatically deleted from a leaf node.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
a. The links between the leaf node and the access node are aggregated automatically.
b. The director issues configuration to the downlink aggregate interface of the leaf node.
c. The access node connected to the downlink aggregate interface reboots.
201812210690
· Symptom: When AAA authentication and password control are enabled, Telnet or SSH login takes about 20 seconds.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if AAA authentication and password control are enabled.
201901280503
· Symptom: An IRF fabric formed by S5560X-30F-EI switches splits twice before it becomes stable.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if abnormal IPC packets are transmitted because the switches do not filter these packets.
201901180043
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric configured through automated deployment, a port not configured with link aggregation joins a link aggregation group after a master/subordinate switchover.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a master/subordinate switchover occurs on an IRF fabric configured through automated deployment.
·
Resolved problems in R1113
201811090456
· Symptom: QoS WRR scheduling and SP scheduling are inaccurate.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ Rate limiting in the outbound direction and QoS WRR queueing are configured on an interface.
¡ Rate limiting in the outbound direction and QoS SP queueing are configured on an interface.
· Workaround: None.
201810290425
· Symptom: The maximum number of IGMP multicast groups decreases.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if both the multicast incoming interface and the multicast outgoing interface are Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces, and then the outgoing interface is changed to a VLAN interface.
201812070260
· Symptom: IMC displays incorrect information about the four 25-GE breakout interfaces split from a 100-GE interface on the LSWM2ZSP2P module.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if two 100-GE interfaces on the LSWM2ZSP2P module are split into 25-GE breakout interfaces.
201812100295
· Symptom: When the switch forwards unfragmentable IPv4 packets larger than the MTU of the outgoing interface, it sends ICMP error messages sourced from 0.0.0.0 or 127.0.0.1 instead of the IP address of the Layer 3 management interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the switch forwards unfragmentable IPv4 packets larger than the MTU of the outgoing interface.
201901240507
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, the MAC addresses obtained by using SNMP are inconsistent with those displayed by using the display mac-address command.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist on an IRF fabric:
¡ No multichassis aggregation group is configured.
¡ MAC address synchronization is disabled.
¡ No inter-chassis traffic exists.
201901090479
· Symptom: The switch reboots unexpectedly and cannot be accessed if certain transceiver modules are installed on a large number of interfaces.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if certain transceiver modules have frequent RxLOS signal changes after being installed on some interfaces.
201812250549
· Symptom: A PC Telnets to Device A, and Device A Telnets to Device B. If the Telnet connection of the PC is closed when Device A and Device B are communicating with each other, Device A has residual Telnet processes, high CPU usage, and service interruption.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ A PC Telnets to Device A, and Device A Telnets to Device B.
¡ The Telnet connection of the PC is closed when Device A and Device B are communicating with each other.
Resolved problems in R1112
201711270359
· Symptom: IPv6 packets passing a GRE over IPv4 tunnel are not correctly forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a GRE over IPv4 tunnel is established, and IPv6 packets pass the tunnel.
201808200560
· Symptom: The memory usage of the device is too high, and alarms are generated.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The number of DHCPv6 snooping entries that an interface can learn is not limited.
¡ DHCPv6 clients apply for a large number of IPv6 addresses from the DHCPv6 server through the DHCPv6 snooping device.
201809030214
· Symptom: When sFlow-related commands are executed on a device, the CLI is stuck.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if sFlow is enabled on multiple interfaces and the device continuously receives traffic, which will be sampled by sFlow.
201809260190
· Symptom: The qinq enable command configuration on an interface is lost.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ISSU is used to upgrade/downgrade the software or reboot the device after an interface is configured with both QinQ and VLAN mapping.
201811270062
· Symptom: The device does not generate IPSG entries for 802.1X users.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if 802.1X user come online and obtain IP addresses through DHCPv6.
201811230729
· Symptom: An access node is automated and connected to a leaf node through two uplinks and the two links are automatically aggregated. However, the topology shows that there are multiple links between the access node and the leaf node, and there is no aggregate interface in the interface group of each node.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an access node is automated and connected to a leaf node through two uplinks and the two links are automatically aggregated.
201811220103
· Symptom: ARP packets cannot be sent to the CPU.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an OpenFlow entry that sends ARP packets to the CPU is deployed to the device and then the corresponding VLAN is configured.
201811190549
· Symptom: IPv6 or MPLS packets of an aggregate interface cannot be matched.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if OpenFlow deploys a flow entry that matches the incoming traffic of an aggregate interface and uses a physical interface as the outgoing interface.
201811160063
· Symptom: An interface cannot join a voice VLAN again after leaving the voice VLAN.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ On an IRF fabric, enable LLDP on an interface on the subordinate device and assign the interface to a voice VLAN. Connect the interface to a voice device that supports LLDP or CDP.
¡ Establish or disconnect the LLDP neighbor relationship on the subordinate device.
201811160037
· Symptom: Some clients cannot access the network.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if 802.1X is enabled on an aggregate interface, 1000 users come online in a VLAN, and each user obtains IP addresses through DHCP.
201811120127
· Symptom: The memory leaks.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if DHCP/DHCPv6 flood attack protection is repeatedly enabled and disabled and a member device is repeatedly rebooted on an IRF fabric.
201811100117
· Symptom: The service chain that forwards traffic is not the one configured by the user.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the apply service-chain command is used to set the service chain information when applying a PBR policy to the outbound direction of a VXLAN tunnel interface.
201811100091
· Symptom: OpenFlow issues an IPv6 flow entry unexpectedly when issuing an IPv4 flow entry.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if OpenFlow issues an IPv4 flow entry that matches the Ethernet type 0x0800.
201811070218
· Symptom: DHCP flood attack protection errors are printed if a master/subordinate switchover is performed for an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a master/subordinate switchover is performed for an IRF fabric.
201809300526
· Symptom: The buildruns and prompt messages for the proxy-nd enable and local-proxy-nd enable commands are different on the master device and subordinate device. After a master/subordinate switchover is performed for the IRF fabric, the configurations of the two commands are lost.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the proxy-nd enable and local-proxy-nd enable commands are executed on an IRF fabric and then a master/subordinate switchover is performed for the IRF fabric.
201812100822
· Symptom: Layer 3 traffic of a Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface is falsely forwarded by using a route entry of the VPN instance bound to the main interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a Layer 3 Ethernet interface and its subinterface are bound to different VPN instances.
201811230526
· Symptom: When port security is enabled, the switch halts after the display port-security command is executed until the Ctrl+C key combination is used.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
a. Secure MAC addresses are configured, the maximum number of secure MAC addresses allowed on an interface is set to 1, and the intrusion protection mode is set to disableport-temporarily on the interface.
b. A user PC comes online on the interface, and the switch learns the MAC address of the PC. Then an LLDP-capable PC comes online on the same interface.
201812140651
· Symptom: If all IRF physical interfaces on an IRF member device are provided by the extension interface modules in the same slot, the IRF physical interfaces might go down and then come up in 30 seconds, which causes unwanted IRF fabric split and reunion.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if all IRF physical interfaces on an IRF member device are provided by the extension interface modules in the same slot.
· Workaround: Use extension interface modules in different slots to provide IRF physical interfaces on an IRF member device, or use both the interfaces on the front panel and the interfaces on extension interface modules as IRF physical interfaces.
201812180280
· Symptom: It takes the switch 40 to 70 seconds to learn a MAC address when Layer 3 aggregate interfaces are performing Layer 3 forwarding.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the switch learns MAC addresses when Layer 3 aggregate interfaces are performing Layer 3 forwarding.
Resolved problems in R1111
201810090296
· Symptom: The following problems occur:
¡ When a portal user performs authentication, the portal authentication page does not open on the user's endpoint.
¡ After a portal user comes online and then clicks Log out on the portal page, the user can still access the network.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Multiple MAC-portal users first perform authentication to come online in the BYOD VSI. Then, a user performs second authentication to come online in the service VSI. Then, the user in the service VSI goes offline and then comes online through one of the following operations:
- The user goes offline and then comes online when the transparent authentication status of the user expires and becomes invalid on the Director server.
- The user clicks Log out on the authentication success page to go offline, and then comes online.
b. All users go offline and then come online, and users in the BYOD VSI first come online.
201809300345
· Symptom: When the device is running, the CLI might be stuck and you cannot enter commands at the CLI.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ACLs containing counting rules are repeatedly added and deleted.
201810150207
· Symptom: A portal user fails to come online, and ACL resources remain.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the ACL resources of the device are insufficient when a portal user is being assigned an ACL after coming online.
201806040553
· Symptom: The NMS fails to synchronize the ACL and VLAN information through SNMP.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the NMS synchronizes the ACL and VLAN information through SNMP.
201808200580
· Symptom: The port index is calculated incorrectly. The port does not match the port issued on the device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if sFlow is issued by IMC.
201809180685
· Symptom: When an aggregate interface to which ACLs are issued by IP source guard is deleted, ACLs rules are not correctly deleted, and some ACLs remain. ACLs issued by IP source guard do not meet the specifications.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an aggregate interface is configured with multiple ACs and the IP source guard feature, which will issue ACLs to the aggregate interface.
201804020003
· Symptom: When the MTU is set to 64000 for a tunnel interface, the value that actually takes effect is 1480.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the MTU is set to 64000 for a tunnel interface.
201803140144
· Symptom: Traffic storms exist on IRF physical interfaces transiently.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a member device of a ring-topology IRF fabric receives unknown unicast or multicast packets and the device is rebooted at the same time.
201805280088
· Symptom: Though the member priority of a device with more interfaces is high, it cannot become the master device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if S6520X switches of the same series but with different number of interfaces form an IRF fabric.
201808210429
· Symptom: After the priority trust mode is set to DSCP and a DSCP-DSCP priority mapping table is applied to an interface, the interface fails to modify the DSCP value of packets.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the priority trust mode is set to DSCP and a DSCP-DSCP priority mapping table is applied to an interface.
201807240090
· Symptom: The device cannot internally synchronize the learned MAC address entries.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the port-security free-vlan command is executed in interface view to configure the port security free VLANs.
201803140626
· Symptom: An aggregate interface learns MAC address entries incorrectly. As a result, the aggregate interface forwards traffic improperly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the whole device is rebooted when the aggregate interface has configuration.
201811080922
· Symptom: The device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the qos sp command is executed on an interface of a subcard.
201810220659
· Symptom: An interface bound to a VPN cannot be successfully pinged from a directly connected device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the interface is bound to a VPN by using the ip binding vpn-instance vpn-instance-name command.
Resolved problems in R1110P06
201808100515
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, two copies of each BUM packet of VXLAN are forwarded on the IRF physical interfaces.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the IRF fabric acts as a VTEP and the IRF fabric has a member device with slot number 1.
201808060514
· Symptom: In an EVPN network, BGP and tunnel states flap.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an aggregation group is configured with a large number of ACs and IP source guard configurations, and the default command is executed on the corresponding aggregate interface to restore the default settings.
201808160633
· Symptom: The STP status of ports on an STP-enabled device is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if three devices form a ring network, one device has STP disabled and TC snooping enabled and the other two devices has STP enabled.
Resolved problems in R1110P05
201805070687
· Symptom: The memory leaks.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the configuration file contains QinQ-related configuration and configuration rollback is repeatedly performed for the device.
201808240158
· Symptom: Packets matching a deny node of a routing policy are not forwarded by routes.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a routing policy is configured with a deny node.
201808100627
· Symptom: A user might fail to log in through Web authentication.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ An interface has both 802.1X authentication and Web authentication enabled.
¡ A user logs in through Web authentication, and sends ARP packets to the device during the login process.
201808070475
· Symptom: When a user uses packets that carry VLAN tags not permitted by the authentication interface to perform MAC authentication, the user can successfully come online mistakenly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the authentication interface is an aggregate interface.
201807250096
· Symptom: On a distributed VXLAN gateway network, a DHCP or DHCPv6 client cannot obtain an IP or IPv6 address from the DHCP or DHCPv6 server.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the VTEP where the distributed VXLAN gateway acting as the DHCP or DHCPv6 server resides is different from the VTEP to which the DHCP or DHCPv6 client is attached.
Resolved problems in R1110
201804120630
· Symptom: Some member devices fail to download the upgrade file from the FTP server. The display smartmc upgrade status command output shows that the upgrade status of some member devices is always Downloading.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the smartmc upgrade boot-loader command is executed on the commander to upgrade the startup software for multiple member devices at the same time in a SmartMC network.
201804220003
· Symptom: On a multichassis IRF fabric of the daisy-chain topology, broadcast storms occur on the IRF physical interfaces.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The IRF physical interfaces of an IRF member device are connected to common service interfaces of another IRF member device.
¡ There is an IRF physical interface with the internal port number as 0 (the value in the Port column in the output from the debug port mapping command in probe view).
201804230140
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, if a member port on an IRF member device joins or leaves a multichassis aggregation group, the ports with the same number on the other member devices become invalid.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if member ports join or leave a multichassis aggregation group on an IRF fabric.
201804230274
· Symptom: MAC address entries remain in the lower layer.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if multiple multiport unicast MAC address entries are configured and then deleted.
201712260679
· Symptom: Packets cannot be forwarded through short-mask ECMP routes.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if short-mask static ECMP routes are first issued and then long-mask static ECMP routes are issued and these ECMP routes overlap.
201808060061
· Symptom: Port isolation does not take effect on packets forwarded through the CPU.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if interfaces are assigned to a port isolation group.
201808140149
· Symptom: When ARP attack protection is enabled, the rate of ARP packets sent to the CPU is limited to 50 pps.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the rate of packets sent to the CPU is 490 pps, which triggers ARP attack protection.
Resolved problems in E1109
201802270713
· Symptom: The device might reboot in an endless loop.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device is configured as the DHCP server and some packets are forwarded through the CPU.
201802060662
· Symptom: When a 1000-Mbps transceiver module is plugged in a 10-GE interface, the interface cannot forward traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the 10-GE interface with a 1000-Mbps transceiver module plugged receives Layer 3 packets longer than 86 bytes.
201802080178
· Symptom: When a 40G cable with product code LSWM1QSTK2 (produced by AMPHENO) is installed in an interface, the device cannot start.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a QSFP+ interface on the front panel has a 40G cable with product code LSWM1QSTK2 (produced by AMPHENO) installed and the device is started.
201711270652
· Symptom: Layer 3 packets with the destination unreachable do not match the default route. Instead, these packets are sent to the CPU for software forwarding.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Configure the default route 0.0.0.0/0.
b. Configure the ip unreachables enable command.
201711100161
· Symptom: The master IRF member device reboots because the memory is exhausted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if interactions exist between the IRF member devices (for example, a large number of configurations are repeatedly added and deleted for a long period of time), which cause the master and subordinate member devices to continuously perform synchronization.
201711040204
· Symptom: On a distributed gateway, the vxlan vni 1 command is configured in VLAN view. The system prompts that the configuration succeeds. However, the vxlan vni 1 command configuration does not exist in VLAN view.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed when there are a large number of ACs and VLANs (for example, 3000 ACs and 500 VLANs):
¡ Associate a VLAN with the specified VXLAN.
¡ Execute the undo vlan command.
201711030393
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, the ARP flood suppression entry configuration is not the same on the master and subordinate member devices.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the arp suppression enable and vxlan commands are executed for many times.
201711270365
· Symptom: In a VXLAN network, traffic cannot be forwarded if the VXLAN tunnel interface and the corresponding AC interface are on the same interface module.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The VXLAN tunnel interface and AC interface are on the same interface module.
¡ VXLAN packets from the tunnel are received, with the outgoing interface as the AC interface on the same interface module.
¡ The AC interface has a 1000_BASE_T_AN_SFP transceiver module installed.
201711290205
· Symptom: When the ACL used in step c is deleted, the ACL resource is not released.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Create an advanced IPv4 or IPv6 ACL.
b. Use the operator lt, gt, neq, or range in an ACL rule to specify multiple port numbers to match packets.
c. Use the ACL created in step a for packet filtering in the outbound direction of an interface.
201711290337
· Symptom: In a VXLAN network, AC resources are not released.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a large number of ACs are configured on an aggregate interface and then the aggregate interface is deleted.
201711240609
· Symptom: In a multiport ARP network, the device connected to multiple ports cannot communicate with a device configured with multiport ARP.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a multiport ARP network is configured..
Resolved problems in E1108
First release.
Troubleshooting resources
To obtain troubleshooting resources for the product:
1. Access Technical Documents at http://www.h3c.com/en/Technical_Documents.
2. Select the device category and model.
3. Select the Maintain or Maintenance menu.
Related documentation
· H3C S6520X-EI & S6520X-HI Switch Series Installation Quick Start
· H3C S6520X-EI & S6520X-HI Switch Series Installation Guide
· H3C PSR250-12A & PSR250-12A1 Power Modules User Manual
· H3C LSWM1FANSCE & LSWM1FANSCBE Fan Trays User Guide
· H3C LSWM2QP2P Interface Card User Manual
· H3C LSWM2SP8PM & LSWM2SP8P Interface Cards User Manual
· H3C LSWM4SP8PM Interface Card User Manual
· H3C S6520X-EI & S6520X-HI Switch Series Configuration Guides
· H3C S6520X-EI & S6520X-HI Switch Series Command References
· H3C LSWM2SP2PM Interface Card User Manual
· H3C LSPM6FWD Card Manual
· H3C LSWM2ZQP2P Interface Card User Manual
· H3C LSWM2ZSP8P Interface Card User Manual
Technical support
To obtain technical assistance, contact H3C by using one of the following methods:
· Email:
h3cts@h3c.com (countries and regions except Hong Kong, China)
service_hk@h3c.com (Hong Kong, China)
· Technical support hotline number. To obtain your local technical support hotline number, go to the H3C Service Hotlines website: https://www.h3c.com/en/Support/Online_Help/Service_Hotlines/
To access documentation, go to the H3C website at http://www.h3c.com/en/.
Please refer to H3C S6520X-EI & S6520X-HI Switch Series Installation Guide.
Feature | S6520X-30QC-EI S6520X-30QC-HI | S6520X-54QC-EI S6520X-54QC-HI | S6520X-30HC-EI S6520X-30HC-HI | S6520X-54HC-EI S6520X-54HC-HI |
Link aggregation | · Aggregation of 10-GE ports · Aggregation of 40-GE ports · Static link aggregation · Dynamic link aggregation · Inter-device aggregation · A maximum of 128 inter-device aggregation groups · A maximum of 32 ports for each aggregation group | · Aggregation of 10-GE ports · Aggregation of 100-GE ports · Static link aggregation · Dynamic link aggregation · Inter-device aggregation · A maximum of 128 inter-device aggregation groups · A maximum of 32 ports for each aggregation group | ||
Flow control | · IEEE 802.3x flow control | |||
Jumbo Frame | · Supports maximum frame size of 10000 | |||
MAC address table | · 128K MAC addresses | · 256K MAC addresses | · 128K MAC addresses | · 256K MAC addresses |
· 1K static MAC addresses · Blackhole MAC addresses · MAC address learning limit on a port | ||||
VLAN | · A maximum of 4094 port-based VLANs · QinQ, selective QinQ, VLAN mapping · Voice VLANs · Protocol-based VLANs · MAC-based VLANs | |||
ARP | ARP uni mode not configured: up to 7.5K - 8 ARP uni mode configured: up to 64K - 1 | ARP uni mode not configured: up to 23K - 24 ARP uni mode configured: up to 128K - 1 | ARP uni mode not configured: up to 7.5K - 8 ARP uni mode configured: up to 64K - 1 | ARP uni mode not configured: up to 23K - 24 ARP uni mode configured: up to 128K - 1 |
· A maximum of 2K static ARP entries · Gratuitous ARP · ARP attack detection based on DHCP snooping entries, 802.1X entries, and static IPSG bindings · ARP rate limit | ||||
ND | · 7.5K entries | · 23K entries | · 7.5K entries | · 23K entries |
· 2K static entries · ND Snooping | ||||
VLAN virtual interface | 1K | |||
DHCP | · DHCP client · DHCP snooping · DHCP relay · DHCP server · DHCP Option82 | |||
DNS | · Static DNS · Dynamic DNS · IPv4 and IPv6 DNS | |||
unicast route | · IPv4 and IPv6 static routes · RIP/RIPng · OSPF/OSPFv3 · BGP/IPv6 BGP · ISIS/ISISv6 | |||
Multicast | · IGMP Snooping · MLD Snooping · Multicast VLAN · PIM SM · PIM DM · MSDP · BIDIR-PIM | |||
Broadcast/multicast/unicast storm control | · Storm control based on port rate percentage · PPS-based storm control · Bps-based storm control | |||
MSTP | · STP/RSTP/MSTP protocol · 64 Spanning Tree instances · STP Root Guard · BPDU Guard | |||
SmartLink | · 32 | |||
RRPP | · RRPP | |||
QoS/ACL | · Remarking of 802.1p and DSCP priorities · Packet filtering at L2 (Layer 2) through L4 (Layer 4) · Eight output queues for each port · SP/WRR/SP+WRR queue scheduling algorithms · WRED · Port-based rate limiting · Flow-based redirection · Time range | |||
Mirroring | · Local port mirroring · A maximum number of 7 mirroring groups · Layer 2 remote port mirroring | |||
Security | · Hierarchical management and password protection of users · AAA authentication · RADIUS authentication · HWTACACS · SSH 2.0 · Port isolation · 802.1X · Port security · User Profile · MAC-address-based authentication · IP Source Guard · HTTPS · PKI · EAD | |||
802.1X | · Up to 2K users · Port-based and MAC address-based authentication · Guest VLAN · Trunk port authentication · Dynamic 802.1X-based ACL/VLAN assignment | |||
Open Flow | · 16 Instances · 1500 flow entries (issued by using ACL) · MAC-IP | |||
Loading and upgrading | · Loading and upgrading through XModem protocol · Loading and upgrading through FTP · Loading and upgrading through the trivial file transfer protocol (TFTP) | |||
Management | · Configuration at the command line interface · Remote configuration through Telnet · Configuration through Console port · Simple network management protocol (SNMP) · Remote Monitoring(RMON) · IMC NMS · Web network management (later version) · System log · Hierarchical alarms · IRF · NTP · Power supply alarm function · Fan and temperature alarms | |||
Maintenance | · Debugging information output · Ping and Tracert · Remote maintenance through Telnet · NQA · 802.1ag · 802.3ah · DLDP · Virtual Cable Test | |||
Appendix B Fixed security vulnerabilities
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6652P05
CVE-2023-2650
Issue summary: Processing some specially crafted ASN.1 object identifiers or data containing them may be very slow. Impact summary: Applications that use OBJ_obj2txt() directly, or use any of the OpenSSL subsystems OCSP, PKCS7/SMIME, CMS, CMP/CRMF or TS with no message size limit may experience notable to very long delays when processing those messages, which may lead to a Denial of Service. An OBJECT IDENTIFIER is composed of a series of numbers - sub-identifiers - most of which have no size limit. OBJ_obj2txt() may be used to translate an ASN.1 OBJECT IDENTIFIER given in DER encoding form (using the OpenSSL type ASN1_OBJECT) to its canonical numeric text form, which are the sub-identifiers of the OBJECT IDENTIFIER in decimal form, separated by periods. When one of the sub-identifiers in the OBJECT IDENTIFIER is very large (these are sizes that are seen as absurdly large, taking up tens or hundreds of KiBs), the translation to a decimal number in text may take a very long time. The time complexity is O(n^2) with 'n' being the size of the sub-identifiers in bytes (*). With OpenSSL 3.0, support to fetch cryptographic algorithms using names / identifiers in string form was introduced. This includes using OBJECT IDENTIFIERs in canonical numeric text form as identifiers for fetching algorithms. Such OBJECT IDENTIFIERs may be received through the ASN.1 structure AlgorithmIdentifier, which is commonly used in multiple protocols to specify what cryptographic algorithm should be used to sign or verify, encrypt or decrypt, or digest passed data. Applications that call OBJ_obj2txt() directly with untrusted data are affected, with any version of OpenSSL. If the use is for the mere purpose of display, the severity is considered low. In OpenSSL 3.0 and newer, this affects the subsystems OCSP, PKCS7/SMIME, CMS, CMP/CRMF or TS. It also impacts anything that processes X.509 certificates, including simple things like verifying its signature. The impact on TLS is relatively low, because all versions of OpenSSL have a 100KiB limit on the peer's certificate chain. Additionally, this only impacts clients, or servers that have explicitly enabled client authentication. In OpenSSL 1.1.1 and 1.0.2, this only affects displaying diverse objects, such as X.509 certificates. This is assumed to not happen in such a way that it would cause a Denial of Service, so these versions are considered not affected by this issue in such a way that it would be cause for concern, and the severity is therefore considered low.CVE-2022-32221
When doing HTTP(S) transfers, libcurl might erroneously use the read callback (`CURLOPT_READFUNCTION`) to ask for data to send, even when the `CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS` option has been set, if the same handle previously was used to issue a `PUT` request which used that callback. This flaw may surprise the application and cause it to misbehave and either send off the wrong data or use memory after free or similar in the subsequent `POST` request. The problem exists in the logic for a reused handle when it is changed from a PUT to a POST.
CVE-2023-2953
A vulnerability was found in openldap. This security flaw causes a null pointer dereference in ber_memalloc_x() function.
CVE-2023-0465
Applications that use a non-default option when verifying certificates may be vulnerable to an attack from a malicious CA to circumvent certain checks. Invalid certificate policies in leaf certificates are silently ignored by OpenSSL and other certificate policy checks are skipped for that certificate. A malicious CA could use this to deliberately assert invalid certificate policies in order to circumvent policy checking on the certificate altogether. Policy processing is disabled by default but can be enabled by passing the ‘-policy’ argument to the command line utilities or by calling the `X509_VERIFY_PARAM_set1_policies()' function.
CVE-2023-24329
An issue in the urllib.parse component of Python before 3.11.4 allows attackers to bypass blocklisting methods by supplying a URL that starts with blank characters.
CVE-2023-0286
There is a type confusion vulnerability relating to X.400 address processing inside an X.509 GeneralName. X.400 addresses were parsed as an ASN1_STRING but the public structure definition for GENERAL_NAME incorrectly specified the type of the x400Address field as ASN1_TYPE. This field is subsequently interpreted by the OpenSSL function GENERAL_NAME_cmp as an ASN1_TYPE rather than an ASN1_STRING. When CRL checking is enabled (i.e. the application sets the X509_V_FLAG_CRL_CHECK flag), this vulnerability may allow an attacker to pass arbitrary pointers to a memcmp call, enabling them to read memory contents or enact a denial of service. In most cases, the attack requires the attacker to provide both the certificate chain and CRL, neither of which need to have a valid signature. If the attacker only controls one of these inputs, the other input must already contain an X.400 address as a CRL distribution point, which is uncommon. As such, this vulnerability is most likely to only affect applications which have implemented their own functionality for retrieving CRLs over a network.
CVE-2023-0464
A security vulnerability has been identified in all supported versions of OpenSSL related to the verification of X.509 certificate chains that include policy constraints. Attackers may be able to exploit this vulnerability by creating a malicious certificate chain that triggers exponential use of computational resources, leading to a denial-of-service (DoS) attack on affected systems. Policy processing is disabled by default but can be enabled by passing the `-policy' argument to the command line utilities or by calling the `X509_VERIFY_PARAM_set1_policies()' function.
CVE-2023-0215
The public API function BIO_new_NDEF is a helper function used for streaming ASN.1 data via a BIO. It is primarily used internally to OpenSSL to support the SMIME, CMS and PKCS7 streaming capabilities, but may also be called directly by end user applications. The function receives a BIO from the caller, prepends a new BIO_f_asn1 filter BIO onto the front of it to form a BIO chain, and then returns the new head of the BIO chain to the caller. Under certain conditions, for example if a CMS recipient public key is invalid, the new filter BIO is freed and the function returns a NULL result indicating a failure. However, in this case, the BIO chain is not properly cleaned up and the BIO passed by the caller still retains internal pointers to the previously freed filter BIO. If the caller then goes on to call BIO_pop() on the BIO then a use-after-free will occur. This will most likely result in a crash. This scenario occurs directly in the internal function B64_write_ASN1() which may cause BIO_new_NDEF() to be called and will subsequently call BIO_pop() on the BIO. This internal function is in turn called by the public API functions PEM_write_bio_ASN1_stream, PEM_write_bio_CMS_stream, PEM_write_bio_PKCS7_stream, SMIME_write_ASN1, SMIME_write_CMS and SMIME_write_PKCS7. Other public API functions that may be impacted by this include i2d_ASN1_bio_stream, BIO_new_CMS, BIO_new_PKCS7, i2d_CMS_bio_stream and i2d_PKCS7_bio_stream. The OpenSSL cms and smime command line applications are similarly affected.
CVE-2022-4304
A timing based side channel exists in the OpenSSL RSA Decryption implementation which could be sufficient to recover a plaintext across a network in a Bleichenbacher style attack. To achieve a successful decryption an attacker would have to be able to send a very large number of trial messages for decryption. The vulnerability affects all RSA padding modes: PKCS#1 v1.5, RSA-OEAP and RSASVE. For example, in a TLS connection, RSA is commonly used by a client to send an encrypted pre-master secret to the server. An attacker that had observed a genuine connection between a client and a server could use this flaw to send trial messages to the server and record the time taken to process them. After a sufficiently large number of messages the attacker could recover the pre-master secret used for the original connection and thus be able to decrypt the application data sent over that connection.
CVE-2023-28321
An improper certificate validation vulnerability exists in curl <v8.1.0 in the way it supports matching of wildcard patterns when listed as "Subject Alternative Name" in TLS server certificates. curl can be built to use its own name matching function for TLS rather than one provided by a TLS library. This private wildcard matching function would match IDN (International Domain Name) hosts incorrectly and could as a result accept patterns that otherwise should mismatch. IDN hostnames are converted to puny code before used for certificate checks. Puny coded names always start with `xn--` and should not be allowed to pattern match, but the wildcard check in curl could still check for `x*`, which would match even though the IDN name most likely contained nothing even resembling an `x`.
CVE-2023-28322
An information disclosure vulnerability exists in curl <v8.1.0 when doing HTTP(S) transfers, libcurl might erroneously use the read callback (`CURLOPT_READFUNCTION`) to ask for data to send, even when the `CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS` option has been set, if the same handle previously wasused to issue a `PUT` request which used that callback. This flaw may surprise the application and cause it to misbehave and either send off the wrong data or use memory after free or similar in the second transfer. The problem exists in the logic for a reused handle when it is (expected to be) changed from a PUT to a POST.A vulnerability was found in curl.
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6652P02
CVE-2021-3753
A race problem was seen in the vt_k_ioctl in drivers/tty/vt/vt_ioctl.c in the Linux kernel, which may cause an out of bounds read in vt as the write access to vc_mode is not protected by lock-in vt_ioctl (KDSETMDE). The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality.
CVE-2021-3739
A NULL pointer dereference flaw was found in the btrfs_rm_device function in fs/btrfs/volumes.c in the Linux Kernel, where triggering the bug requires ‘CAP_SYS_ADMIN’. This flaw allows a local attacker to crash the system or leak kernel internal information. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability.
CVE-2021-45868
In the Linux kernel before 5.15.3, fs/quota/quota_tree.c does not validate the block number in the quota tree (on disk). This can, for example, lead to a kernel/locking/rwsem.c use-after-free if there is a corrupted quota file.
CVE-2022-1011
A flaw use after free in the Linux kernel FUSE filesystem was found in the way user triggers write(). A local user could use this flaw to get some unauthorized access to some data from the FUSE filesystem and as result potentially privilege escalation too.
CVE-2022-0854
A memory leak flaw was found in the Linux kernel’s DMA subsystem, in the way a user calls DMA_FROM_DEVICE. This flaw allows a local user to read random memory from the kernel space.
CVE-2022-0492
A vulnerability was found in the Linux kernel’s cgroup_release_agent_write in the kernel/cgroup/cgroup-v1.c function. This flaw, under certain circumstances, allows the use of the cgroups v1 release_agent feature to escalate privileges and bypass the namespace isolation unexpectedly.
CVE-2021-4002
A memory leak flaw in the Linux kernel's hugetlbfs memory usage was found in the way the user maps some regions of memory twice using shmget() which are aligned to PUD alignment with the fault of some of the memory pages. A local user could use this flaw to get unauthorized access to some data.
CVE-2022-25375
An issue was discovered in drivers/usb/gadget/function/rndis.c in the Linux kernel before 5.16.10. The RNDIS USB gadget lacks validation of the size of the RNDIS_MSG_SET command. Attackers can obtain sensitive information from kernel memory.
CVE-2020-7469
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r367402, 11.4-STABLE before r368202, 12.2-RELEASE before p1, 12.1-RELEASE before p11 and 11.4-RELEASE before p5 the handler for a routing option caches a pointer into the packet buffer holding the ICMPv6 message. However, when processing subsequent options the packet buffer may be freed, rendering the cached pointer invalid. The network stack may later dereference the pointer, potentially triggering a use-after-free.
CVE-2021-22924
libcurl keeps previously used connections in a connection pool for subsequenttransfers to reuse, if one of them matches the setup.Due to errors in the logic, the config matching function did not take 'issuercert' into account and it compared the involved paths *case insensitively*,which could lead to libcurl reusing wrong connections.File paths are, or can be, case sensitive on many systems but not all, and caneven vary depending on used file systems.The comparison also didn't include the 'issuer cert' which a transfer can setto qualify how to verify the server certificate.
CVE-2021-3753
A race problem was seen in the vt_k_ioctl in drivers/tty/vt/vt_ioctl.c in the Linux kernel, which may cause an out of bounds read in vt as the write access to vc_mode is not protected by lock-in vt_ioctl (KDSETMDE). The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality.
CVE-2021-3739
A NULL pointer dereference flaw was found in the btrfs_rm_device function in fs/btrfs/volumes.c in the Linux Kernel, where triggering the bug requires ‘CAP_SYS_ADMIN’. This flaw allows a local attacker to crash the system or leak kernel internal information. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability.
CVE-2021-45868
In the Linux kernel before 5.15.3, fs/quota/quota_tree.c does not validate the block number in the quota tree (on disk). This can, for example, lead to a kernel/locking/rwsem.c use-after-free if there is a corrupted quota file.
CVE-2022-1011
A flaw use after free in the Linux kernel FUSE filesystem was found in the way user triggers write(). A local user could use this flaw to get some unauthorized access to some data from the FUSE filesystem and as result potentially privilege escalation too.
CVE-2022-0854
A memory leak flaw was found in the Linux kernel’s DMA subsystem, in the way a user calls DMA_FROM_DEVICE. This flaw allows a local user to read random memory from the kernel space.
CVE-2022-0492
A vulnerability was found in the Linux kernel’s cgroup_release_agent_write in the kernel/cgroup/cgroup-v1.c function. This flaw, under certain circumstances, allows the use of the cgroups v1 release_agent feature to escalate privileges and bypass the namespace isolation unexpectedly.
CVE-2021-4002
A memory leak flaw in the Linux kernel's hugetlbfs memory usage was found in the way the user maps some regions of memory twice using shmget() which are aligned to PUD alignment with the fault of some of the memory pages. A local user could use this flaw to get unauthorized access to some data.
CVE-2022-25375
An issue was discovered in drivers/usb/gadget/function/rndis.c in the Linux kernel before 5.16.10. The RNDIS USB gadget lacks validation of the size of the RNDIS_MSG_SET command. Attackers can obtain sensitive information from kernel memory.
CVE-2020-7469
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r367402, 11.4-STABLE before r368202, 12.2-RELEASE before p1, 12.1-RELEASE before p11 and 11.4-RELEASE before p5 the handler for a routing option caches a pointer into the packet buffer holding the ICMPv6 message. However, when processing subsequent options the packet buffer may be freed, rendering the cached pointer invalid. The network stack may later dereference the pointer, potentially triggering a use-after-free.
CVE-2020-25577
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r368250, 11.4-STABLE before r368253, 12.2-RELEASE before p1, 12.1-RELEASE before p11 and 11.4-RELEASE before p5 rtsold(8) does not verify that the RDNSS option does not extend past the end of the received packet before processing its contents. While the kernel currently ignores such malformed packets, it passes them to userspace programs. Any programs expecting the kernel to do validation may be vulnerable to an overflow.
CVE-2020-8284
A malicious server can use the FTP PASV response to trick curl 7.73.0 and earlier into connecting back to a given IP address and port and this way potentially make curl extract information about services that are otherwise private and not disclosed for example doing port scanning and service banner extractions.
CVE-2020-8285
Curl 7.21.0 to and including 7.73.0 is vulnerable to uncontrolled recursion due to a stack overflow issue in FTP wildcard match parsing.
CVE-2021-22924
"libcurl keeps previously used connections in a connection pool for subsequenttransfers to reuse, if one of them matches the setup.Due to errors in the logic, the config matching function did not take 'issuercert' into account and it compared the involved paths *case insensitively*,which could lead to libcurl reusing wrong connections.File paths are, or can be, case sensitive on many systems but not all, and caneven vary depending on used file systems.The comparison also didn't include the 'issuer cert' which a transfer can setto qualify how to verify the server certificate."
CVE-2021-22925
curl supports the `-t` command line option, known as `CURLOPT_TELNETOPTIONS`in libcurl. This rarely used option is used to send variable=content pairs toTELNET servers.Due to flaw in the option parser for sending `NEW_ENV` variables, libcurlcould be made to pass on uninitialized data from a stack based buffer to theserver. Therefore potentially revealing sensitive internal information to theserver using a clear-text network protocol.This could happen because curl did not call and use sscanf() correctly whenparsing the string provided by the application.
CVE-2022-39028
Telnetd in GNU Inetutils through 2.3, MIT krb5-appl through 1.0.3, and derivative works has a NULL pointer dereference via 0xff 0xf7 or 0xff 0xf8. In a typical installation, the telnetd application would crash but the telnet service would remain available through inetd. However, if the telnetd application has many crashes within a short time interval, the telnet service would become unavailable after inetd logs a "telnet/tcp server failing (looping), service terminated" error. NOTE: MIT krb5-appl is not supported upstream but is shipped by a few Linux distributions. The affected code was removed from the supported MIT Kerberos 5 (aka krb5) product many years ago, at version 1.8.
CVE-2021-29629
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245765-bec0d2c9c841, 12.2-STABLE before r369859, 11.4-STABLE before r369866, 13.0-RELEASE before p1, 12.2-RELEASE before p7, and 11.4-RELEASE before p10, missing message validation in libradius(3) could allow malicious clients or servers to trigger denial of service in vulnerable servers or clients respectively.
CVE-2021-29628
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245764-876ffe28796c, 12.2-STABLE before r369857, 13.0-RELEASE before p1, and 12.2-RELEASE before p7, a system call triggering a fault could cause SMAP protections to be disabled for the duration of the system call. This weakness could be combined with other kernel bugs to craft an exploit.
CVE-2021-29626
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245117, 12.2-STABLE before r369551, 11.4-STABLE before r369559, 13.0-RC5 before p1, 12.2-RELEASE before p6, and 11.4-RELEASE before p9, copy-on-write logic failed to invalidate shared memory page mappings between multiple processes allowing an unprivileged process to maintain a mapping after it is freed, allowing the process to read private data belonging to other processes or the kernel. 5.5 MEDIUM
CVE-2021-29627
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245050, 12.2-STABLE before r369525, 13.0-RC4 before p0, and 12.2-RELEASE before p6, listening socket accept filters implementing the accf_create callback incorrectly freed a process supplied argument string. Additional operations on the socket can lead to a double free or use after free.
CVE-2020-25584
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245118, 12.2-STABLE before r369552, 11.4-STABLE before r369560, 13.0-RC5 before p1, 12.2-RELEASE before p6, and 11.4-RELEASE before p9, a superuser inside a FreeBSD jail configured with the non-default allow.mount permission could cause a race condition between the lookup of ".." and remounting a filesystem, allowing access to filesystem hierarchy outside of the jail.
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r368250, 11.4-STABLE before r368253, 12.2-RELEASE before p1, 12.1-RELEASE before p11 and 11.4-RELEASE before p5 when processing a DNSSL option, rtsold(8) decodes domain name labels per an encoding specified in RFC 1035 in which the first octet of each label contains the label's length. rtsold(8) did not validate label lengths correctly and could overflow the destination buffer.
CVE-2020-7464
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r365730, 11.4-STABLE before r365738, 12.1-RELEASE before p10, 11.4-RELEASE before p4, and 11.3-RELEASE before p14, a programming error in the ure(4) device driver caused some Realtek USB Ethernet interfaces to incorrectly report packets with more than 2048 bytes in a single USB transfer as having a length of only 2048 bytes. An adversary can exploit this to cause the driver to misinterpret part of the payload of a large packet as a separate packet, and thereby inject packets across security boundaries such as VLANs.
CVE-2020-25578
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r368969, 11.4-STABLE before r369047, 12.2-RELEASE before p3, 12.1-RELEASE before p13 and 11.4-RELEASE before p7 several file systems were not properly initializing the d_off field of the dirent structures returned by VOP_READDIR. In particular, tmpfs(5), smbfs(5), autofs(5) and mqueuefs(5) were failing to do so. As a result, eight uninitialized kernel stack bytes may be leaked to userspace by these file systems. 5.3 MEDIUM
CVE-2020-25579
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r368969, 11.4-STABLE before r369047, 12.2-RELEASE before p3, 12.1-RELEASE before p13 and 11.4-RELEASE before p7 msdosfs(5) was failing to zero-fill a pair of padding fields in the dirent structure, resulting in a leak of three uninitialized bytes.
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6628P35
CVE-1999-0524
ICMP information such as (1) netmask and (2) timestamp is allowed from arbitrary hosts.
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6628P30
CVE-2022-0778
A flaw was found in OpenSSL. It is possible to trigger an infinite loop by crafting a certificate that has invalid explicit curve parameters. Since certificate parsing happens before verification of the certificate signature, any process that parses an externally supplied certificate may be subject to a denial of service attack
CVE-2021-40490
A race condition was discovered in ext4_write_inline_data_end in fs/ext4/inline.c in the ext4 subsystem in the Linux kernel through 5.13.13.
CVE-2021-20317
A flaw was found in the Linux kernel. A corrupted timer tree caused the task wakeup to be missing in the timerqueue_add function in lib/timerqueue.c. This flaw allows a local attacker with special user privileges to cause a denial of service, slowing and eventually stopping the system while running OSP.
CVE-2021-3679
A lack of CPU resource in the Linux kernel tracing module functionality in versions prior to 5.14-rc3 was found in the way user uses trace ring buffer in a specific way. Only privileged local users (with CAP_SYS_ADMIN capability) could use this flaw to starve the resources causing denial of service.
CVE-2021-4160
There is a carry propagation bug in the MIPS32 and MIPS64 squaring procedure. Many EC algorithms are affected, including some of the TLS 1.3 default curves. Impact was not analyzed in detail, because the pre-requisites for attack are considered unlikely and include reusing private keys. Analysis suggests that attacks against RSA and DSA as a result of this defect would be very difficult to perform and are not believed likely. Attacks against DH are considered just feasible (although very difficult) because most of the work necessary to deduce information about a private key may be performed offline. The amount of resources required for such an attack would be significant. However, for an attack on TLS to be meaningful, the server would have to share the DH private key among multiple clients, which is no longer an option since CVE-2016-0701. This issue affects OpenSSL versions 1.0.2, 1.1.1 and 3.0.0. It was addressed in the releases of 1.1.1m and 3.0.1 on the 15th of December 2021. For the 1.0.2 release it is addressed in git commit 6fc1aaaf3 that is available to premium support customers only. It will be made available in 1.0.2zc when it is released. The issue only affects OpenSSL on MIPS platforms. Fixed in OpenSSL 3.0.1 (Affected 3.0.0). Fixed in OpenSSL 1.1.1m (Affected 1.1.1-1.1.1l). Fixed in OpenSSL 1.0.2zc-dev (Affected 1.0.2-1.0.2zb).
CNVD-2019-23102/CVE-2019-10638/HSVD-202103-0
In the Linux kernel before 5.1.7, a device can be tracked by an attacker using the IP ID values the kernel produces for connection-less protocols (e.g., UDP and ICMP). When such traffic is sent to multiple destination IP addresses, it is possible to obtain hash collisions (of indices to the counter array) and thereby obtain the hashing key (via enumeration). An attack may be conducted by hosting a crafted web page that uses WebRTC or gQUIC to force UDP traffic to attacker-controlled IP addresses.
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6615P08
CVE-2020-10188
utility.c in telnetd in netkit telnet through 0.17 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via short writes or urgent data, because of a buffer overflow involving the netclear and nextitem functions.
CVE-1999-0511
IP forwarding is enabled on a machine which is not a router or firewall.
This chapter describes types of software used on the switch and how to upgrade software while the switch is operating normally or when the switch cannot correctly start up.
Software required for starting up the switch includes:
· Boot ROM image—A .bin file that comprises a basic section and an extended section. The basic section is the minimum code that bootstraps the system. The extended section enables hardware initialization and provides system management menus. You can use these menus to load software and the startup configuration file or manage files when the switch cannot correctly start up.
· Software images—Includes boot images and system images.
¡ Boot image—A .bin file that contains the operating system kernel. It provides process management, memory management, file system management, and the emergency shell.
¡ System image—A .bin file that contains the minimum modules required for device operation and some basic features, including device management, interface management, configuration management, and routing management.
The software images that have been loaded are called “current software images.” The software images specified to load at next startup are called “startup software images.”
These images might be released separately or as a whole in one .ipe package file. If an .ipe file is used, the system automatically decompresses the file, loads the .bin boot and system images in the file and sets them as startup software images. Typically, the Boot ROM and software images for this switch series are released in an .ipe file named main.ipe.
| NOTE: Boot ROM images are not released along with the boot images and system images. To get a version of Boot ROM image, contact the H3C technical support. |
Upon power-on, the Boot ROM image runs to initialize hardware and then the software images run to start up the entire system, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 System startup process
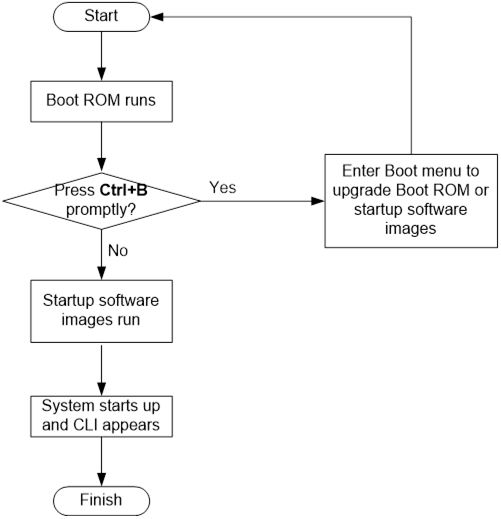
You can upgrade system software by using one of the following methods:
Upgrading method | Software types | Remarks |
Upgrading from the CLI | · Boot ROM image · Software images | · You must reboot the switch to complete the upgrade. · This method can interrupt ongoing network services. |
Upgrading from the Boot menu | · Boot ROM image · Software images | Use this method when the switch cannot correctly start up.
Upgrading an IRF fabric from the CLI instead of the Boot menu. The Boot menu method increases the service downtime, because it requires that you upgrade the member switches one by one. |
The output in this document is for illustration only and might vary with software releases. This document uses boot.bin and system.bin to represent boot and system image names. The actual software image name format is chassis-model_Comware-version_image-type_release, for example, S6520X-CMW710-BOOT-Rxxxx.bin and S6520X-CMW710-SYSTEM-Rxxxx.bin.
This section uses a two-member IRF fabric as an example to describe how to upgrade software from the CLI. If you have more than two subordinate switches, repeat the steps for the subordinate switch to upgrade their software. If you are upgrading a standalone switch, ignore the steps for upgrading the subordinate switch. For more information about setting up and configuring an IRF fabric, see the installation guide and Virtual Technologies configuration guide for the H3C S6520X-EI & S6520X-HI switch series.
Before you upgrade software, complete the following tasks:
1. Log in to the IRF fabric through Telnet or the console port. (Details not shown.)
2. Identify the number of IRF members, each member switch's role, and IRF member ID.
<Sysname> display irf
MemberID Role Priority CPU-Mac Description
*+1 Master 5 0023-8927-afdc ---
2 Standby 1 0023-8927-af43 ---
--------------------------------------------------
* indicates the device is the master.
+ indicates the device through which the user logs in.
The Bridge MAC of the IRF is: 0023-8927-afdb
Auto upgrade : no
Mac persistent : 6 min
Domain ID : 0
3. Verify that each IRF member switch has sufficient storage space for the upgrade images.
| IMPORTANT: Each IRF member switch must have free storage space that is at least two times the size of the upgrade image file. |
# Identify the free flash space of the master switch.
<Sysname> dir
Directory of flash:
0 -rw- 41424 Aug 23 2013 02:23:44 startup.mdb
1 -rw- 3792 Aug 23 2013 02:23:44 startup.cfg
2 -rw- 53555200 Aug 23 2013 09:53:48 system.bin
3 drw- - Aug 23 2013 00:00:07 seclog
4 drw- - Aug 23 2013 00:00:07 diagfile
5 drw- - Aug 23 2013 00:00:07 logfile
6 -rw- 9959424 Aug 23 2013 09:53:48 boot.bin
7 -rw- 9012224 Aug 23 2013 09:53:48 backup.bin
524288 KB total (453416 KB free)
# Identify the free flash space of each subordinate switch, for example, switch 2.
<Sysname> dir slot2#flash:/
Directory of slot2#flash:/
0 -rw- 41424 Jan 01 2011 02:23:44 startup.mdb
1 -rw- 3792 Jan 01 2011 02:23:44 startup.cfg
2 -rw- 93871104 Aug 23 2013 16:00:08 system.bin
3 drw- - Jan 01 2011 00:00:07 seclog
4 drw- - Jan 01 2011 00:00:07 diagfile
5 drw- - Jan 02 2011 00:00:07 logfile
6 -rw- 13611008 Aug 23 2013 15:59:00 boot.bin
7 -rw- 9012224 Nov 25 2011 09:53:48 backup.bin
524288 KB total (453416 KB free)
4. Compare the free flash space of each member switch with the size of the software file to load. If the space is sufficient, start the upgrade process. If not, go to the next step.
5. Delete unused files in the flash memory to free space:
| CAUTION: · To avoid data loss, do not delete the current configuration file. For information about the current configuration file, use the display startup command. · The delete /unreserved file-url command deletes a file permanently and the action cannot be undone. · The delete file-url command moves a file to the recycle bin and the file still occupies storage space. To free the storage space, first execute the undelete command to restore the file, and then execute the delete /unreserved file-url command. |
# Delete unused files from the flash memory of the master switch.
<Sysname> delete /unreserved flash:/backup.bin
The file cannot be restored. Delete flash:/backup.bin?[Y/N]:y
Deleting the file permanently will take a long time. Please wait...
Deleting file flash:/backup.bin...Done.
# Delete unused files from the flash memory of the subordinate switch.
<Sysname> delete /unreserved slot2#flash:/backup.bin
The file cannot be restored. Delete slot2#flash:/backup.bin?[Y/N]:y
Deleting the file permanently will take a long time. Please wait...
Deleting file slot2#flash:/backup.bin...Done.
Downloading software images to the master switch
Before you start upgrading software images packages, make sure you have downloaded the upgrading software files to the root directory in flash memory. This section describes downloading an .ipe software file as an example.
The following are ways to download, upload, or copy files to the master switch:
· FTP download from a server
· FTP upload from a client
· TFTP download from a server
Prerequisites
If FTP or TFTP is used, the IRF fabric and the PC working as the FTP/TFTP server or FTP client can reach each other.
Prepare the FTP server or TFTP server program yourself for the PC. The switch series does not come with these software programs.
You can use the switch as an FTP client to download files from an FTP server.
To download a file from an FTP server, for example, the server at 10.10.110.1:
6. Run an FTP server program on the server, configure an FTP username and password, specify the working directory and copy the file, for example, newest.ipe, to the directory.
7. Execute the ftp command in user view on the IRF fabric to access the FTP server.
<Sysname> ftp 10.10.110.1
Trying 10.10.110.1...
Press CTRL+C to abort
Connected to 10.10.110.1(10.10.110.1).
220 FTP service ready.
User (10.10.110.1:(none)):username
331 Password required for username.
Password:
230 User logged in.
8. Enable the binary transfer mode.
ftp> binary
200 Type set to I.
9. Execute the get command in FTP client view to download the file from the FTP server.
ftp> get newest.ipe
227 Entering Passive Mode (10,10,110,1,17,97).
125 BINARY mode data connection already open, transfer starting for /newest.ipe
226 Transfer complete.
32133120 bytes received in 35 seconds (896. 0 kbyte/s)
ftp> bye
221 Server closing.
You can use the IRF fabric as an FTP server and upload files from a client to the IRF fabric.
To FTP upload a file from a client:
On the IRF fabric:
10. Enable FTP server.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ftp server enable
11. Configure a local FTP user account:
# Create the user account.
[Sysname] local-user abc
# Set its password and specify the FTP service.
[Sysname-luser-manage-abc] password simple pwd
[Sysname-luser-manage-abc] service-type ftp
# Assign the network-admin user role to the user account for uploading file to the working directory of the server.
[Sysname-luser-manage-abc] authorization-attribute user-role network-admin
[Sysname-luser-manage-abc] quit
[Sysname] quit
On the PC:
12. Log in to the IRF fabric (the FTP server) in FTP mode.
c:\> ftp 1.1.1.1
Connected to 1.1.1.1.
220 FTP service ready.
User(1.1.1.1:(none)):abc
331 Password required for abc.
Password:
230 User logged in.
13. Enable the binary file transfer mode.
ftp> binary
200 TYPE is now 8-bit binary.
14. Upload the file (for example, newest.ipe) to the root directory of the flash memory on the master switch.
ftp> put newest.ipe
200 PORT command successful
150 Connecting to port 10002
226 File successfully transferred
ftp: 32133120 bytes sent in 64.58 secs (497.60 Kbytes/sec).
To download a file from a TFTP server, for example, the server at 10.10.110.1:
15. Run a TFTP server program on the server, specify the working directory, and copy the file, for example, newest.ipe, to the directory.
16. On the IRF fabric, execute the tftp command in user view to download the file to the root directory of the flash memory on the master switch.
<Sysname> tftp 10.10.110.1 get newest.ipe
Press CTRL+C to abort.
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 30.6M 0 30.6M 0 0 143k 0 --:--:-- 0:03:38 --:--:-- 142k
To upgrade the software images:
17. Specify the upgrade image file (newest.ipe in this example) used at the next startup for the master switch, and assign the M attribute to the boot and system images in the file.
<Sysname> boot-loader file flash:/newest.ipe slot 1 main
Verifying image file..........Done.
Images in IPE:
boot.bin
system.bin
This command will set the main startup software images. Continue? [Y/N]:y
Add images to target slot.
Decompressing file boot.bin to flash:/boot.bin....................Done.
Decompressing file system.bin to flash:/system.bin................Done.
The images that have passed all examinations will be used as the main startup so
ftware images at the next reboot on slot 1.
18. Specify the upgrade image file as the main startup image file for each subordinate switch. This example uses IRF member 2. (The subordinate switches will automatically copy the file to the root directory of their flash memories.)
<Sysname> boot-loader file flash:/newest.ipe slot 2 main
Verifying image file..........Done.
Images in IPE:
boot.bin
system.bin
This command will set the main startup software images. Continue? [Y/N]:y
Add images to target slot.
Decompressing file boot.bin to flash:/boot.bin....................Done.
Decompressing file system.bin to flash:/system.bin................Done.
The images that have passed all examinations will be used as the main startup so
ftware images at the next reboot on slot 2.
19. Enable the software auto-update function.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] irf auto-update enable
[Sysname] quit
This function checks the software versions of member switches for inconsistency with the master switch. If a subordinate switch is using a different software version than the master, the function propagates the current software images of the master to the subordinate as main startup images. The function prevents software version inconsistency from causing the IRF setup failure.
20. Save the current configuration in any view to prevent data loss.
<Sysname> save
The current configuration will be written to the device. Are you sure? [Y/N]:y
Please input the file name(*.cfg)[flash:/startup.cfg]
(To leave the existing filename unchanged, press the enter key):
flash:/startup.cfg exists, overwrite? [Y/N]:y
Validating file. Please wait.................
Saved the current configuration to mainboard device successfully.
Slot 2:
Save next configuration file successfully.
21. Reboot the IRF fabric to complete the upgrade.
<Sysname> reboot
Start to check configuration with next startup configuration file, please wait.
........DONE!
This command will reboot the device. Continue? [Y/N]:y
Now rebooting, please wait...
The system automatically loads the .bin boot and system images in the .ipe file and sets them as the startup software images.
22. Execute the display version command in any view to verify that the current main software images have been updated (details not shown).
| NOTE: The system automatically checks the compatibility of the Boot ROM image and the boot and system images during the reboot. If you are prompted that the Boot ROM image in the upgrade image file is different than the current Boot ROM image, upgrade both the basic and extended sections of the Boot ROM image for compatibility. If you choose to not upgrade the Boot ROM image, the system will ask for an upgrade at the next reboot performed by powering on the switch or rebooting from the CLI (promptly or as scheduled). If you fail to make any choice in the required time, the system upgrades the entire Boot ROM image. |
In this approach, you must access the Boot menu of each member switch to upgrade their software one by one. If you are upgrading software images for an IRF fabric, using the CLI is a better choice.
| TIP: Upgrading through the Ethernet port is faster than through the console port. |
Make sure the prerequisites are met before you start upgrading software from the Boot menu.
Setting up the upgrade environment
1. Use a console cable to connect the console terminal (for example, a PC) to the console port on the switch.
2. Connect the Ethernet port on the switch to the file server.
| NOTE: The file server and the configuration terminal can be co-located. |
3. Run a terminal emulator program on the console terminal and set the following terminal settings:
¡ Bits per second—9,600
¡ Data bits—8
¡ Parity—None
¡ Stop bits—1
¡ Flow control—None
¡ Emulation—VT100
Preparing for the TFTP or FTP transfer
To use TFTP or FTP:
· Run a TFTP or FTP server program on the file server or the console terminal.
· Copy the upgrade file to the file server.
· Correctly set the working directory on the TFTP or FTP server.
· Make sure the file server and the switch can reach each other.
Verifying that sufficient storage space is available
| IMPORTANT: For the switch to start up correctly, do not delete the main startup software images when you free storage space before upgrading Boot ROM. On the Boot menu, the main startup software images are marked with an asterisk (*). |
When you upgrade software, make sure each member switch has sufficient free storage space for the upgrade file, as shown in Table 6.
Table 6 Minimum free storage space requirements
Upgraded images | Minimum free storage space requirements |
Comware images | Two times the size of the Comware upgrade package file. |
Boot ROM | Same size as the Boot ROM upgrade image file. |
If no sufficient space is available, delete unused files as described in “Managing files from the Boot menu.”
Scheduling the upgrade time
During the upgrade, the switch cannot provide any services. You must make sure the upgrade has a minimal impact on the network services.
Starting......
Press Ctrl+D to access BASIC BOOT MENU
Press Ctrl+T to start heavy memory test
Press Ctrl+E to start flash test
********************************************************************************
* *
* H3C S6520X-30QC-HI Version 105 *
* *
********************************************************************************
Copyright (c) 2004-2016 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Creation Date : Aug 9 2016, 11:29:29
CPU Clock Speed : 800MHz
Memory Size : 2048MB
Flash Size : 512MB
CPLD Version : 002
PCB Version : Ver.B
Mac Address : 703d155618b0
Press Ctrl+B to access EXTENDED BOOT MENU...1
Press one of the shortcut key combinations at prompt.
Shortcut keys | Prompt message | Function | Remarks |
Ctrl+B | Press Ctrl+B to enter Extended Boot menu... | Accesses the extended Boot menu. | Press the keys within 1 second (in fast startup mode) or 5 seconds (in full startup mode) after the message appears. You can upgrade and manage system software and Boot ROM from this menu. |
Ctrl+D | Press Ctrl+D to access BASIC BOOT MENU | Accesses the basic Boot menu. | Press the keys within 1 seconds after the message appears. You can upgrade Boot ROM or access the extended Boot ROM segment from this menu. |
If the extended Boot ROM segment has corrupted, you can repair or upgrade it from the basic Boot menu.
Press Ctrl+D within 1 seconds after the "Press Ctrl+D to access BASIC BOOT MENU" prompt message appears. If you fail to do this within the time limit, the system starts to run the extended Boot ROM segment.
********************************************************************************
* *
* H3C S6520X-30QC-HI BOOTROM, Version 105 *
* *
********************************************************************************
BASIC BOOT MENU
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
4. Boot extended BootRom
0. Reboot
Ctrl+U: Access BASIC ASSISTANT MENU
Enter your choice(0-4):
Table 8 Basic Boot ROM menu options
Option | Task |
1. Update full BootRom | Update the entire Boot ROM, including the basic segment and the extended segment. To do so, you must use XMODEM and the console port. For more information, see Using XMODEM to upgrade Boot ROM through the console port. |
2. Update extended BootRom | Update the extended Boot ROM segment. To do so, you must use XMODEM and the console port. For more information, see Using XMODEM to upgrade Boot ROM through the console port. |
3. Update basic BootRom | Update the basic Boot ROM segment. To do so, you must use XMODEM and the console port. For more information, see Using XMODEM to upgrade Boot ROM through the console port. |
4. Boot extended BootRom | Access the extended Boot ROM segment. For more information, see Accessing the extended Boot menu. |
0. Reboot | Reboot the switch. |
Ctrl+U: Access BASIC ASSISTANT MENU | Press Ctrl + U to access the BASIC ASSISTANT menu (see Table 9). |
Table 9 BASIC ASSISTANT menu options
Option | Task |
1. RAM Test | Perform a RAM self-test. |
0. Return to boot menu | Return to the basic Boot menu. |
Accessing the extended Boot menu
Press Ctrl+B within 1 second (in fast startup mode) or 5 seconds (in full startup mode) after the "Press Ctrl-B to enter Extended Boot menu..." prompt message appears. If you fail to do this, the system starts decompressing the system software.
Alternatively, you can enter 4 in the basic Boot menu to access the extended Boot menu.
The "Password recovery capability is enabled." or "Password recovery capability is disabled." message appears, followed by the extended Boot menu. Availability of some menu options depends on the state of password recovery capability (see Table 10). For more information about password recovery capability, see Fundamentals Configuration Guide in H3C S6520X-EI & S6520X-HI Switch Series Configuration Guides.
Password recovery capability is enabled.
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-8):
Table 10 Extended Boot ROM menu options
Option | Tasks |
1. Download image to flash | Download a software image file to the flash. |
2. Select image to boot | · Specify the main and backup software image file for the next startup. · Specify the main and backup configuration files for the next startup. This task can be performed only if password recovery capability is enabled. |
3. Display all files in flash | Display files on the flash. |
4. Delete file from flash | Delete files to free storage space. |
5. Restore to factory default configuration | Delete the current next-startup configuration files and restore the factory-default configuration. This option is available only if password recovery capability is disabled. |
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu | Access the Boot ROM upgrade menu. |
7. Skip current system configuration | Start the switch without loading any configuration file. This is a one-time operation and takes effect only for the first system boot or reboot after you choose this option. This option is available only if password recovery capability is enabled. |
8. Set switch startup mode | Set the startup mode to fast startup mode or full startup mode. |
0. Reboot | Reboot the switch. |
Ctrl+F: Format file system | Format the current storage medium. |
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login | Skip the authentication for console login. This is a one-time operation and takes effect only for the first system boot or reboot after you choose this option. This option is available only if password recovery capability is enabled. |
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run | Download a system software image and start the switch with the image. This option is available only if password recovery capability is enabled. |
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU | Access the EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU. For options in the menu, see Table 11. |
Table 11 EXTENDED ASSISTANT menu options
Option | Task |
1. Display Memory | Display data in the memory. |
2. Search Memory | Search the memory for a specific data segment. |
0. Return to boot menu | Return to the extended Boot ROM menu. |
Upgrading Comware images from the Boot menu
You can use the following methods to upgrade Comware images:
· Using TFTP to upgrade software images through the Ethernet port
· Using FTP to upgrade software images through the Ethernet port
· Using XMODEM to upgrade software through the console port
Using TFTP to upgrade software images through the Ethernet port
1. Enter 1 in the Boot menu to access the file transfer protocol submenu.
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 1 to set the TFTP parameters.
Load File Name :update.ipe
Server IP Address :192.168.0.3
Local IP Address :192.168.0.2
Subnet Mask :255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Address :0.0.0.0
Table 12 TFTP parameter description
Item | Description |
Load File Name | Name of the file to download (for example, update.ipe). |
Server IP Address | IP address of the TFTP server (for example, 192.168.0.3). |
Local IP Address | IP address of the switch (for example, 192.168.0.2). |
Subnet Mask | Subnet mask of the switch (for example, 255.255.255.0). |
Gateway IP Address | IP address of the gateway (in this example, no gateway is required because the server and the switch are on the same subnet). |
| NOTE: · To use the default setting for a field, press Enter without entering any value. · If the switch and the server are on different subnets, you must specify a gateway address for the switch. |
3. Enter all required parameters, and enter Y to confirm the settings. The following prompt appears:
Are you sure to download file to flash? Yes or No (Y/N):Y
4. Enter Y to start downloading the image file. To return to the Boot menu without downloading the upgrade file, enter N.
Loading.........................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................Done!
5. Enter the M (main), B (backup), or N (none) attribute for the images. In this example, assign the main attribute to the images.
Please input the file attribute (Main/Backup/None) M
Image file boot.bin is self-decompressing...
Free space: 534980608 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
................................................................................
...................................................................Done!
Image file system.bin is self-decompressing...
Free space: 525981696 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
.......................................................................Done!
| NOTE: · The switch always attempts to boot with the main images first. If the attempt fails, for example, because the main images are not available, the switch tries to boot with the backup images. An image with the none attribute is only stored in flash memory for backup. To use it at reboot, you must change its attribute to main or backup. · If an image with the same attribute as the image you are loading is already in the flash memory, the attribute of the old image changes to none after the new image becomes valid. |
6. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new software images.
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-8): 0
Using FTP to upgrade software images through the Ethernet port
1. Enter 1 in the Boot menu to access the file transfer protocol submenu.
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 2 to set the FTP parameters.
Load File Name :update.ipe
Server IP Address :192.168.0.3
Local IP Address :192.168.0.2
Subnet Mask :255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Address :0.0.0.0
FTP User Name :switch
FTP User Password :***
Table 13 FTP parameter description
Item | Description |
Load File Name | Name of the file to download (for example, update.ipe). |
Server IP Address | IP address of the FTP server (for example, 192.168.0.3). |
Local IP Address | IP address of the switch (for example, 192.168.0.2). |
Subnet Mask | Subnet mask of the switch (for example, 255.255.255.0). |
Gateway IP Address | IP address of the gateway (in this example, no gateway is required because the server and the switch are on the same subnet). |
FTP User Name | Username for accessing the FTP server, which must be the same as configured on the FTP server. |
FTP User Password | Password for accessing the FTP server, which must be the same as configured on the FTP server. |
| NOTE: · To use the default setting for a field, press Enter without entering any value. · If the switch and the server are on different subnets, you must specify a gateway address for the switch. |
3. Enter all required parameters, and enter Y to confirm the settings. The following prompt appears:
Are you sure to download file to flash? Yes or No (Y/N):Y
4. Enter Y to start downloading the image file. To return to the Boot menu without downloading the upgrade file, enter N.
Loading.........................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................Done!
5. Enter the M (main), B (backup), or N (none) attribute for the images. In this example, assign the main attribute to the images.
Please input the file attribute (Main/Backup/None) M
Image file boot.bin is self-decompressing...
Free space: 534980608 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
................................................................................
...................................................................Done!
Image file system.bin is self-decompressing...
Free space: 525981696 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
.......................................................................Done!
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-8):0
| NOTE: · The switch always attempts to boot with the main images first. If the attempt fails, for example, because the main images not available, the switch tries to boot with the backup images. An image with the none attribute is only stored in flash memory for backup. To use it at reboot, you must change its attribute to main or backup. · If an image with the same attribute as the image you are loading is already in the flash memory, the attribute of the old image changes to none after the new image becomes valid. |
6. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new software images.
Using XMODEM to upgrade software through the console port
XMODEM download through the console port is slower than TFTP or FTP download through the Ethernet port. To save time, use the Ethernet port as long as possible.
1. Enter 1 in the Boot menu to access the file transfer protocol submenu.
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 3 to set the XMODEM download baud rate.
Please select your download baudrate:
1.* 9600
2. 19200
3. 38400
4. 57600
5. 115200
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-5):5
3. Select an appropriate download rate, for example, enter 5 to select 115200 bps.
Download baudrate is 115200 bps
Please change the terminal's baudrate to 115200 bps and select XMODEM protocol
Press enter key when ready
4. Set the serial port on the terminal to use the same baud rate and protocol as the console port. If you select 9600 bps as the download rate for the console port, skip this task.
a. Select Call > Disconnect in the HyperTerminal window to disconnect the terminal from the switch.
Figure 2 Disconnecting the terminal from the switch
b. Select File > Properties, and in the Properties dialog box, click Configure.
Figure 3 Properties dialog box
c. Select 115200 from the Bits per second list and click OK.
Figure 4 Modifying the baud rate
d. Select Call > Call to reestablish the connection.
Figure 5 Reestablishing the connection
5. Press Enter. The following prompt appears:
Are you sure to download file to flash? Yes or No (Y/N):Y
6. Enter Y to start downloading the file. (To return to the Boot menu, enter N.)
Now please start transfer file with XMODEM protocol
If you want to exit, Press <Ctrl+X>
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
7. Select Transfer > Send File in the HyperTerminal window.
Figure 6 Transfer menu
8. In the dialog box that appears, click Browse to select the source file, and select Xmodem from the Protocol list.
Figure 7 File transmission dialog box
9. Click Send. The following dialog box appears:
Figure 8 File transfer progress
10. Enter the M (main), B (backup), or N (none) attribute for the images. In this example, assign the main attribute to the images.
Please input the file attribute (Main/Backup/None) m
The boot.bin image is self-decompressing...
# At the Load File name prompt, enter a name for the boot image to be saved to flash memory.
Load File name : default_file boot-update.bin (At the prompt,
Free space: 470519808 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
.............Done!
The system-update.bin image is self-decompressing...
# At the Load File name prompt, enter a name for the system image to be saved to flash memory.
Load File name : default_file system-update.bin
Free space: 461522944 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
.............Done!
Your baudrate should be set to 9600 bps again!
Press enter key when ready
| NOTE: · The switch always attempts to boot with the main images first. If the attempt fails, for example, because the main images not available, the switch tries to boot with the backup images. An image with the none attribute is only stored in the flash memory for backup. To use it at reboot, you must change its attribute to main or backup. · If an image with the same attribute as the image you are loading is already in flash memory, the attribute of the old image changes to none after the new image becomes valid. |
11. If the baud rate of the HyperTerminal is not 9600 bps, restore it to 9600 bps as described in step a. If the baud rate is 9600 bps, skip this step.
| NOTE: The console port rate reverts to 9600 bps at a reboot. If you have changed the baud rate, you must perform this step so you can access the switch through the console port after a reboot. |
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-8): 0
12. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the system with the new software images.
Upgrading Boot ROM from the Boot menu
You can use the following methods to upgrade the Boot ROM image:
· Using TFTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the Ethernet port
· Using FTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the Ethernet port
· Using XMODEM to upgrade Boot ROM through the console port
Using TFTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the Ethernet port
1. Enter 6 in the Boot menu to access the Boot ROM update menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 1 in the Boot ROM update menu to upgrade the full Boot ROM.
The file transfer protocol submenu appears:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
3. Enter 1 to set the TFTP parameters.
Load File Name :update.btm
Server IP Address :192.168.0.3
Local IP Address :192.168.0.2
Subnet Mask :255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Address :0.0.0.0
Table 14 TFTP parameter description
Item | Description |
Load File Name | Name of the file to download (for example, update.btm). |
Server IP Address | IP address of the TFTP server (for example, 192.168.0.3). |
Local IP Address | IP address of the switch (for example, 192.168.0.2). |
Subnet Mask | Subnet mask of the switch (for example, 255.255.255.0). |
Gateway IP Address | IP address of the gateway (in this example, no gateway is required because the server and the switch are on the same subnet). |
| NOTE: · To use the default setting for a field, press Enter without entering any value. · If the switch and the server are on different subnets, you must specify a gateway address for the switch. |
4. Enter all required parameters and press Enter to start downloading the file.
Loading.................................................Done!
5. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the basic Boot ROM section.
Will you Update Basic BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating Basic BootRom...........Done.
6. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the extended Boot ROM section.
Updating extended BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating extended BootRom.........Done.
7. Enter 0 in the Boot ROM update menu to return to the Boot menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
8. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new Boot ROM image.
Using FTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the Ethernet port
1. Enter 6 in the Boot menu to access the Boot ROM update menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 1 in the Boot ROM update menu to upgrade the full Boot ROM.
The file transfer protocol submenu appears:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
3. Enter 2 to set the FTP parameters.
Load File Name :update.btm
Server IP Address :192.168.0.3
Local IP Address :192.168.0.2
Subnet Mask :255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Address :0.0.0.0
FTP User Name :switch
FTP User Password :123
Table 15 FTP parameter description
Item | Description |
Load File Name | Name of the file to download (for example, update.btm). |
Server IP Address | IP address of the FTP server (for example, 192.168.0.3). |
Local IP Address | IP address of the switch (for example, 192.168.0.2). |
Subnet Mask | Subnet mask of the switch (for example, 255.255.255.0). |
Gateway IP Address | IP address of the gateway (in this example, no gateway is required because the server and the switch are on the same subnet). |
FTP User Name | Username for accessing the FTP server, which must be the same as configured on the FTP server. |
FTP User Password | Password for accessing the FTP server, which must be the same as configured on the FTP server. |
| NOTE: · To use the default setting for a field, press Enter without entering any value. · If the switch and the server are on different subnets, you must specify a gateway address for the switch. |
4. Enter all required parameters and press Enter to start downloading the file.
Loading.................................................Done!
5. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the basic Boot ROM section.
Will you Update Basic BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating Basic BootRom...........Done.
6. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the extended Boot ROM section.
Updating extended BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating extended BootRom.........Done.
7. Enter 0 in the Boot ROM update menu to return to the Boot menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
8. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new Boot ROM image.
Using XMODEM to upgrade Boot ROM through the console port
XMODEM download through the console port is slower than TFTP or FTP download through the Ethernet port. To save time, use the Ethernet port as long as possible.
1. Enter 6 in the Boot menu to access the Boot ROM update menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 1 in the Boot ROM update menu to upgrade the full Boot ROM.
The file transfer protocol submenu appears:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
3. Enter 3 to set the XMODEM download baud rate.
Please select your download baudrate:
1.* 9600
2. 19200
3. 38400
4. 57600
5. 115200
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-5):5
4. Select an appropriate download rate, for example, enter 5 to select 115200 bps.
Download baudrate is 115200 bps
Please change the terminal's baudrate to 115200 bps and select XMODEM protocol
Press enter key when ready
5. Set the serial port on the terminal to use the same baud rate and protocol as the console port. If you select 9600 bps as the download rate for the console port, skip this task.
a. Select Call > Disconnect in the HyperTerminal window to disconnect the terminal from the switch.
Figure 9 Disconnecting the terminal from the switch

b. Select File > Properties, and in the Properties dialog box, click Configure.
Figure 10 Properties dialog box
c. Select 115200 from the Bits per second list and click OK.
Figure 11 Modifying the baud rate

d. Select Call > Call to reestablish the connection.
Figure 12 Reestablishing the connection

6. Press Enter to start downloading the file.
Now please start transfer file with XMODEM protocol
If you want to exit, Press <Ctrl+X>
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
7. Select Transfer > Send File in the HyperTerminal window.
Figure 13 Transfer menu

8. In the dialog box that appears, click Browse to select the source file, and select Xmodem from the Protocol list.
Figure 14 File transmission dialog box
9. Click Send. The following dialog box appears:
Figure 15 File transfer progress
10. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the basic Boot ROM section.
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCCCCCC ...Done!
Will you Update Basic BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating Basic BootRom...........Done.
11. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the extended Boot ROM section.
Updating extended BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating extended BootRom.........Done.
12. If the baud rate of the HyperTerminal is not 9600 bps, restore it to 9600 bps at the prompt, as described in step a. If the baud rate is 9600 bps, skip this step.
Please change the terminal's baudrate to 9600 bps, press ENTER when ready.
| NOTE: The console port rate reverts to 9600 bps at a reboot. If you have changed the baud rate, you must perform this step so you can access the switch through the console port after a reboot. |
13. Press Enter to access the Boot ROM update menu.
14. Enter 0 in the Boot ROM update menu to return to the Boot menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
15. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new Boot ROM image.
Managing files from the Boot menu
From the Boot menu, you can display files in flash memory to check for obsolete files, incorrect files, or space insufficiency, delete files to release storage space, or change the attributes of software images.
Displaying all files
Enter 3 in the Boot menu to display all files in flash memory and identify the free space size.
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-8): 3
The following is a sample output:
Display all file(s) in flash:
File Number File Size(bytes) File Name
================================================================================
1 8177 flash:/testbackup.cfg
2(*) 53555200 flash:/system.bin
3(*) 9959424 flash:/boot.bin
4 3678 flash:/startup.cfg_backup
5 30033 flash:/default.mdb
6 42424 flash:/startup.mdb
7 18 flash:/.pathfile
8 232311 flash:/logfile/logfile.log
9 5981 flash:/startup.cfg_back
10(*) 6098 flash:/startup.cfg
11 20 flash:/.snmpboots
Free space: 464298848 bytes
The current image is boot.bin
(*)-with main attribute
(b)-with backup attribute
(*b)-with both main and backup attribute
Deleting files
If storage space is insufficient, delete obsolete files to free up storage space.
To delete files:
1. Enter 4 in the Boot menu:
Deleting the file in flash:
File Number File Size(bytes) File Name
================================================================================
1 8177 flash:/testbackup.cfg
2(*) 53555200 flash:/system.bin
3(*) 9959424 flash:/boot.bin
4 3678 flash:/startup.cfg_backup
5 30033 flash:/default.mdb
6 42424 flash:/startup.mdb
7 18 flash:/.pathfile
8 232311 flash:/logfile/logfile.log
9 5981 flash:/startup.cfg_back
10(*) 6098 flash:/startup.cfg
11 20 flash:/.snmpboots
Free space: 464298848 bytes
The current image is boot.bin
(*)-with main attribute
(b)-with backup attribute
(*b)-with both main and backup attribute
2. Enter the number of the file to delete. For example, enter 1 to select the file testbackup.cfg.
Please input the file number to change: 1
3. Enter Y at the confirmation prompt.
The file you selected is testbackup.cfg,Delete it? (Y/N):Y
Deleting....................................Done!
Changing the attribute of software images
Software image attributes include main (M), backup (B), and none (N). System software and boot software can each have multiple none-attribute images but only one main image and one backup image on the switch. You can assign both the M and B attributes to one image. If the M or B attribute you are assigning has been assigned to another image, the assignment removes the attribute from that image. If the removed attribute is the sole attribute of the image, its attribute changes to N.
For example, the system image system.bin has the M attribute and the system image system-update.bin has the B attribute. After you assign the M attribute to system-update.bin, the attribute of system-update.bin changes to M+B and the attribute of system.bin changes to N.
To change the attribute of a system or boot image:
1. Enter 2 in the Boot menu.
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-8): 2
2. 1 or 2 at the prompt to set the attribute of a software image. (The following output is based on the option 2. To set the attribute of a configuration file, enter 3.)
1. Set image file
2. Set bin file
3. Set configuration file
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3): 2
File Number File Size(bytes) File Name
================================================================================
1(*) 53555200 flash:/system.bin
2(*) 9959424 flash:/boot.bin
3 13105152 flash:/boot-update.bin
4 91273216 flash:/system-update.bin
Free space: 417177920 bytes
(*)-with main attribute
(b)-with backup attribute
(*b)-with both main and backup attribute
Note:Select .bin files. One but only one boot image and system image must be included.
3. Enter the number of the file you are working with. For example, enter 3 to select the boot image boot-update.bin. and enter 4 to select the system image system-update.bin.
Enter file No.(Allows multiple selection):3
Enter another file No.(0-Finish choice):4
4. Enter 0 to finish the selection.
Enter another file No.(0-Finish choice):0
You have selected:
flash:/boot-update.bin
flash:/system-update.bin
5. Enter M or B to change its attribute to main or backup. If you change its attribute to M, the attribute of boot.bin changes to none.
Please input the file attribute (Main/Backup) M
This operation may take several minutes. Please wait....
Next time, boot-update.bin will become default boot file!
Next time, system-update.bin will become default boot file!
Set the file attribute success!
Handling software upgrade failures
If a software upgrade fails, the system runs the old software version.
To handle a software upgrade failure:
1. Verify that the software release is compatible with the switch model and the correct file is used.
2. Verify that the software release and the Boot ROM release are compatible. For software and Boot ROM compatibility, see the hardware and software compatibility matrix in the correct release notes.
3. Check the physical ports for a loose or incorrect connection.
4. If you are using the console port for file transfer, check the HyperTerminal settings (including the baud rate and data bits) for any wrong setting.
5. Check the file transfer settings:
¡ If XMODEM is used, you must set the same baud rate for the terminal as for the console port.
¡ If TFTP is used, you must enter the same server IP addresses, file name, and working directory as set on the TFTP server.
¡ If FTP is used, you must enter the same FTP server IP address, source file name, working directory, and FTP username and password as set on the FTP server.
6. Check the FTP or TFTP server for any incorrect setting.
7. Check that the storage device has sufficient space for the upgrade file.

