| Title | Size | Downloads |
|---|---|---|
| H3C S6825-CMW710-R6715P01 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes).pdf | 3.95 MB | |
| H3C S6825-CMW710-R6715P01 release notes.pdf | 1.89 MB | |
| S6825-CMW710-R6715P01.zip | 186.32 MB | |
| S6825-CMW710-R6715P01 MD5.zip | 0.25 KB |
|
H3C S6825-CMW710-R6715P01 Release Notes |
|
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. The information in this document is subject to change without notice. |
|
Contents
Hardware and software compatibility matrix· 2
Upgrade restrictions and guidelines· 4
Software feature and command updates· 5
Operation changes in R6715P01· 7
Operation changes in E6712· 12
Operation changes in E6711· 12
Operation changes in R6710· 15
Operation changes in E6707· 16
Operation changes in E6706· 16
Operation changes in E6702· 17
Registering and installing licenses· 19
Obtaining license server software and documentation· 19
Open problems and workarounds· 19
Resolved problems in R6715P01· 23
Resolved problems in R6715· 27
Resolved problems in E6712· 36
Resolved problems in E6711· 38
Resolved problems in R6710· 40
Resolved problems in E6707· 45
Resolved problems in E6706· 47
Resolved problems in E6702· 52
Appendix B Fixed security vulnerabilities· 59
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6715P01· 59
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6715· 60
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6712· 62
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6711· 62
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6707· 63
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6706· 64
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6702· 64
Appendix C Upgrading software· 65
System software file types· 65
Downloading software to the master switch· 69
Upgrading the software images· 71
Installing a patch package· 72
Upgrading from the Boot menu· 73
Using TFTP to upgrade software images through the management Ethernet port 74
Using FTP to upgrade software through the management Ethernet port 76
Using XMODEM to upgrade software through the console port 78
Using TFTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the management Ethernet port 82
Using FTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the management Ethernet port 83
Using XMODEM to upgrade Boot ROM through the console port 85
Managing files from the Boot menu· 89
List of tables
Table 2 Hardware and software compatibility matrix· 2
Table 3 ISSU compatibility list 3
Table 5 S6825 series hardware features· 53
Table 6 Software features of the S6825 series· 54
Table 7 TFTP parameter description· 74
Table 8 FTP parameter description· 76
Table 9 TFTP parameter description· 83
Table 10 FTP parameter description· 84
Introduction
This document describes the features, restrictions and guidelines, open problems, and workarounds for version R6715P01. Before you use this version on a live network, back up the configuration and test the version to avoid software upgrade affecting your live network.
Use this document in conjunction with H3C S6825-CMW710-R6715P01 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes) and the documents listed in “Related documentation”.
Version information
Version number
H3C Comware Software, Version 7.1.070, Release 6715P01
Note: You can see the version number with the display version command in any view. Please see Note ②.
Version history
Version number | Last version | Release date | Release type | Remarks |
S6825-CMW710-R6715P01 | S6825-CMW710-R6715 | 2024-06-27 | Release version | · Added features. · Modified features. · Fixed bugs. |
S6825-CMW710-R6715 | S6825-CMW710-E6712 | 2024-03-25 | Release version | · Added features. · Modified features. · Fixed bugs. |
S6825-CMW710- E6712 | S6825-CMW710-E6711 | 2023-06-16 | ESS version | · Added features. · Modified features. · Fixed bugs. |
S6825-CMW710-E6711 | S6825-CMW710- R6710 | 2023-04-21 | ESS version | · Added features. · Modified features. · Fixed bugs. |
S6825-CMW710-R6710 | S6825-CMW710-E6707 | 2022-12-28 | Release version | · Added features. · Modified features. · Fixed bugs. |
S6825-CMW710-E6707 | S6825-CMW710-E6706 | 2022-09-30 | ESS version | · Added features. · Modified features. · Fixed bugs. |
S6825-CMW710-E6706 | S6825-CMW710-E6702 | 2022-09-02 | ESS version | · Added features. · Modified features. · Fixed bugs. |
S6825-CMW710-E6702 | First release | 2022-04-13 | ESS version | None |
Hardware and software compatibility matrix
| CAUTION: To avoid an upgrade failure, use Table 2 to verify the hardware and software compatibility before performing an upgrade. |
Table 2 Hardware and software compatibility matrix
Item | Specifications |
Product family | H3C S6825 Series |
Hardware platform | H3C S6825-54HF H3C S6825-54HF (with product code LS-6825-54HF-H1) Please see Note① |
Memory | 4GB 8G (with product code LS-6825-54HF-H1) |
Flash | 4GB |
Boot ROM version | Basic BootWare—Version 309 or higher Extended BootWare—Version 309 or higher (Note: Perform the command display version command in any view to view the version information. Please see Note③) |
Software images and their MD5 checksums | S6825-CMW710-R6715P01.ipe:b57376e8cd0696cf69b93b248c38bd6c |
iMC version | iMC PLAT 7.3 (E0710) iMC EAD 7.3 (E0629) iMC MVM 7.3 (E0511) iMC QoSM 7.3 (E0506) iMC VXLAN 7.3 (E0710) iMC BIMS 7.3 (E0509H01) UCenter SHM 7.3 (E0716) UCenter NTA 7.3 (E0716) iMC EIA 7.3 (E0628) |
iNode version | iNode(E0595) |
ADDC version | ADDC 6.5 |
Note① LS-6825-XXXX represents a product code, which is printed on the lower right corner of the bar code label on the rear panel or upper panel of the device.
To display version information for the system software and Boot ROM of S6825-54HF:
<H3C>dis version
H3C Comware Software, Version 7.1.070, Release 6715P01 ------- 注②
Copyright (c) 2004-2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
H3C S6825-54HF uptime is 0 weeks, 0 days, 2 hours, 31 minutes
Last reboot reason : User reboot
Boot image: flash:/s6825-cmw710-boot-r6715p01.bin
Boot image version: 7.1.070, Release 6715P01
Compiled Jun 06 2024 16:00:00
System image: flash:/s6825-cmw710-system-r6715p01.bin
System image version: 7.1.070, Release 6715P01
Compiled Jun 06 2024 16:00:00
MPU(M) Slot 1:
Uptime is 0 weeks,0 days,2 hours,31 minutes
H3C S6825-54HF MPU(M) with 1 Processor(s)
BOARD TYPE: S6825-54HF
DRAM: 4096M bytes
FLASH: 3568M bytes
NVRAM: 0K bytes
PCB 1 Version: VER.A
PCB 2 Version: VER.A
Basic BootWare Version: 309 ------ 注②
Extended BootWare Version: 309 ------ 注②
CPLD 1 Version: 004
CPLD 2 Version: 002
CPLD 3 Version: 001
Release Version: H3C S6825-54HF-6715P01
Patch Version: None
Reboot Cause: UserReboot
[SubSlot 0] 48SFP28 + 6QSFP28
ISSU upgrade type matrix
ISSU provides two upgrade types: compatible upgrade and incompatible upgrade. Table 3 provides the approved ISSU upgrade types only between the current version and the history versions within the past 18 months. This matrix does not include history versions that are 18 months earlier than the current version, for which, no ISSU upgrade verification is performed.
For more information about ISSU, see the fundamental configuration guide for the device.
| NOTE: · To prevent routing neighbor flapping when upgrading the software from E6702 to E6706 by using step-by-step ISSU, use the irf mac-address persistent always command to enable the IRF bridge MAC address to be permanent. · When a software version earlier than R6710 is upgraded to R6710 through an ISSU, VXLAN Layer 3 traffic loss persists for longer than 2 seconds. In a lab environment, traffic loss persists for 21 seconds during a one-click upgrade and 35 seconds during a distributed upgrade. · Release 6710 and earlier versions does not support upgrading the switch to E6711 or later through ISSU. |
Table 3 ISSU compatibility list
Current version | History version | ISSU upgrade method |
S6825-CMW710-R6715P01 | S6825-CMW710-R6715 | Compatible |
| S6825-CMW710-E6712 | Compatible |
| S6825-CMW710-E6711 | Compatible |
| S6825-CMW710-R6710 | Not support |
| S6825-CMW710-E6707 | Not support |
| S6825-CMW710-E6706 | Not support |
| S6825-CMW710-E6702 | Not support |
Upgrade restrictions and guidelines
1. To prevent routing neighbor flapping when upgrading the software from E6702 to E6706 by using step-by-step ISSU, use the irf mac-address persistent always command to enable the IRF bridge MAC address to be permanent.
2. When a software version earlier than R6710 is upgraded to R6710 through an ISSU, VXLAN Layer 3 traffic loss persists for longer than 2 seconds. In a lab environment, traffic loss persists for 21 seconds during a one-click upgrade and 35 seconds during a distributed upgrade.
3. Release 6710 and earlier versions does not support upgrading the switch to E6711 or later through ISSU.
4. When an S6825-54HF device starts, the “ERROR:Bootware feature reserve bits is not zero(uiFeatureEx)” message might be printed, because the CPU check-related fields are not set. The S6825-54HF switches dot not involve the check. Therefore, the printed message does not affect the switch functionality, and you do not need to pay attention to the message.
5. Before you upgrade a version earlier than E6706 to Release 6710, identify whether a license has been activated or installed. If yes, the upgrade will cause the license to be lost or to fail to be installed. To avoid this issue, first uninstall the license and obtain uninstall key, and then re-activate the license (the DID file must be obtained again) in Release 6710 through license transfer.
If you upgrade to R6710HS03, you can use the boot-loader file command. The license will not be lost or fail to be installed.
6. Before you upgrade or down upgrade a version between E6706 and Release 6710 or install or uninstall R6710HS03 or a later version, identify whether a license has been activated or installed. If yes, first uninstall the license and obtain uninstall key, and then re-activate the license (the DID file must be obtained again) in the new version through license transfer.
7. As from E6711, password recovery capability is enabled by default in the initial configuration instead of the factory defaults on the device.
8. The S6825-54HF (with product code LS-6825-54HF-H1) are not supported in software versions earlier than R6715P.
9. As from R6715P01, lossless related features are no longer restricted to licenses and are supported by default. The display license feature command no longer displays information about lossless related features. You can still activate and install lossless licenses, without affecting the lossless features. To roll back to the R6715 version or earlier with feature-based licensing, remove the IPCC-related settings, activate lossless licenses, and then reconfigure IPCC.
Hardware feature updates
R6715P01
Added support for the SFP-25G-CSR-MM850 transceiver module.
R6715
Added support for S6825-54HF (LS-6825-54HF-H1).
E6712
The transceiver module QSFP-40G-LX4-WDM1300 was supported.
E6711
None.
R6710
None.
E6707
None.
E6706
None.
E6702
First release.
Software feature and command updates
For more information about the software feature and command update history, see H3C S6825-CMW710-R6715P01(Software Feature Changes).
MIB updates
Item | MIB file | Module | Description |
S6825-CMW710-R6715P01 | |||
New | None | None | None |
Modified | None | None | None |
S6825-CMW710-R6715 | |||
New | IP mib.docx HH3C-RRPP-MIB.docx | IP module RRPP module | Added the IP mib.docx document. Added information about the hh3cRrrpRingRecover, hh3cRrrpRingFail, hh3cRrrpMultiMaster, and hh3cRrrpMajorFault notification objects. |
Modified | HH3C-ACL-MIB.docx HH3C-PORT-SECURITY-MIB.docx | hh3cAclIPAclNamedBscTable hh3cAclIPAclNamedAdvTable hh3cSecureRalmObjects hh3cSecurePortTable hh3cSecureAddressTable | Modified object names to hh3cAclIPAclNamedBscTRangeName and h3cAclIPAclNamedAdvTRangeName. Changed the value range of the hh3cSecureRalmHoldoffTime object to 1 to 3600. The value of the hh3cSecureRalmAuthUsername object added support for spaces. Added needToKnowAuto(9) to the value range of the hh3cSecureNeedToKnowMode object. Changed the access permission, severity, and default status of the hh3cSecureAddrVlanID object to read-create, warning, and OFF, respectively. |
S6825-CMW710-E6712 | |||
New | None | None | None |
Modified | None | None | None |
S6825-CMW710-E6711 | |||
New | None | None | None |
Modified | None | None | None |
S6825-CMW710-R6710 | |||
New | First release | First release | First release |
Modified | First release | First release | First release |
Operation changes
Operation changes in R6715P01
[202402010243] Capitalized the first letter of the parameter comments for each option in hardware-resource commands
Before modification: The first letter of the parameter comments for each option in the hardware-resource commands is not capitalized.
After modification: The first letter of the parameter comments for each option in the hardware-resource commands is capitalized.
Related commands:
· hardware-resource clock-mode
· hardware-resource flex-mode
· hardware-resource routing-mode
[202403270041] Lossless related features are no longer restricted to licenses and are supported by default
As from R6715P01, lossless related features are no longer restricted to licenses and are supported by default. The display license feature command no longer displays information about lossless related features. You can still activate and install lossless licenses, without affecting the lossless features. To roll back to the R6715 version or earlier with feature-based licensing, remove the IPCC-related settings, activate lossless licenses, and then reconfigure IPCC.
[202310251525] The identifier character for commands delayed to take effect is changed
Before modification: The identifier character for commands delayed to take effect is a tilde (~).
After modification: The identifier character for commands delayed to take effect is an asterisk (*).
[202406120202] In PIM-SM, traffic can still be forwarded after the ingress replication MVXLAN configuration is deleted
Before modification: After the ingress replication MVXLAN configuration is deleted, traffic cannot be forwarded in PIM-SM, but traffic can still be forwarded in PIM-SSM.
After modification: After the ingress replication MVXLAN configuration is deleted, traffic can still be forwarded in both PIM-SM and PIM-SSM.
Operation changes in R6715
[202402260239]Setting the maximum number of supported BFD sessions
Before modification: The device supports a maximum of 256 BFD sessions.
After modification: The device supports a maximum of 512 BFD sessions.
Remarks: In software BFD mode, set the BFD detection time to at least 300ms*5 if the number of BFD sessions is greater than 64, and set the BFD detection time to at least 400ms*5 if the number of BFD sessions is greater than 256 as a best practice. Since the BFD protocol is time-sensitive, high CPU pressure on the device can lead to BFD flapping, which affects network stability. To avoid this issue, increase the BFD detection time as much as possible to enhance network stability.
In hardware BFD mode, set the BFD detection time to at least 100ms*3 as a best practice. Additionally, the hardware BFD mode has certain usage restrictions. For more information about these restrictions, see hardware BFD configuration in the configuration guides.
[202402220271] Changed the MAC authentication specification from 8K to 2K
Before modification: The MAC authentication specification is 8K.
After modification: The MAC authentication specification is 2K.
[202402061133] Support for executing the lacp transparent enable command through NETCONF
Before modification: The lacp transparent enable command cannot be executed through NETCONF.
After modification: The lacp transparent enable command can be executed through NETCONF.
[202312052129]When the free-memory space decreases below 224 MB, the minor, severe, and critical alarms are triggered. When a critical alarm occurs, the device generates a log message and then restarts.
Before modification: The minor, severe, and critical free-memory thresholds are 448 MB, 224 MB, and 128 MB, respectively. When the free-memory space decreases below 224 MB, the device generates a severe alarm and then restarts. The device generates a log message only when the free-memory space decreases below the critical free-memory threshold.
After modification: All free-memory thresholds (minor, severe, critical) are set to 224 MB. When the free-memory space decreases below 224 MB, it triggers all alarms. If a critical alarm occurs, the device logs the event and then restarts.
[202310131260]gRPC sensor path buffermonitor/commbufferusages can collect the cumulative numbers of multicast and unicast packets
Before modification: The information collected by gRPC sensor path buffermonitor/commbufferusages does not contain the MulticastTransPkts (the cumulative number of multicast packets) and UnicastTransPkts (the cumulative number of unicast packets) fields.
After modification: The information collected by gRPC sensor path buffermonitor/commbufferusages has the MulticastTransPkts and UnicastTransPkts fields.
[202303170413] hh3c-bgp4v2.mib is supported. Traps are generated upon IPv4 IPv6 or peer state changes
Before modification: hh3c-bgp4v2.mib is not supported. The system only generates traps about IPv4 peer state changes.
After modification: hh3c-bgp4v2.mib is supported. The system can generate traps about IPv4 or IPv6 peer state changes.
[202305170768] Interface traffic statistics are also displayed if the device obtains the traffic from ifInUcastPkts in the MIB
Before modification: Interface traffic statistics cannot be displayed if the device obtains the traffic from ifInUcastPkts in the MIB.
After modification: When the statistics enable command is executed in VSI view, interface traffic statistics are also displayed if the device obtains the traffic from ifInUcastPkts in the MIB.
[202306290192] Both the DRNI/Base table and MLAG/Base table of NETCONF support the ExtraVlan and ReservedVlanList fields
Before modification: The fields in the DRNI/Base table and MLAG/Base table are inconsistent in NETCONF. The DRNI/Base table contains only the ExtraVlan field. The MLAG/Base table contains only the ReservedVlanList field.
After modification: In NETCONF, both the DRNI/Base table and MLAG/Base table support the ExtraVlan and ReservedVlanList fields.
[202306290462] The MLAG/Keepalive table of NETCONF contains the TrackID attribute column
Before modification: The MLAG/Keepalive table of NETCONF does not contain the TrackID attribute column.
After modification: The MLAG/Keepalive table of NETCONF contains the TrackID attribute column.
[202307010905] Data from the device/transceivers and device/transceiverchannels sensor paths can be pushed in GPB encoding format
Before modification: When the device uses the three-layer telemetry data model architecture to push data, it does not support using GPB to encode data from the device/transceivers and device/transceiverchannels sensor paths.
After modification: When the device uses the three-layer telemetry data model architecture to push data, it supports using GPB to encode data from the device/transceivers and device/transceiverchannels sensor paths.
[202307011061] Aggregate interfaces support configuring global CRC error packet alarm parameters
Before modification: Aggregate interfaces do not support configuring global CRC error packet alarm parameters by using the ifmonitor crc-error command.
After modification: Aggregate interfaces support configuring global CRC error packet alarm parameters by using the ifmonitor crc-error command.
[202307071286] When all the specified temperature alarm thresholds are invalid, the value range for the temperature sensor number is not displayed
Before modification: When all the specified temperature alarm thresholds are invalid, the command output from the temperature-limit { hotspot | inflow | outflow } ? command displays the value range for the temperature sensor number as an invalid value.
After modification: When all the specified temperature alarm thresholds are invalid, the command output from the temperature-limit { hotspot | inflow | outflow } ? command does not display the value range for the temperature sensor number.
[202308070845] Support for statistics for all types of tunnel interfaces, including GRE, IPv4 over IPv4, and IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel interfaces
Before modification: You cannot use the display interface tunnel command to view traffic statistics for GRE, IPv4 over IPv4, and IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel interfaces.
After modification: You can use the display interface tunnel command to view traffic statistics for GRE, IPv4 over IPv4, and IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel interfaces.
[202309132121] The VLAN interface limit is 4K
Before modification: The VLAN interface limit is 2K.
Before modification: The VLAN interface limit is 4K.
[202309211555] Supported the [undo] snmp-agent trap enable igmp/mld commands in private-mode system view
Before modification: The [undo] snmp-agent trap enable igmp and [undo] snmp-agent trap enable mld commands cannot be executed in private-mode system view.
After modification: The [undo] snmp-agent trap enable igmp and [undo] snmp-agent trap enable mld commands can be executed in private-mode system view.
[202309211558] Supported the [undo] snmp-agent trap enable pim/pim6 commands in private-mode system view
Before modification: The [undo] snmp-agent trap enable pim and [undo] snmp-agent trap enable pim6 commands cannot be executed in private-mode system view.
After modification: The [undo] snmp-agent trap enable pim and [undo] snmp-agent trap enable pim6 commands can be executed in private-mode system view.
[202304120566] Supported a maximum of four DSCP mappings in the priority-flow-control dscp-mapping command
Before modification: A maximum of two DSCP mappings can be configured.
After modification: A maximum of four DSCP mappings can be configured.
[202303281927] The device monitors incorrect TPCE messages on ports and generates log messages and traps for notification
Before modification: The device does not monitor incorrect TPCE messages on ports.
After modification: The device monitors incorrect TPCE messages on ports, counts incorrect TPCE messages if any, and generates log messages and traps for notification.
[202307310775] Optimized health check for IRF members
Before modification: The health check feature does not include checks on MMUs of IRF members, port down, LACP selection, memory, CPLD status, and PHY status.
After modification: The health check feature adds checks for MMU of IRF members, port down, LACP selection, memory, CPLD status, and PHY status as follows:
· MMU fault check: Checks the number of cells occupied by MMUs for all the ports on the device. When the cell count exceeds the threshold, the health value increases by 1.
· Port down check: Checks the status of all the ports on the device. If all the ports are down during the device operation, the health value increases by 3.
· LACP selection check: Checks the status of port LACP selection on the device. If the number of unselected ports is equal to or greater than 48, the health value increases by 1.
· Memory check: Checks the free memory space. If the memory space is smaller than 128M, the health value increases by 1.
· CPLD check: Checks CPLD components on the device. If an incorrect CPLD register value is incorrect, the health value increases by 1.
· PHY check: Checks PHY components on the device. If an incorrect PHY register value is incorrect, the health value increases by 1.
[202302170010] Changed the dscp dscp-value option in the priority-flow-control dscp-mapping command from required to optional
Before modification: The dscp dscp-value option is required in priority-flow-control dscp-mapping command.
After modification: The dscp dscp-value option is optional in priority-flow-control dscp-mapping command. If this option is not specified, the DSCP value of packets is not changed.
[202207120205]Changed the execution of the undo mac-address static source-check enable command on a Layer 2 aggregate interface configured as a peer-link interface.
Before modification: To successfully forward Layer 3 traffic over the peer link, you must manually execute the undo mac-address static source-check enable command on a Layer 2 aggregate interface configured as a peer-link interface.
After modification: After a Layer 2 aggregate interface is configured as a peer-link interface, the system automatically executes the undo mac-address static source-check enable command on it.
[202210290537] ARP/ND learning and remote MAC address learning are disabled for automatic tunnels by default in an EVPN network
Before modification: To disable ARP/ND learning for tunnels in an EVPN network, execute the vxlan tunnel arp-learning disable/vxlan tunnel nd-learning disable command. To disable remote MAC address learning for tunnels in an EVPN network, execute the vxlan tunnel mac-learning disable command.
After modification: ARP/ND learning and remote MAC address learning are disabled for automatic tunnels by default in an EVPN network.
NOTE: This change only applies to automatic tunnels in an EVPN network, and does not affect manually created VXLAN tunnels.
[202209270016] MAC address learning is disabled by default
Before modification: MAC address learning is enabled by default.
After modification: MAC address learning is disabled by default.
[202401171983] uRPF loose mode and the default route configuration
Before modification: If you enable the ip urpf loose command first, and then configure a blackhole static route or configure a default route pointing to the management interface or gateway, packets with mismatched source IPs will be forwarded through the default route.
After modification: If you enable the ip urpf loose command first, and then configure a blackhole static route or configure a default route pointing to the management interface or gateway, packets with mismatched source IPs will not be forwarded.
[202302081531/202306151058] Change to the default NSR enabling status
Before modification: By default, NSR is disabled in IS-IS/OSPF/OSPFv3/RIP/RIPng/BGP/RIB/LDP view.
After modification: By default, NSR is enabled in IS-IS/OSPF/OSPFv3/RIP/RIPng/BGP/RIB/LDP view.
[202305081549] Command effect on authentication failed and fail-permit users changed
Before modification: The following commands take effect only on users passing authentication and they do not take effect on authentication failed users and fail-permit users: mac-authentication offline-detect enable, mac-authentication packet-detect enable, dot1x offline-detect enable, and dot1x packet-detect enable.
After modification: The following commands take effect on users passing authentication, authentication failed users and fail-permit users: mac-authentication offline-detect enable, mac-authentication packet-detect enable, dot1x offline-detect enable, and dot1x packet-detect enable.
Authentication failed users and fail-permit users: Users added to the critical or Auth-Fail VLAN, VSI, or microsegment after they failed the authentication on the device where dot1x critical, dot1x guest, dot1x auth-fail, mac-authentication guest, and mac-authentication critical features are configured.
[202304181578] Changes to supported algorithms in FIPS mode
Before modification: In FIPS mode, the HMAC-SHA-1 algorithm can be specified in the ntp-service authentication-keyid and sntp authentication-keyid commands for authentication.
After modification: No HMAC-SHA-1 algorithm can be specified in the ntp-service authentication-keyid and sntp authentication-keyid commands for authentication.
Operation changes in E6712
[202303171926] ip binding vpn-instance command on Layer 3 interfaces with private VLANs configured
Before modification: Layer 3 interfaces with private VLAN enabled do not support the ip binding vpn-instance command.
After modification: Layer 3 interfaces with private VLAN enabled support the ip binding vpn-instance command.
[202305250499]Maximum number of supported PBR policy nodes
Before modification: The device supports configuring a maximum of 50 PBR policy nodes.
After modification: The device supports configuring a maximum of 1024 PBR policy nodes.
[202304111948] Support of switches for sampling packets according to the entered sampling rate
Before modification: A sampler supports only the sampling rate that is 2 to the nth power, where n is the entered sampling rate. One packet is sampled from every 2 to the nth power packets.
After modification: A sampler supports sampling packets according to the entered sampling rate. For example, if you set the sampling rate to 100, one packet is sampled from every 100 packets.
[202208241350] The Instances table of MVPN NETCONF and the StaticGroups table of IGMP NETCONF changed
Before modification:
· The PmsiTunnelType column of the Instances table cannot be configured as 5 (ingress replication MVXLAN).
· The StaticGroups table (static group member) cannot be deployed.
After modification:
· The PmsiTunnelType column of the Instances table can be configured as 5 (ingress replication MVXLAN).
· The StaticGroups table (static group member) can be deployed.
Operation changes in E6711
[202208170830] Loopback testing
Before modification: Loopback testing can be enabled on an Ethernet interface by using the loopback { external | internal } command.
After modification: Loopback testing can be enabled on an Ethernet interface by using the loopback-test { external | internal } command.
[202211070131] Forwarding of unknown frames after the MAC learning limit on a Layer 2 aggregate interface is reached
Before modification: A Layer 2 aggregate interface does not support forwarding unknown frames after the MAC learning limit on the Layer 2 aggregate interface is reached.
After modification: The mac-address max-mac-count enable-forwarding command is added in Layer 2 aggregate interface view. A Layer 2 aggregate interface supports forwarding unknown frames after the MAC learning limit on the Layer 2 aggregate interface is reached.
[202208060328] Support for IP precedence marking actions in an outbound QoS policy
Before modification: The IP precedence marking action (remark ip-precedence) is not supported in a QoS policy applied to the outbound direction of an interface.
After modification: The IP precedence marking action (remark ip-precedence) is supported in a QoS policy applied to the outbound direction of an interface.
[202208081419] Support for applying a QoS policy to the outbound direction of a Layer 3 aggregate subinterface
Before modification: A QoS policy cannot be applied to the outbound direction of a Layer 3 aggregate subinterface.
After modification: A QoS policy can be applied to the outbound direction of a Layer 3 aggregate subinterface.
[202211241281] Support of NETCONF for the bgp as-path-relax ebgp/ibgp command
Before modification: In NETCONF mode, the bgp as-path-relax ebgp and bgp as-path-relax ibgp commands are not supported. You cannot use only EBGP or IBGP routes for BGP load sharing.
After modification: In NETCONF mode, the bgp as-path-relax ebgp and bgp as-path-relax ibgp commands are supported. You use only EBGP or IBGP routes for BGP load sharing.
[202302031073] Traffic statistics collection for Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces in inbound and outbound directions
Before modification: Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces do not support inbound or outbound traffic statistics collection. The counts in the input and output traffic statistics are 0 in the output from the display interface command.
After modification: Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces support inbound and outbound traffic statistics collection. The display interface command can display traffic statistics in both the inbound and outbound directions.
[202209240884] Support for the rewrite inbound tag remark 1-to-2 command
Before modification: The rewrite inbound tag remark 1-to-2 command is not supported in Ethernet service instance view.
After modification: The rewrite inbound tag remark 1-to-2 command is supported in Ethernet service instance view.
[202212030374] Support for enabling IPv6 PIM snooping in VSI view
Before modification: The ipv6 pim-snooping enable command is not supported in VSI view.
After modification: The ipv6 pim-snooping enable command is supported in VSI view.
[202212050036] Aging mechanism for ND flood suppression entries
Before modification: Before an ND flood suppression entry ages out, the device will send an NS message. If the IPv6 address of the involved VSI interface is not on the same subnet as the IPv6 address in the ND flood suppression entry, or if the VSI is not associated with a VSI gateway interface, the source IPv6 address in the NS message will be an all-zero IPv6 address. If the receiving end is a third-party device, it might mistakenly identify the NS message as an address conflict.
After modification: If the IPv6 address of a VSI interface is not on the same subnet as the IPv6 address in an ND flood suppression entry, or if a VSI is not associated with a VSI gateway interface, the device does not send an NS message before the entry ages out. The entry will be learned again from subsequent ND messages.
[202302070640] Support for NETCONF deployment of stp transparent enable/lldp transparent enable
Before modification: The stp transparent enable and lldp transparent enable commands do not support NETCONF deployment .
After modification: The stp transparent enable and lldp transparent enable commands support NETCONF deployment.
[202209160614] Support of DCI Layer 3 multicast for the SSM group address
Before modification: DCI Layer 3 multicast does not support SSM group address 232.0.0.0/8.
After modification: DCI Layer 3 multicast supports SSM group address 232.0.0.0/8.
[202301121136] Password recovery capability is enabled by default in the initial configuration instead of the factory defaults on the device.
Before modification: Password recovery capability is enabled by default in the factory defaults on the device. You can use display default-configuration, display current-configuration, and display current-configuration all to view the configuration of password recovery capability.
After modification: Password recovery capability is enabled by default in the initial configuration on the device. You can use only display current-configuration all to view the configuration of password recovery capability.
[202208111132] Changes to supported commands in FIPS mode
Before modification:
· In FIPS mode, the following commands are supported:
¡ ntp-service multicast-client
¡ ntp-service multicast-server
¡ ntp-service ipv6 multicast-client
¡ ntp-service ipv6 multicast-server
¡ ntp-service broadcast-client
¡ ntp-service broadcast-server
· In FIPS mode, the MD5 algorithm can be specified in the ntp-service authentication-keyid and sntp authentication-keyid commands for authentication.
· In FIPS mode, the value range for the version number parameter in the ntp-service unicast-peer, ntp-service unicast-server, and sntp unicast-server commands is 1 to 4.
After modification:
· The following commands are not supported in FIPS mode:
¡ ntp-service multicast-client
¡ ntp-service multicast-server
¡ ntp-service ipv6 multicast-client
¡ ntp-service ipv6 multicast-server
¡ ntp-service broadcast-client
¡ ntp-service broadcast-server
· In FIPS mode, no MD5 algorithm can be specified in the ntp-service authentication-keyid and sntp authentication-keyid commands for authentication.
· In FIPS mode, the value for the version number parameter in the ntp-service unicast-peer, ntp-service unicast-server, and sntp unicast-server commands is 3 or 4.
Operation changes in R6710
[202211111499]Added information for troubleshooting unexpected reboots due to Intel C3XXX CPU microcode
The device records Machine Check Error (MCE) register information for troubleshooting when it reboots due to Intel C3XXX CPU microcode.
[202209280283] Added support for automatic saving of power supply monitoring/power-on sequence controller fault information
Before modification: Fault information of the power supply monitoring/power-on sequence controller cannot be obtained.
After modification: The following probe commands are available for obtaining fault information of the power supply monitoring/time sequence controller. The device will save fault information of the power supply monitoring/ power-on sequence controller to the flash once every day automatically to facilitate fault locating.
The following probe commands (executed in probe view) were added:
1. debug system blackbox-info slot slot-number current: Reads fault information of the power supply monitoring/power-on sequence controller.
2. debug system blackbox-info slot slot-number flash: Reads fault information of the power supply monitoring/power-on sequence controller stored in flash.
[202212071604] Added support for NETCONF/gRPC collection of the system power consumption in real time
Before modification: The chassis and boards data collected through NETCONF/gRPC does not include the total power, residual power, and nominal power data.
After modification: The chassis and boards data collected through NETCONF/gRPC includes the total power, residual power, and nominal power data.
[202207130194]Changed the BGP VPNv4 route advertisement behavior when the peer next-hop-vpn and advertise l3vpn route are executed
Before modification: BGP VPNv4 routes are not advertised through the BGP EVPN address family even if the peer next-hop-vpn and advertise l3vpn route are executed.
After modification: BGP VPNv4 routes are advertised through the BGP EVPN address family if the peer next-hop-vpn and advertise l3vpn route are executed.
[202210171050]Restrictions for an interface to join a Layer 2 aggregation group
Before modification:
· An interface can join a Layer 2 aggregation group only when the interface meets the following requirements:
¡ It uses default VLAN configuration.
¡ Its port isolation configuration is the same as that on the aggregate interface.
· After leaving a Layer 2 aggregation group, an interface restores its VLAN configuration to the default.
After modification:
· An interface cannot join a Layer 2 aggregation group if it has different attribute configurations from the aggregate interface.
· After leaving a Layer 2 aggregation group, an interface retains the VLAN configuration inheriting from the aggregate interface.
[202406121103] Changed the conditions for the L3VNI VSI interface packet statistics feature to take effect
Before modification: The VSI interfaces of L3VNIs support interface statistics by default. You can use the display l2vpn vsi verbose and display interface vsi commands to obtain the statistics.
After modification: The VSI interfaces of L3VNIs do not support interface statistics by default. To enable the statistics feature, execute the l2vpn statistics vsi l3-vni command.
Operation changes in E6707
[202209051705] The displayed IPv6 peers in the display bgp peer command output are too long and so they are displayed in multiple lines
Before modification: A peer IP address exceeding 15 characters will be displayed in multiple lines.
After modification: A peer IP address is displayed in one line.
Operation changes in E6706
[202207121259] Changed the maximum MTU allowed for an interface to 9216 bytes
Before modification: The maximum MTU allowed for an interface is 9008 bytes.
After modification: The maximum MTU allowed for an interface is 9216 bytes.
[202208151044]Changed the traffic forwarding behavior for link aggregation management VLANs
Before modification: The unicast packets, ARP packets, or DHCP packets are load shared across the Selected ports of the aggregation group even if link aggregation management VLANs are configured.
After modification: The unicast packets, ARP packets, or DHCP packets are forwarded through only the management port if link aggregation management VLANs are configured.
[202112171336] Modified feature: Displaying kernel information upon power cycling of a device
Before modification: After you execute the reboot command to reboot the device, the device can display kernel-related commands. After you power cycle the device, the device cannot display kernel-related commands.
After modification: After you power cycle the device, the device cannot display the following kernel-related commands:
· display kernel deadloop: Displays kernel thread deadloop information.
· display kernel exception: Displays kernel thread exception information.
· display kernel reboot: Displays reboot information for the device.
· display kernel starvation: Displays kernel thread starvation information.
[202201190744/202204191564] Modified feature: Optimizing downlink interface state switchover time for Monitor Link
Before modification: In a monitor link group, when the uplink interfaces go down, the state switchover for all downlink interfaces takes a relatively long time.
After modification: In a monitor link group, when the uplink interfaces go down, the state switchover for all downlink interfaces takes less than 5 seconds.
[202203071738] Restrictions for an interface to join a Layer 2 aggregation group
Before modification:
· An interface cannot join a Layer 2 aggregation group if it has different attribute configurations from the aggregate interface.
· After leaving a Layer 2 aggregation group, an interface retains the VLAN configuration inheriting from the aggregate interface.
After modification:
· An interface can join a Layer 2 aggregation group only when the interface meets the following requirements:
It uses default VLAN configuration.
Its port isolation configuration is the same as that on the aggregate interface.
· After leaving a Layer 2 aggregation group, an interface restores its VLAN configuration to the default.
[202205301755]Modified the value range for the default CPU MAC address of a device
Before modification: The default CPU MAC address of a device is 00E0-FC00-XXXX.
After modification: The default CPU MAC address of a device is a MAC address in the range of F010-90DB-7400 to F010-90DB-740F.
[202205301735] Adjusted the limit on the MAC addresses assigned to VSI interfaces
Before modification: A maximum of 1000 MAC addresses different from the default MAC address can be assigned to VSI interfaces. Two VSI interfaces are considered to use two MAC addresses even through you assign the same MAC address to them.
After modification: A maximum of 1000 MAC addresses different from the default MAC address can be assigned to VSI interfaces. Multiple VSI interfaces are considered to use one MAC address if you assign the same MAC address to them. When Layer 3 traffic is forwarded to a VXLAN network, the traffic matches MAC addresses of VSI interfaces instead of VSIs. Therefore, Layer 3 traffic might be sent to an incorrect VSI.
Operation changes in E6702
First release.
Restrictions and cautions
Restrictions
1. When the clock node type of the device is configured as E2ETC or P2PTC, up to 10 synchronization devices can be attached to the device.
2. On an S6825-54HF switch, to use an SFP transceiver module for an SFP28 port to connect to the peer, you must disable autonegotiation on the peer.
3. Executing the following commands will cause traffic interruption on interfaces BFD flapping, and LLDP flapping:
¡ buffer apply
¡ buffer egress cell queue shared
¡ qos wred apply
¡ qos wrr weight
¡ qos wrr group weight
¡ priority-flow-control no-drop dot1p
4. After the switch is upgraded from a DRNI version (version earlier than E6705) to an M-LAG version (E6705 or later), all drni keywords are automatically replace with m-lag keywords. The switch cannot automatically replace keywords after an M-LAG version is rolled back to a DRNI version. You must prepare a configuration file with drni keywords, specify it as the startup configuration file, and reboot the switch.
An M-LAG version cannot be rolled back to a DRNI version by using the configuration replace file command. To roll back, you must prepare a configuration file with drni keywords, specify it as the startup configuration file, and reboot the switch.
The name and terms were changed for the DRNI feature as follows:
¡ The feature name was changed to M-LAG.
¡ The drni keyword was changed to m-lag or mlag.
¡ The intra-portal-port keyword was changed to peer-link.
¡ The ipp keyword was changed to peer-link.
¡ The dr keyword was changed to m-lag-interface.
For more information, see H3C S9850_6850-CMW710-E6705 Release Notes (Software Feature Changes).
5. In version E67xx/F67xx, the user-defined ACL rules configured by using the rule command do not support matching GRE packets with the specified flags. That is, the udf-format argument does not support the following values:
· gre-c0r0k1: Matches GRE packets with c=0, r=0, and k=1.
· gre-c1r0k1: Matches GRE packets with c=1, r=0, and k=1.
· gre-k1r1: Matches GRE packets with k=1 and r=1.
6. A 100G port on the device might fail to come up when a 100G DAC cable is used to connect the port to an Intel network card, for example, Intel (rainbow) Eth E810-CQDA2. As a best practice, use an AOC cable or transceiver module for connection to the Intel network card.
7. When a software version earlier than R6710 is upgraded to R6710 or E6711 through an ISSU, VXLAN Layer 3 traffic loss persists for longer than 2 seconds. In a lab environment, traffic loss persists for 21 seconds during a one-click upgrade and 35 seconds during a distributed upgrade.
8. Mirroring outgoing VXLAN packets of a port is supported only when the first mirroring group is configured to mirror outgoing packets of that port. In other cases, if the first mirroring group is configured to mirror both incoming and outgoing packets of a port, or any non-first mirroring group is configured to mirror both incoming and outgoing packets or outgoing packets of a port, mirroring outgoing VXLAN packets of that port is not supported.
9. To issue PFC commands to an interface range, make sure all interfaces in the interface range are of the same type.
Cautions
None.
Licensing
About licensing
H3C offers licensing options for you to deploy features and expand resource capacity on an as needed basis. To use license-based features, purchase licenses from H3C and install the licenses. For more information about the license-based features and licenses available for them, see H3C Switches License Matrixes.
Registering and installing licenses
To register and transfer licenses, access H3C license services at http://www.h3c.com/en/License.
For information about registering licenses, installing activation files, and transferring licenses, see H3C Switches and Routers Licensing Guide.
Obtaining license server software and documentation
To perform remote licensing, first download and install the H3C license server software.
· To obtain the H3C license server software package, click
H3C license server software package
· To obtain H3C license server documentation, click
H3C license server documentation
Open problems and workarounds
202204210001
· Symptom: Two EDs form a DR system. After the uplink or downlink on one ED fails, its traffic fails over to the other ED through the IPL. As a result, the other ED reflects the traffic back to the sender data center site and forwards multiple replicas of the traffic.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an uplink or downlink fails and traffic fails over between the EDs through the IPL.
· Workaround: None.
202205091692
· Symptom: The device erroneously deletes outgoing Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces from the multicast forwarding entries of a multicast group after an interface leaves the multicast group and joins another one.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following events occur:
a. Fast-leave processing is enabled on Layer 2 and Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces.
b. Multiple interfaces join multicast group 1.
c. An interface leaves multicast group 1 and then joins multicast group 2, and the report message for joining multicast group 2 and the leave message for leaving multicast group 1 are encapsulated into one packet.
· Workaround: Do not execute the igmp fast-leave command on Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces.
202208181547
· Symptom: The same gRPC packet type has different packet formats in different software versions (for example, R6635 and E6706).
· Condition: This symptom occurs if two switches loaded with different software version are configured to send gRPC packets of the same type to a gRPC server.
· Workaround: Configure the gRPC server to accept different packet formats of the same gRPC packet type.
202209212126
· Symptom: The PVST state is abnormal. As a result, traffic cannot be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if Device A and Device B are interconnected and run PVST, the private VLAN feature is configured on Device A, and the port private-vlan trunk secondary command is executed on the interface connecting Device A to Device B.
· Workaround: Do not execute the port private-vlan trunk secondary command on a PVST network.
202303250552
· Symptom: On an M-LAG system, a small number of packets are loss during a GIR upgrade.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if traffic is present on the AC on the M-LAG interface.
· Workaround: None.
202401040403
· Symptom: If you execute the shutdown command on the VLAN interface, hardware BFD cannot detect that the interface state has changed to down.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you use an IP address to configure a hardware BFD session on a VLAN interface, and then execute the shutdown command on the VLAN interface to shut it down.
· Workaround: Use software BFD to replace hardware BFD for detecting state changes of the VLAN interface.
202402030162
· Symptom: The dhcp snooping trust command cannot take effect on a VSI.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you perform the following operations:
a. Configure the dhcp snooping trust command in a VSI and on an AC port.
b. Undo the dhcp snooping trust command on the AC port. This operation mistakenly removes the related flag from the VSI, causing the symptom.
· Workaround: Undo the dhcp snooping trust command in the VSI, and then reconfigure the command.
202402041660
· Symptom: On the 6850 or 9850 device, even when loose uRPF check is enabled and a default route is configured with a reachable next hop, traffic forwarding may still encounter issues.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you enable loose uRPF check on the 6850/9850 device and manually set the next hop of the default route to the CPU.
· Workaround: Ensure that the manually configured default route's next hop is valid and does not point to the CPU or a blackhole address.
202401290949
· Symptom: Duplicate traffic exists in the network.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if FRR is enabled and it affects broadcast traffic in an ES network.
· Workaround: Use unicast forwarding.
202310301520
· Symptom: BFD flapping occurs with a certain probability.
· Condition: This symptom occurs in an M-LAG network where devices that support hardware BFD are configured. If you shut down the physical interface directly connected to a downlink device to have the reachable path traverse the IPL, BFD flapping occurs.
· Workaround: N/A.
202402200464
· Symptom: The device experiences an abnormal reboot.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when multiple interfaces on the device are configured with sFlow sampling and the interfaces receive a large amount of traffic.
· Workaround: In interface view, configure a higher sFlow packet sampling rate to reduce the number of packets sampled by sFlow.
202403070954
· Symptom: When both ARP snooping and ARP suppression are configured on a VSI, the local ARP flood suppression entries migrate from the M-LAG interface to the peer-link interface, and static ARP snooping entries are generated. As a result, ARP entries do not have outgoing interfaces. The same situation can also occur with the ND protocol.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ARP snooping and ARP suppression are configured, and endpoint migrate from the M-LAG interface to the single-homed mode on an EVPN+M-LAG network.
· Workaround: Disable ARP snooping, or prevent endpoints from switching to the single-homed mode.
202403090085
· Symptom: Traffic is interrupted on the M-LAG interface due to the dispute guard feature.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ In the network configured with both the spanning tree protocol and M-LAG, upgrade the M-LAG system by using the traditional method: first upgrade the secondary member device, and then disable the downlink interfaces on the primary member device.
¡ The rlink reliability settings are different between versions before and after upgrade.
· Workaround: Before upgrade, execute the undo stp dispute-protection command to disable the dispute guard feature on the M-LAG device.
202401051728
· Symptom: When an FTP client copies a file from the device, the following RAS alarm is generated: EEPROM read/write failed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device acts as an FTP server and the connection is established for the first time.
· Workaround: None.
202403181643
· Symptom: Failed to log in to the device through Telnet.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you enter ASCII code 19 in decimal notation (default stop character for PTY) in the password for Telnet login, which causes login timeout and failure to close the Telnet connection.
· Workaround: Do not enter ASCII code 19 in decimal notation when you enter a password for login.
202404130067
· Symptom: If ECMP contains 128 next hops, and you shut down one or multiple interfaces, a number of 2 to 10 packets might be lost.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if ECMP contains 128 next hops, and you shut down one or multiple interfaces.
· Workaround: If ECMP contains too many next hops, do not shut down interfaces.
202405060191
· Symptom: The Ethernet link aggregation mode LBN group feature does not take effect when the following conditions are met:
¡ Both the ECMP-mode LBN group feature and the Ethernet link aggregation mode LBN group feature are configured.
¡ LBN group member interface delete actions are performed (such as Layer 2/3 mode switching, port split and combination, and removal of LBN group member interfaces).
· Condition: This symptom might occur when the following conditions are met:
¡ Both the ECMP-mode LBN group feature and the Ethernet link aggregation mode LBN group feature are configured.
¡ LBN group member interface delete actions are performed (such as Layer 2/3 mode switching, port split and combination, and removal of LBN group member interfaces).
· Workaround: Do not configure both the ECMP-mode LBN group feature and the Ethernet link aggregation mode LBN group feature or perform LBN group member interface delete actions such as Layer 2/3 mode switching, port split and combination, and removal of LBN group member interfaces.
202406200682
· Symptom: The switch reboots due to memory exhaustion after the buffer transient-capture enable command is executed on an interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you specify an ACL in the command and the captured packets are not TCP or UDP packets.
· Workaround: Do not specify an ACL in the buffer transient-capture enable command if the captured packets are not TCP or UDP packets.
202406261321
· Symptom: In a multicast VXLAN, the switch fails to forward multicast traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Execute the reset multicast forwarding-table command or stop traffic forwarding after traffic is switched to the data group.
b. Forward traffic again when multicast forwarding entries are cleared.
· Workaround: Do not configure a data group.
202406190225
· Symptom: In a multicast VXLAN, the switch fails to forward traffic from the source to a receiver.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ An L3 VXLAN ID is configured for the public instance.
¡ Multicast VXLAN is not configured for the public instance.
· Workaround: Configure Multicast VXLAN for the public instance.
List of resolved problems
Resolved problems in R6715P01
202401161819
· Symptom: A device fails to roll back BGP configuration.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the AS number of a BGP peer changes after BGP configuration rollback.
202302141258
· Symptom: On an EVPN M-LAG system, learned dynamic ND entries never age.
· Condition: This symptom occurs after an M-LAG member device is rebooted.
202312271152
· Symptom: The BFD session flaps once if the statistics l3-packet enable inbound command is configured on a network enabled with BFD.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the statistics l3-packet enable inbound command is configured on a network enabled with BFD.
202401050745
· Symptom: The M-LAG table reports an error.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you read MIB node information.
202401151855
· Symptom: After you configure an inband management VLAN by using the in-band management vlan command, packets on the corresponding VLAN interface should only pass through hardware forwarding. However, ARP packets are actually copied and sent to the controller during hardware forwarding.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if two OpenFlow instances on the device both match packets of the specified VLAN interface, and the corresponding VLAN is configured as the inband management VLAN for one instance.
202402020349
· Symptom: Broadcast packets passing through a real tunnel are not dropped.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if broadcast packets pass through a real tunnel in an M-LAG VXLAN network.
202312011980
· Symptom: The device restarts abnormally.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a large amount of route oscillation occurs.
202404021174
· Symptom: No output is displayed after you execute the display transceiver power command.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you execute the display transceiver power command to power information for transceiver modules.
202403080772
· Symptom: The device restarts abnormally.
· Condition: This symptom might occur in the following conditions:
¡ The device uses gRPC to subscribe to RoCEv2 traffic events and reports flow tables containing generated RoCEv2 traffic via gRPC.
¡ The gRPC process restarts abnormally.
202403120391
· Symptom: The if-match any command in a class-behavior association cannot match IPv4 packets in a QoS policy applied to the outbound direction.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Configure a QoS policy with three class-behavior associations. The first class-behavior association is used to match any packets (if-match any), the second class-behavior association is used to match IPv4 packets, and the third class-behavior association is used to match IPv6 packets.
b. Enable statistics collection for outgoing Layer 3 packets on an interface and apply the QoS policy to the outbound direction of the interface.
c. Delete the second class-behavior association.
202402060902
· Symptom: Failed to deploy a static ARP entry that contains a VSI. However, when the device starts with the configuration, the configuration succeeds but does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure a static ARP entry that contains a VSI not bound to a tunnel interface.
202402260716
· Symptom: After you execute the arp route-direct advertise tag tag-value command on an interface and ARP advertises ARP entries to generate direct routes, ARP does not update route management information if you edit the route tag or preference for the ARP-advertised direct routes.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you edit the route tag or preference for the ARP-advertised direct routes after you configure ARP direct route advertisement on an interface.
202401111026
· Symptom: If you repeatedly use the evpn edge group command to configure and delete the virtual ED address, tunnel address information might be incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ In an EVPN VXLAN network, BGP is configured with multiple RR-oriented peers. The source addresses used for peer session establishment are not specified on those peers.
¡ The evpn edge group command is repeatedly use to configure and delete the virtual ED address.
202401311793
· Symptom: The sysmand process abnormally quits and the device generates core files.
· Condition: This symptom might occur is a corrupted .bin file is uploaded to the device.
202401230998
· Symptom: MAC learning does not take effect on an interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you disable MAC learning globally, perform port splitting or merging, and then enable MAC learning globally.
202402211655
· Symptom: Ports on the device do not recognize Alibaba or ACT 100G ZR4 modules.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you install an Alibaba or ACT 100G ZR4 module on a port of the device.
202403130948
· Symptom: After running for a period of time, the PTP loses clock and fails to synchronize the time, with an offset exceeding 400,000 ns per second if the frequency offset remains below 10 ns after PTP convergence and clock source lock.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the frequency offset remains below 10 ns after PTP convergence and clock source lock.
· Remarks: After the clock converges to a narrow range of accuracy, frequency offset adjustments fail to take effect. This causes abnormal accumulations of frequency values, which continuously build up and eventually trigger a frequency reset callback. This causes the clock to become unlocked and unable to recover.
202402201209
· Symptom: The multicast packets with a group address in the 224.0.0.0 or 224.0.1.0 network are dropped in a VLAN.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if dropped unknown multicast data packets is enabled for the VLAN.
202403211980
· Symptom: An interface failed to come up on the device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device is inserted with a third-party 100G LR4 long-reach transceiver module.
· Remarks: The impacted modules include LR4, ER4L, DWDM2, ZR4, DR1, LR1, and FR1.
202208050810
· Symptom: The protocol queue on the device is congested and has packet loss, causing frequent IS-IS flapping
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
a. The controller has issued an ACL to filter DHCP messages sent to the controller.
b. A large number of packets with unreachable destination IPs are received from the VXLAN tunnel interface.
202404291067
· Symptom: ND/IGMP protocol packets are forwarded abnormally on blocked ports.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist on the overlay network:
a. The spanning tree protocol is enabled globally and an AC interface is created on the device.
b. An interface or aggregate interface is blocked by STP.
202404090532
· Symptom: The ND outgoing interface learned by the gateways on both M-LAG member devices is the peer-link interface. As a result, a traffic loop is generated and traffic fails to be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed in a VLAN M-LAG network:
a. The gateways on both M-LAG member devices have local ND proxy enabled.
b. An M-LAG member device initiates ND detection to an unknown IPv6 host.
202404291194
· Symptom: Failed to bind a VSI to a VXLAN ID, but no log indicating a failure caused by hash conflict is printed.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when you configure a large number of ACs or VSIs.
202404100492
· Symptom: When you configure the ip load-sharing mode per-flow command, you can specify the algorithm, tunnel, and five-tuple parameters together. However, if you delete the algorithm, tunnel, or five-tuple configuration, the other per-flow configurations will also be deleted. For example, after you execute the undo ip load-sharing mode per-flow algorithm command, the other per-flow configurations will be deleted, including the tunnel and five-tuple configurations.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when you delete the configuration of any parameter in the ip load-sharing mode per-flow command.
202404220719
· Symptom: Traffic forwarding based on ECMP routes fail.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if IPv6 routes with prefixes longer than 64 bits form ECMP routes when the hardware resource mode is IPv6-64.
202405061402
· Symptom: LBN configuration fails to take effect after upgrading the primary and backup in an IRF environment.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the interfaces acting as group members are Layer 3 interfaces.
· Remarks: If this issue occurs after the device is upgraded from R6715 or an earlier version to R6715P01, you can delete the LBN configuration, and then re-configure LBN configuration.
202401041128
· Symptom: After the external egress recovers from a fault, multicast traffic is interrupted for a long period of time when the primary border device resumes carrying multicast traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
¡ Multicast traffic from an external source is forwarded to leaf devices through the border devices of two DCs in a cross-DC EVPN network. In normal conditions, multicast traffic is forwarded through the primary border device.
¡ When the external egress on the primary border device experiences a fault, multicast traffic is forwarded to the leaf devices through the secondary border device and the ED DCI path.
202406121282
· Symptom: After you configure flow sampling on an interface to sample the inbound packets and configure the sampling rate, the outbound packets of the interface are also sampled.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure sFlow to sample the inbound packets of an interface.
202406121195
· Symptom: The received VLAN-tagged packets do not carry VLAN tags after they are sampled by sFlow.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure sFlow sampling on a main Layer 3 Ethernet interface and configure IP addresses for its Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces.
202405060248
· Symptom: In an M-LAG network, when the peer-link flaps, messages about configuration inconsistency are reported, but the display m-lag consistency command shows no relevant information.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when the M-LAG interface does not exist or is not associated with a VSI and the peer-link interface flaps.
202405292207
· Symptom: In an EVPN+IRF network, two leaf nodes use the same MAC address. As a result, the MAC address entries of the other leaf nodes point to incorrect destinations.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the MAC address synchronized from the EVPN remote device is overridden when the subordinate IRF member device synchronizes its MAC address to the master IRF member device. As a result, the deletion and addition of the local MAC address might not be timely reported.
202405131762
· Symptom: Peer device Leaf2 did not correctly record the proxy status of Leaf1, leading to the erroneous forwarding of IGMP general query packets to Leaf1, resulting in superfluous packets.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when you first set up an EVPN network, and then execute the igmp-snooping proxy enable command on Leaf1.
202401250136
· Symptom: The device might fail to withdraw routes on a peer.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
a. First-AS-number check is enabled for EBGP routes on the device by the peer-as-check enable command, and the device has multiple peers.
b. The device updates and withdraws BGP routes simultaneously.
Resolved problems in R6715
202306070923
· Symptom: After you execute the undo ospf command on a device in a certain large-scale network, the kernel of the device gets stuck, and the device reboots unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed on a certain large-scale network with a large number of devices interconnected by using IGP:
a. Establish BGP and IBGP neighbors among these devices through BGP RRs.
b. Enable the label capability and labeled routes.
c. Execute the undo ospf command.
202306152080
· Symptom: VRRP cannot learn unicast ARP entries with the destination MAC addresses as VRRP virtual MAC addresses.
· Condition: This symptom occurs on an M-LAG+VRRP network.
202212221227
· Symptom: A security risk exists on the switch.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a self-signed certificate is saved in the PKCS#12 certificate file format without an encryption password and can be parsed by a third-party tool.
202306082492
· Symptom: After the configuration of a device is rolled back or a device is rebooted with configuration, ARP requests will be broadcast and Layer 3 unicast packets will be transparently transmitted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a large number of Layer 3 Ethernet interface exist on the device, and the configuration of the device is rolled back or the device is rebooted with configuration.
202305291896
· Symptom: During a step-by-step ISSU on an IRF fabric, the convergence time of some traffic is 2 seconds.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the configuration file of a member device include EVPN and VXLAN settings.
202312062097
· Symptom: Network congestion occurs when inter-VPN traffic is repeatedly forwarded by the device-internal loopback interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if traffic matching static route configuration is forwarded through repeated routing table lookups in two VPN instances on the same device. Because the TTL of packets is not decreased by 1 when they pass through a loopback interface, traffic loop forwarding occurs, resulting in congestion.
202312191442
· Symptom: Timeout occurs when NETCONF retrieves the full configuration of the device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if NETCONF retrieves the full configuration of the device about 1000 times.
202312270219
· Symptom: A port is down, but it still can forward traffic normally.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the port firmware malfunctions and the port does not have STP configured.
202401080838
· Symptom: The class-based accounting action in a QoS policy cannot count IPv6 traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the if-match any clause is configured in the traffic class.
202401101931
· Symptom: Next hop loss occurs after a refresh of the tunnel next hop.
· Condition: The symptom occurs if you configure link-delay on the tunnel-side interface, which causes the interface to disconnect and then triggers a tunnel next hop refresh.
202402061134
· Symptom: Authentication-related configuration fails to deploy.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when you use NETCONF to configure authentication settings.
202312260590
· Symptom: Obtaining the full device configuration through NETCONF timed out.
· Condition: This symptom occurs after you obtain the full device configuration through NETCONF for more than 1000 times.
202311230241
· Symptom: The following problems might occur with a low probability:
¡ The PVID of an aggregate interface is 1. However, VLAN 1 is not permitted on the aggregate interface, and the VLANs in STG 1 are not permitted either.
¡ The state of an aggregate interface is forwarding in the display stp brief command output, but the state of the corresponding aggregation member ports is block in STG 1 in the hardware.
¡ An AC created on an aggregate interface cannot forward traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the PVID of the aggregate interface is in STG instance 1 and the aggregate interface does not permit any VLANs in STG instance 1.
202310230059
· Symptom: For the C2000 device, the flash file system changes to read-only with a low probability, which might cause configuration file saving failures.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if USB2244 is faulty, which causes the flash file system to change to read-only.
202309111514
· Symptom: On an EVPN network, rule ARP entries are incorrectly deleted.
· Condition: This symptom might occur in one of the following conditions:
¡ The number of ARP entries has reached the upper limit and the device cannot learn new ARP entries.
¡ In an M-LAG overlay scenario, ARP packets are received by peer-link interfaces. ARP learning fails because the M-LAG interfaces take priority to learn ARP entries.
¡ If you have configured ARP attack protection features on the device, these features might incorrectly delete valid ARP entries.
¡ Gratuitous ARP packets are injected to the device with gratuitous ARP packet learning unconfigured.
¡ The source and destination IP addresses in the ARP packets reside on different network segments and proxy ARP is not configured.
202305311737
· Symptom: The mac-address mac-learning pdu command fails to be configured if interface splitting is configured first after the device starts up and then the mac-address mac-learning pdu command is configured.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if interface splitting is configured first after the device starts up and then the mac-address mac-learning pdu command is configured.
202309271663
· Symptom: After the ND detection feature is enabled in VLAN view and global static IPSG bindings are configured, ND messages from the VLAN cannot be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if global static IPSG bindings are configured and no permit rules are configured on the related VLAN interface.
202204121359
· Symptom: During a step-by-step ISSU, the OSPFv3 neighbor of a Layer 3 aggregate interface flaps.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The upgrade is from F6701L01 to E6702.
¡ The irf mac-address persistent timer command is executed.
202311171824
· Symptom: The device restarts because the ports on the device fail to come up properly.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a module is inserted during the device operation.
202309260387
· Symptom: The ovsdb-server process abnormally exits with a low probability.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the controller deploys the configuration.
202209230460
· Symptom: If multiple dial-in sessions in gRPC gNMI mode issue subscriptions concurrently, a session might fail to receive data.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if multiple dial-in sessions in gRPC gNMI mode issue subscriptions concurrently.
202211140499
· Symptom: OSPF BFD sessions flap repeatedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you use borrowed loopback interface addresses to establish OSPF neighbor relationships, configure BFD for OSPF, and then reboot the device.
202304120566
· Symptom: Only a maximum of two DSCP mappings in one priority-flow-control dscp-mapping command can take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when you configure more than two DSCP mappings in one priority-flow-control dscp-mapping command.
202110191607
· Symptom: When the initialization of the CPU management port fails on the S6850, S9850, S9820, S9820-8C, or S6805 device, the output from the display interface command still shows inbound statistics and CRC errors.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the initialization of the CPU management port on the S6850, S9850, S9820, S9820-8C, or S6805 device has failed.
202303250672
· Symptom: After the vxlan vlan-based command is executed, a Layer 2 aggregate interface of the access type is moved between VLANs. As a result, ACs cannot be created on the aggregation member ports based on the new VLAN ID.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ The vxlan vlan-based command is executed.
¡ The link type of the Layer 2 aggregate interface is access.
¡ The Layer 2 aggregate interface is configured as an edge port with the lacp edge-port command.
¡ Member ports of the Layer 2 aggregate interface are in individual state.
202305290148
· Symptom: The device cannot forward untagged traffic correctly on a VXLAN network.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if VXLAN is configured and the dhcp snooping trust tunnel command is executed.
202306021684
· Symptom: The hh3cStackBoardRole node in the MIB Browser can obtain only one role from all member devices in an IRF fabric.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when you use the MIB Browser to view the information of the hh3cStackBoardRole node for the IRF fabric.
202306131838
· Symptom: The device generates the following alarm message: Operation failed. The minimum interval between IRF bridge MAC address modifications is 30 seconds. Please try again later.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when you execute the irf mac-address command to configure the IRF bridge MAC address.
202306141412
· Symptom: The controller disconnects from the device during patch installation and the NETCONF over SOAP configuration on the device is lost.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when you install a patch by using the controller, which restarts the xmlcfgd process.
202306161118
· Symptom: After a Layer 2 interface is rolled back to a member port of a Layer 3 aggregation group enabled with PIM-SM, it fails to forward to multicast traffic because no VFP ACL is deployed to it.
· Condition: This symptom occurs after a Layer 2 interface is rolled back to a member port of a Layer 3 aggregation group enabled with PIM-SM.
202306190397
· Symptom: Traffic forwarding exceptions occur on a 1G interface or an interface negotiated to 1G.
· Condition: This symptom might occur on a 1G interface or an interface negotiated to 1G.
202307041942
· Symptom: No prompt message is displayed when you configure multiport ARP entries or multiport MAC entries without specifying a service loopback interface on an underlay network. The entries cannot be deployed to the hardware.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you do not specify a service loopback interface when you configure multiport ARP entries or multiport MAC address entries.
202307111015
· Symptom: A QoS policy applied to an aggregate interface does not take effect on new member ports that join the aggregation group.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you apply a QoS policy to an aggregate interface and then add new ports to the aggregation group.
202307111828
· Symptom: The arp snooping enable command failed to be executed in VLAN view on some products and the system prompted an operation failure.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when you execute the arp snooping enable in VLAN view on some products. The command has a command word that specifies RARP packet redirection to the CPU, which is not supported by some products.
202307210952
· Symptom: On an M-LAG system with VRRP configured, the backup device in a VRRP group cannot learn ARP entries.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the backup device receives ARP unicast packets.
202308110863
· Symptom: After sending ICMP redirect messages and sending ICMPv6 redirect messages are enabled synchronously, they always function even if you disable them.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if both the ip redirects enable command and the ipv6 redirects enable command are executed synchronously to enable sending ICMP and ICMPv6 redirect messages.
202308141250
· Symptom: When DHCPv6 relay agent features are configured on a device, the device delivers traversing unicast IPv6 DHCP packets to its CPU, causing packet loss.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if DHCPv6 relay agent features are configured on the device.
202309041408
· Symptom: The device reboots repeatedly and cannot start up correctly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you perform the following operations:
a. Configure PTP in INT-PTP mode and then save the configuration and reboot the device.
b. Modify the hardware-resource firmware mode to INT-BFD.
202309042691
· Symptom: A BFD session flapping occurs.
· Condition: This symptom occurs with a certain probability if you bring up a device interface with the undo shutdown command to perform bulk software BFD negotiation and bring up the BFD session. The BFD session might come up after a flapping.
202309071510
· Symptom: The primary device and the secondary device in an M-LAG system have different DHCP snooping entries within a period.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if DHCP snooping is disabled when the peer-link interfaces are flapping and is enabled after peer-link interface flapping.
202309071523
· Symptom: DHCPv6 commands fail to be deployed after users come online and the DHCP process starts
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the address pool uses the prefix configured by the ipv6 prefix command and the network prefix command is configured in the address pool.
202309110535
· Symptom: When an IRF fabric forwards traffic across member devices, it cannot obtain outbound traffic statistics for a GRE tunnel interface even if that interface is configured with the statistics l3-packet enable outbound command.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the IRF fabric forwards traffic across member devices and cannot match the next hop class ID of the output interface for collecting outbound statistics for tunneled traffic.
202309110575
· Symptom: An IPv4 ACL will be deployed if a traffic class in a QoS policy applied to the outbound direction is configured to match the EtherType.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a traffic class in a QoS policy applied to the outbound direction is configured to match the EtherType.
202309111302
· Symptom: The device sends ICMP error packets if only Layer 2 multicast is configured.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you enable only Layer 2 multicast, enable the IGMP snooping querier, and enable sending ICMP destination unreachable messages.
202309120444
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, a host still receives multicast data from an output interface after sending a leave message.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the output interface is an aggregate interface.
202309132177
· Symptom: After an IRF master/subordinate switchover, the MAC address of a VLAN interface repeatedly moves among the physical interfaces in that VLAN if BFD MAD is enabled on that VLAN interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you enable MAC move on an IRF fabric.
202309261948
· Symptom: Statistics about ECMP resources are incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if ECMP flaps.
202306060568
· Symptom: Other routers cannot learn the OSPF external routes and default routes advertised by a device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if no interfaces are added into the OSPF process on the device and the nssa default-route-advertise command is configured in the OSPF process.
202305091145
· Symptom: The ARP entries learned through LLDP on the local device are refreshed, which might cause route flapping.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when the description information of the peer device, such as the system name, is changed.
202305190212
· Symptom: A new switch ID does not take effect after modification.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the mirror-to interface command is executed with the erspanv3 and sampler keywords to modify the switch ID in ERSPANv3 mirroring packets.
202306072180
· Symptom: On a physical interface of a DCI ED, cross-subnet rate limiting does not take effect on traffic that carries an unknown inner source MAC address.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if L2VPN is enabled, tunneled traffic with an unknown inner source MAC address is received, and cross-subnet rate limiting is configured on a physical interface.
202307131776
· Symptom: In the IRF environment, the BFD session established on the backup card interface repeatedly flaps,
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you reboot the device after configuring BFD session parameters in the IRF environment.
202307211459
· Symptom: CFD packets are not forwarded correctly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you execute the cfd enable command globally, and then execute the undo cfd enable command for the device.
202307260983
· Symptom: The virtual IP address of the IPv4 VRRP group configured on a VLAN interface cannot be pinged.
· Condition: This symptom occurs with a low probability if you repeatedly enable and disable the spanning tree protocol globally when the spanning tree operates in PVST mode in a network configured with M-LAG and VRRP.
202309121717
· Symptom: The spanning tree status displayed in the output from the display stp command is inconsistent with the actual condition.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you add a port that does not belong to any STG to the M-LAG aggregation group.
202207071638
· Symptom: When the device is enabled with BGP Graceful Restart (GR) capability and has BGP sessions to non-H3C devices, the GR feature does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when the following conditions exist:
¡ The device is enabled with BGP GR capability and has established BGP sessions to non-H3C devices.
¡ The value for the Forwarding State(F) field is 0 in the OPEN messages from those non-H3C devices. In this situation, if you use the display bgp peer verbose command on the local device, the Forwarding State preserved by Peer for following Address families field in the command output is empty.
202212010145
· Symptom: Member devices in an EVPN M-LAG system do not synchronize ARP flood suppression entries.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if ARP flood suppression entries move from a remote VTEP to a single-homed interface of an M-LAG member device.
202303131032
· Symptom: In the output of the display ipv6 interface command, the IPv6 address, interface name, and VPN fields are displayed on different lines, which should be displayed on the same line.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you execute the display ipv6 interface command.
202304100930
· Symptom: Packets matching a QoS policy applied to the outbound direction of a VSI interface are mistakenly dropped.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following operations are performed:
a. Apply QoS policies to the outbound direction of two or more VSI interfaces.
b. Apply a QoS policy to the outbound direction of a physical interface.
202304191794
· Symptom: BFD flapping occurs on the device with a low probability.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a VSI interface receives a large number of ARP or RARP packets in an EVPN network, and VSIs or VSI configuration is changed.
202305110201
· Symptom: On a multicast VXLAN network, multicast traffic cannot be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device starts with the factory defaults and then you configure multicast VXLAN in the following order: first configure tunnels and VSIs, and then configure multicast.
202305200097
· Symptom: The xmlcfgd process on the device has exceptions after a patch is loaded on the device. Then, the controller cannot be reconnected to the device or the NETCONF feature has exceptions.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a patch for the xmlcfgd process is loaded on the controller connected to the device.
202306152032
· Symptom: Static MAC address entries are configured for overlay MAC addresses that have been dynamically learned by an M-LAG member device, and the static MAC address entries cannot be synchronized to the M-LAG peer.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if static MAC address entries are configured for overlay MAC addresses that have been dynamically learned by the M-LAG member device.
202307181232
· Symptom: The peer-link interface incorrectly learns ARP entries. As result, remote IP addresses on the same subnet might fail to be accessed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if proxy ARP is configured for the M-LAG dual-active VLAN gateways or VRRP, and automatic ARP scanning is enabled by using the arp scan auto enable command.
202307200892
· Symptom: Due to hash conflicts, the creation of AC-attached interfaces fails without any log prompts on the device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if a large number of AC-attached interfaces are configured on the device.
202307210976
· Symptom: After you configure the network command in OSPF view, OSPF neighbor relationship establishment fails.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you perform the following operations:
a. Add or remove the ospf 1 area and ospf network-type configurations.
b. Configure the network command in OSPF view.
202309041301
· Symptom:On an M-LAG system, packets received on an M-LAG interface are forwarded over the peer link and then forwarded out of the M-LAG interface in the same M-LAG group.
· Condition:This symptom might occur if an M-LAG aggregation group flaps.
202309070112
· Symptom: On an S6805-54HT switch, for port 51 and port 52, the LEDs are lit only when the breakout interfaces 51:1 and 52:1 are connected.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if breakout interfaces 51:1 and 52:1 are disconnected and any other interfaces are connected.
202402061677
· Symptom: IPv4 traffic fails to be forwarded correctly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist on an MVXLAN network:
¡ Configurations exist in both MVXLAN IPv4 address family view and MVXLAN IPv6 address family view.
¡ When IPv4 and IPv6 traffic is forwarded correctly, delete the configuration in MVXLAN IPv6 address family view.
202401170145
· Symptom: When you view electronic label information of power modules on the S6805 and S6825 devices, NONE might be displayed with a low probability.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you restart the device after the power modules are installed on the device or you re-install the power modules.
202402060953
· Symptom: The configured static ARP entry fails the check.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you specify a VSI and a tunnel interface when configuring a static ARP entry but no binding exists between them.
202309110615
· Symptom: BGP flaps on a device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist on the device:
a. The device receives a large number of ipv4 BGP attack packets with TTL=1.
b. The rate of delivering BGP packets to the CPU exceeds the upper hardware limit.
202310100263
· Symptom: After the m-lag extra-vlan command is executed, the M-LAG member devices cannot synchronize ARP or ND entries for the extra VLANs through the peer-link interface.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if some M-LAG interfaces are not assigned to the extra VLANs, and the device is rebooted or the peer-link interface flaps.
202309090022
· Symptom: When NETCONF is used for device management and configuration, no information is displayed when you perform the operation of reading all device configurations.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if only automatic tunnels exist and you execute the get-bulk operation to obtain the tunnel configuration.
Resolved problems in E6712
202305041124
· Symptom: The switch cannot obtain an IPv6 address after it is rebooted, and IPv6 automatic deployment fails.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the controller deploys the configuration to change the hardware resource mode during automatic deployment and the controller does not assign a fixed IPv6 address.
202305101923
· Symptom: The system sends probe packets out of the VSI interface to the IP address in an aging ARP suppression entry even if the interface has been down.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you enable ARP suppression for a VSI and the VSI interface is down.
202305120015
· Symptom: Packets matching a QoS policy applied to the outbound direction of a VSI interface are mistakenly dropped.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following operations are performed:
a. Apply QoS policies to the outbound direction of two or more VSI interfaces.
b. Apply a QoS policy to the outbound direction of a physical interface.
202305180008
· Symptom: In an EVPN or VXLAN distributed gateway network, when the device receives a tunneled packet with a source IP address the same as a VSI interface address, the device will reply with a gratuitous ARP response, which can lead to high CPU usage.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the distributed gateways perform ARP probing in response to traffic.
202305120953
· Symptom: In a VXLAN network, VXLAN tunnel interfaces are not outgoing interfaces in multicast forwarding entries, and multicast forwarding fails.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if VXLAN tunnels and VSIs are configured prior to multicast forwarding.
202305122075
· Symptom: In a VXLAN network, traffic loss persists for longer than 2 seconds during an ISSU load.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an ISSU load or active/standby MPU switchover occurs in a VXLAN network.
202305041113
· Symptom: The BFD session cannot come up.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if frequent flapping occurs for the physical interfaces attached to the link associated with the BFD session.
202305220010
· Symptom: In an EVPN network, the CPU usage of a leaf device is very high.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if attached devices move between leaf devices, and the leaf device is enabled with ARP suppression.
202305232222
· Symptom: Packets that enter the device from an AC on a Layer 2 aggregate interface cannot be forwarded out through the Layer 2 aggregate interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the aggregate interface has multiple member ports and the Selected states the member ports change when the AC is configured.
202304070641
· Symptom: In the display mac-address statistics command output, the Total Multicast and Multiport MAC Addresses Available field displays 4000.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you execute the display mac-address statistics command to display MAC address table statistics after the device is rebooted.
202304060743
· Symptom: A MAC authentication user is still online and cannot go offline after the offline detection timer expires.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a MAC authentication user stops sending traffic after coming online successfully. After the offline detection timer expires, execute the display mac-authentication command to identify whether the MAC authentication user is offline.
202305041120
· Symptom: With VLAN-based VXLAN assignment enabled, after the permitted VLAN is modified on a Layer 2 aggregate interface of the access type, the Ethernet service instance corresponding to the VLAN cannot be generated.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you modify the permitted VLAN on the Layer 2 aggregate interface of the access type that is configured as an edge aggregate interface.
202305200364
· Symptom: In the configuration file, the key for BGP MD5 authentication is displayed in plain text.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the value for the PasswordType field in the BGP CfgSession table is 2.
202305180009
· Symptom: Route flapping occurs when ARP entries are updated due to LLDP information modification.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the LLDP packet length changes on the peer. For example, the sysname of the peer is edited.
Resolved problems in E6711
202212050034
· Symptom: In an EVPN VXLAN network, a third-party device with an AC attached reports IPv6 address conflicts.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the peer H3C device has ND flood suppression enabled for the related VSI and no VSI interface is assigned to the VSI.
202207011235
· Symptom: When MVXLAN supports M-LAG, the packets sent out of an M-LAG device are more than those received.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a large number of entries are configured on the M-LAG device, and the DCI and source configurations repeatedly change.
202208190593
· Symptom: A QoS policy fails to be applied to a Layer 2 aggregate interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the traffic behavior is configured with a traffic policing action.
202208050810
· Symptom: The Effective count field is always displaying 0 in the output from the display grpc verbose command.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you execute the display grpc verbose command after configuring periodical sampling in gRPC dial-out mode.
202302130821
· Symptom: When an aggregation member port comes up, its state will transition to Selected, then Unselected, and finally back to Selected again.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Configure the short LACP timeout interval on the port.
b. Execute the link-delay down 5 command to configure the link state change suppression interval as 5 seconds on the port.
c. Bring up the port.
202302140214
· Symptom: Packets that are flow-mirrored to an interface are encapsulated abnormally.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you specify the IPv6 encapsulation method and configure a sampler when you configure flow-mirroring traffic to an interface.
202302131035
· Symptom: Data collected in the ifmgr/trafficstatistics/interfaces path is abnormal. The collected data at the NMS side displays a jagged line in the data chart.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when you specify the ifmgr/trafficstatistics/interfaces data collection path in gRPC dial-out mode.
202301170521
· Symptom: Lower-layer ACL entries of OpenFlow entries are lost after VMs migrate, and some traffic fails to be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if VMs migrate.
202302031011
· Symptom: The buffer apply command does not take effect on interfaces on a subcard or new breakout interfaces.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you insert a subcard or split an interface after executing the buffer apply command.
202302200113
· Symptom: In an M-LAG system, after an ND entry migrates between the member devices, its outgoing interface becomes incorrect, and traffic interruption occurs.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if an M-LAG member device reboots and synchronizes the ND entries of the M-LAG peer, and then an ND entry migrates.
202209291014
· Symptom: Duplicate multicast packets exist after one of the two outgoing tunnels for a static multicast group is flapped.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the static multicast group has more than 128 VSI interfaces as the outgoing interfaces and the actual outgoing interface is a tunnel interface.
202301120577
· Symptom: After an incremental patch is uninstalled, the display boot-loader command does not display information about a non-incremental patch.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if both an incremental patch and a non-incremental patch are installed.
202301150100
· Symptom: Failed to apply ERSPAN-type QoS policies due to insufficient resources.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you apply a ERSPAN-type QoS policy to the inbound direction globally or apply ERSPAN-type QoS policies to the inbound direction of more than four interfaces.
202302090611
· Symptom: The log file fabric.log generated by VCF fabric exhausts the memory.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the automated deployment scenario of VCF fabric runs for a long period of time or interfaces flap.
Resolved problems in R6710
202208241285
· Symptom: A QoS policy applied to a control plane cannot filter the protocol packets to the control plane
· Condition: This symptom occurs when you apply a QoS policy to a control plane to filter protocol packets.
202209211461
· Symptom: A port that should be down periodically, repeatedly comes up and goes down.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The speed 1000 command is executed on a 10-GE port.
¡ The port has an SFP-GE-T/SFP-GE-T-D transceiver module installed.
¡ The shutdown command is not executed on the port.
202302070183
· Symptom: After the igmp-snooping router-port-discard command is executed in a VLAN, the switch cannot forward IGMP protocol packets to the router ports in the VLAN.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the igmp-snooping router-port-discard command is executed in a VLAN.
202210202895
· Symptom: IPv6 autoconfiguration fails on a device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur when the device uses a third-party DHCPv6 server for IPv6 autoconfiguration and the DHCPv6 server checks the DUID in Option 1.
202211301422
· Symptom: The device does not respond or reboots unexpectedly because the Intel C3XXX CPU is faulty.
· Condition: This symptom occurs with a low probability when the system runs for a long time.
202212190854
· Symptom: Multicast traffic cannot be broadcast in a VLAN when the hardware resource operating mode of the switch is ARP or MAC.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the hardware resource operating mode of the switch is ARP or MAC.
202207011516
· Symptom: The link-delay down setting is configured on both ends of a link, and the link traverses an optical transmission device. After an optical link switchover occurs on the optical transmission device, the link-delay down setting does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an optical link switchover occurs on the optical transmission device.
202207060567
· Symptom: In the outbound direction of an interface, mirroring traffic to the CPU and packet capturing do not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure mirroring traffic to the CPU and packet capturing in the outbound direction of an interface.
202209130556
· Symptom: Memory leaks occur.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The device uses a large number of VLAN interfaces and Layer 2 interfaces to forward multicast traffic.
¡ The device receives multicast traffic of different source-group pairs after multicast entries age out.
202209010367
· Symptom: The traffic rate of the ifmgr/statistics node appears as a saw-tooth in Grafana.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The json row-timestamp enable command is executed to enable per-row time-stamping for JSON-encoded subscription data.
¡ The switch uses gRPC to report the ifmgr/statistics node data at 5-second intervals.
202209270925
· Symptom: If the buffer egress/ingress command is executed on an interface and then the operating mode of the interface is switched between Layer 2 and Layer 3, the buffer egress/ingress command configuration in the configuration file is lost. However, the configuration still takes effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the buffer egress/ingress command is executed on an interface and then the operating mode of the interface is switched between Layer 2 and Layer 3.
202210211599
· Symptom: The switch gets stuck when the NETCONF <get-config> operation is used to retrieve information about the Ifmgr/Suppression table. The switch remains stuck until the set timeout time expires.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when the NETCONF <get-config> operation is used to retrieve information about the Ifmgr/Suppression table.
202210191104
· Symptom: VXLAN default decapsulation can be deployed from the CLI. When this feature is deployed through NETCONF, the device reports deployment success even through the deployment fails.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if VXLAN default decapsulation is deployed through NETCONF.
202210171204
· Symptom: A VSI with the igmp-snooping drop-unknown setting configured still can forward unknown multicast traffic in a VXLAN Layer 2 multicast environment.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the igmp-snooping drop-unknown command is executed in VSI view in a VXLAN Layer 2 multicast environment.
202210141248
· Symptom: The BGP process is abnormal.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if FRR is enabled globally for EVPN VXLAN.
202210110425
· Symptom: The switch reboots after you apply a QoS policy to an interface and delete all actions in the traffic behavior in the QoS policy.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you apply a QoS policy to an interface and delete all actions in the traffic behavior in the QoS policy.
202209261332
· Symptom: When a device is cold or warm rebooted, the MIB nodes hh3cSysColdStartTrap and hh3cSysWarmStartTrap do not normally report traps.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device is configured with SNMP and then rebooted.
202210090116
· Symptom: On an EVPN VXLAN network, the outgoing traffic of an AC is forwarded in queue 2 by default, which is different from the queue to which the 802.1p priority is mapped.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the incoming port of an AC trusts the 802.1p priority of packets and the access mode of the AC is VLAN on an EVPN VXLAN network.
202210210266
· Symptom: A MAC address might fail to move between IRF member devices.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a device attached to an IRF fabric moves between IRF member device and sends Layer 3 traffic to the IRF fabric.
202211100661
· Symptom: On an EVPN VXLAN network, some routes cannot guide traffic forwarding.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if multiple VPN instances exist on an EVPN VXLAN network and the automatically created VPN routes sent for the first time are withdrawn.
202210270699
· Symptom: On a VXLAN network, broadcast traffic cannot be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if VSIs are repeatedly added and deleted on the device and the VFI entry index in the hardware exceeds 4095.
202211181011
· Symptom: On a DRNI+EVPN network, a MAC address is migrated from an IPP to a single-homed interface, and the single-homed interface is shut down by the shutdown command. However, the ARP entries learned by the single-homed interface are not deleted.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device MAC address is migrated from an IPP to a single-homed interface, and the single-homed interface is shut down by the shutdown command.
202211161812
· Symptom: ARP packets cannot be flooded to different AC ports and tunnels in the same VSI.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following steps are performed:
a. Execute the arp suppression enable command to enable ARP suppression in a VSI view.
b. Execute the gateway vsi-interface command to specify a gateway interface for the VSI, and then delete this setting.
c. Remove ARP suppression settings.
202211300367
· Symptom: After you use the ecmp mode enhanced command to enable the enhanced ECMP mode, the hash consistency of ECMP routes will be affected by the flapping of next hops of unrelated routes.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you use the ecmp mode enhanced command to enable the enhanced ECMP mode and the next hops of multiple unrelated routes flap.
202211110382
· Symptom: The display mac-address command does not display the dynamic secure MAC address entries and static secure MAC address entries of an aggregate interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the display mac-address command is executed on the device to display the MAC address entries of an aggregate interface.
202211171005
· Symptom: After the device is rebooted, the mirroring configuration is lost, but the hardware resources in the underlayer remain. As a result, the later mirroring configuration fails.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Configure port mirroring.
b. Specify multiple mirroring source ports for a mirroring group. First configure the member ports of an aggregate interface as mirroring source ports, and then configure the aggregate interface as a mirroring source port.
c. Save the configuration and reboot the device.
202212011911
· Symptom: On an EVPN M-LAG network, the device cannot forward ARP requests from endpoints and cannot send ARP replies with the gateway address to the endpoints.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the VSI interface with ARP flood suppression enabled and acting as the gateway is down.
202209120036
· Symptom: A QoS policy has multiple class-behavior (CB) associations (for example, CB associations 1 and 2). Typically, only CB association 1 takes effect on traffic matching both CB associations 1 and 2. If you modify the actions in CB association 1, CB association 2 might take effect on the traffic matching both CB associations with a low probability.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. In a QoS policy applied, the accounting or CAR action exists in a behavior.
b. Modify the actions in any behavior or modify the match criteria in any class of the QoS policy, or apply the QoS policy again.
202209070077
· Symptom: A DCI tunnel flaps or multiple next hops of a DCI tunnel switch. As a result, traffic matching the PBR policy cannot be forwarded.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the next hop of the PBR policy is a DCI tunnel, and the DCI tunnel flaps or multiple next hops of the DCI tunnel switch.
202209160292
· Symptom: The device might not send some routes to peers.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device filters the route receivers based on the first AS number in EBGP routes (configurable with the peer-as-check enable command) and exchange routes with multiple EBGP peers.
202209200263
· Symptom: On an EVPN network, another device might fail to ping the IPv4 or IPv6 address of the local device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if microsegments are applied on the EVPN network.
202208050116
· Symptom: When you modify the parameters for WRR queuing or WFQ queuing, packets will be dropped transiently.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you modify the parameters for WFQ queuing or WRR queuing.
202208090444
· Symptom: The switch disconnects from the BMP server frequently.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the number of messages sent over the TCP connection between the switch and the BMP server exceeds the limit allowed by the buffer.
· Remarks: When the switch detects that the number of messages sent over the TCP connection exceeds the limit allowed by the buffer, it prints the following log message: BGP BGP instance name: Disconnected from BMP Server BMP server number for maximum limit of sending buffer reached. To resolve the issue, configure the BMP server to use the asynchronous receive mode. If the issue persists, configure the BMP server to receive messages faster or contact H3C Support.
202208090448
· Symptom: BFD sessions flap after the multicast routing command is executed.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the multicast routing command is executed.
202206240525
· Symptom: The flow mirroring configuration affects the PBR function.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if both flow mirroring and PBR are configured.
202208050141
· Symptom: In an M-LAG system configured with multicast settings, ICMPv6 packets are matched by an IPv4 ACL.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the ICMPv6 packets have a specific format.
202207050544
· Symptom: In an EVPN-DCI network, an ED device fails to forward IP unicast packets at Layer 2.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the ED device removes VXLAN encapsulation from the IP unicast packets whose inner TTL is 1 and forwards the packets at Layer 2.
202208021466
· Symptom: Some behaviors do not take effect in a QoS policy that contains multiple class-behavior associations.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the class of the first class-behavior association is configured to match an IPv4 ACL and Layer 2 attributes.
202206120009
· Symptom: The value of the IGMPv3 specific queries field in the display igmp-snooping statistics command output is incorrect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an IGMPv3 leave message with the multicast group as the Exclude mode triggers the sending of IGMPv3 last member queries.
202206060838
· Symptom: On a multicast network that supports multiple levels of DR systems, IGMP packets form a loop between DR interfaces.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if DR interfaces receive IGMP group-specific query packets on a multicast network that supports multiple levels of DR systems.
202207050871
· Symptom: Executing the undo mac-address mac-learning enable command in system view or executing the undo mac-learning enable command in VSI view cannot disable MAC address learning in the corresponding view.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when you execute the undo mac-address mac-learning enable command in system view or execute the undo mac-learning enable command in VSI view.
202208190680
· Symptom: In an M-LAG system that use VLAN interfaces to act as dual-active gateways for the same VLAN, an M-LAG member device cannot successfully ping an endpoint.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the other M-LAG member device receives ICMP replay packets.
202206230765
· Symptom: The switch prompts the Permission denied. error message.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. Enable command authorization.
b. Repeat a command in the command history buffer for more than 1000 times.
Resolved problems in E6707
202208031661
· Symptom: The LED for the master's IRF physical interface is on, and the LEDs for the subordinates' IRF physical interfaces are off.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the device loads Bootware in full startup mode and performs system inspection.
202208221073
· Symptom: Loop detection is enabled and the loop protection action is set to block on an interface. When the interface detects a loop, it stays in forwarding state, and the loop is not removed.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if loop detection is enabled and the loop protection action is set to block by using the loopback-detection action block command on an interface.
202209131298
· Symptom: When an interface is shut down by M-LAG MAD, the Current state field displays DRNI MAD down, which should be M-LAG MAD down, for the interface in the display interface command output.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you use the display interface command to display interface information when an interface is shut down by M-LAG MAD.
202208311310
· Symptom: Auto configuration is interrupted during IPv6 auto deployment of the switch, and IPv6 auto deployment fails.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when the switch performs IPv6 auto deployment.
202208261550
· Symptom: In an EVPN VXLAN network where Layer 3 multicast traffic is forwarded over DCI tunnels, traffic loss lasts for a significant period of time before new traffic flows are forwarded correctly.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if Layer 3 multicast traffic is forwarded over DCI tunnels in an EVPN VXLAN network and new traffic flows are forwarded in the network.
202209010441
· Symptom: An M-LAG member device cannot ping the single-homed device on the other member device through the M-LAG interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the M-LAG R interface and the single-homed device are in the same VLAN.
202208270465
· Symptom: Layer 3 multicast packets cannot be forwarded through a GRE tunnel.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you enable Layer 3 multicast and specify the tunnel mode of the outgoing interface as GRE.
202208310792
· Symptom: VRRP flaps on a DR system collocated with VRRP gateways.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if VRRP gateways are configured on a DR system, the gateways receive a large number of ARP requests, ARP replies, ND packets, or NS packets, and the IPL is used to synchronize a large number of ARP and ND entries.
202209191590
· Symptom: On a multicast VXLAN network, the multicast routing entries of the PIM protocol on the public network remain.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
a. The MVXLAN IPv4 address family and the MVXLAN IPv6 address family are created at the same time.
b. The MVXLAN IPv4 address family is deleted.
c. The MVXLAN IPv6 address family is deleted.
202208250185
· Symptom: PBR uses an invalid next hop, which cause traffic steering exceptions.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you set the action to be taken on a node to apply next-hop or apply default-next-hop for PBR, but one of the following situations exists:
¡ The outgoing interfaces of the next hops or default next hops update.
¡ The route status changes rapidly and frequently.
For example, the action to be taken on a node is apply next-hop 1.1.1.1, but the outgoing interface for 1.1.1.1 updates or the route status changes rapidly and frequently.
202209130044
· Symptom: The device forwards passing MPLS packets or VXLAN packets out of other Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces, which causes a broadcast storm.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ All physical interfaces of the device are configured as Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces.
¡ The destination MAC address in the outer header of received passing MPLS packets or VXLAN packets is an unknown MAC address.
202209170584
· Symptom: On a VXLAN DR system, a VSI interface is disassociated from a VSI, and DR-synchronized ARP entries are also deleted for other VSIs.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if no VXLAN ID is assigned to the VSI from which a VSI interface is disassociated.
Resolved problems in E6706
202204011571
· Symptom: In an MVXLAN, the leaf device connected to the multicast source does not have output interfaces for some hardware entries.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if you clear multicast route entries on the leaf device and then reset BGP sessions on the device.
202207080423
· Symptom: On an IRF fabric, a MAC authentication user comes online and goes offline repeatedly after the user comes online on an aggregate interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the MAC authentication offline detection is enabled on aggregate interface and the member port on the master device is receiving traffic.
202207081486
· Symptom: The bgpd process becomes abnormal when a gateway interface is specified for a VSI.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the VSI has been bound to an EVPN instance by using the evpn encapsulation vxlan binding instance command.
202205050433
· Symptom: The function of forcibly bringing up a fiber Ethernet port is mutually exclusive with the function of assigning the fiber Ethernet port to an aggregation group.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you attempt to configure both functions.
202207261804
· Symptom: After the switch cannot encapsulate incoming packets as VXLAN packets and send them to a downstream device, the downstream device cannot load balance the VXLAN packets.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following conditions exist:
¡ The link-aggregation global load-sharing mode destination-ip source-ip destination-port source-port command is executed on the switch.
¡ The source IP address and destination IP address of the incoming packets do not change.
202206291177
· Symptom: The device does not learn an ND entry when receiving an NA message without the target link-layer address (TLLA) field.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device receives an NA message without the TLLA field.
202208090428
· Symptom: On a VXLAN-enabled IRF fabric, packet loss persists after an ISSU from F6623 or earlier to a version later than F6623.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if IRF subordinate members receive ARP packets on aggregate links during the upgrade process.
202208081526
· Symptom: The switch does not forward incoming GRE packets with the dscp field as 0x10 from the correct queue on the output interface. The GRE packets are sent out from queue 2 instead of queue 5 according to the priority map.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the qos trust dscp command is executed on the input interface.
202205191660
· Symptom: A multicast tunnel interface of MVXLAN might be down.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if MVXLAN is configured and then PIM is enabled on interfaces in a VPN instance.
202204210918
· Symptom: The files in the flash memory are lost, the flash memory cannot be written to, and the flash memory size is 0 KB in the display version command output.
· Condition: None. This symptom occurs with a very low probability.
· Remarks: This patch can only collect information on devices with the C35xx CPU for flash troubleshooting. If the problem has occurred, contact H3C Support for problem location.
202203170583
· Symptom: The aggregate interface isolation feature takes effect on IPPs unexpectedly. As a result, the member ports of IPPs cannot become Selected.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you first configure the aggregate interface isolation feature and then configure aggregate interfaces as IPPs.
202203170584
· Symptom: The aggregate interface isolation feature takes effect on static aggregate interfaces unexpectedly. As a result, the member ports of static aggregate interfaces cannot become Selected.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you first configure the aggregate interface isolation feature and then change dynamic aggregate interfaces to static aggregate interfaces.
202107050021
· Symptom: On a VXLAN network, the route convergence time is long.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device is in an IRF fabric and several aggregate interfaces are shut down on the device. As a result, the number of load sharing links is reduced.
202204090439
· Symptom: The console gets stuck after repeated execution of the port-security enable or port-security port-mode command.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the port-security enable or port-security port-mode command is repeatedly executed.
202204090268
· Symptom: An interface bound to VPN 1 receives packets destined for an IP address in VPN 2 and forwards the packets in VPN 2 even though the operation type for the MPLS label in the packets is POP in the forwarding table of VPN 2.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the single-labeled MPLS packets received on an interface in one subnet are forwarded out of an interface in another subnet.
202203260366
· Symptom: In an MVXLAN, a leaf device connected to a multicast receiver cannot forward multicast traffic.
· Condition: This symptom occurs after you repeatedly add and delete VSI settings on the leaf device.
· Workaround: Do not repeatedly add and delete VSIs bound to the same VSI interface.
202112071015
· Symptom: In an M-LAG system that acts as a leaf node, packet loss lasts for 961 milliseconds after all uplink interfaces on one member device are shut down.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the M-LAG system has two member devices and a server is connected to the M-LAG system in single-homing mode.
202112070974
· Symptom: In an M-LAG system that acts as a leaf node, packet loss lasts for 602 milliseconds after all uplink interfaces on one member device are shut down.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the M-LAG system has two member devices and a server is connected to the M-LAG system in Bond4 mode.
202105150186
· Symptom: After an aggregate interface authenticates a MAC authentication user, an IRF master/subordinate switchover occurs, and the user goes offline 10 minutes later.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an aggregate interface authenticates a MAC authentication user and an IRF master/subordinate switchover occurs.
202206240523
· Symptom: A downstream device attached to an M-LAG EVPN system cannot ping the gateway.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the VSI interfaces acting as gateways are assigned different IP addresses and the downstream device pings one gateway address.
202206010902
· Symptom: BFD MAD flaps.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if BFD MAD is enabled on a VLAN interface on two IRF fabrics and one IRF fabric has a master/subordinate switchover.
202204151727
· Symptom: In an MPLS VPLS network, the PE device cannot transparently transmit IGMP packets when multicast features are enabled on the PE device.
· Condition: This symptom occurs when the device acts as a PE of an MPLS VPLS network, and Layer 2 or Layer 3 multicast features are enabled on the device.
202204201063
· Symptom: The input errors value in the display interface command output is different from that obtained through SNMP.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if an interface receives packets smaller than 64 bytes.
202205030067
· Symptom: Some member ports in an aggregation group do not forward traffic, and traffic is unevenly distributed among the member links.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ Member ports of the aggregation group are located on multiple IRF member devices.
¡ The aggregate interface is one of the outgoing interfaces for a VXLAN tunnel.
¡ The member ports on one IRF member device flap.
202204230201
· Symptom: MAC address moves might not trigger ND entry moves on a DR system.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the mac-address mac-move fast-update command is executed and MAC addresses move in the underlay network.
202205171718
· Symptom: When identical static ARP entries are configured on the DR member devices in a DR system, configuration fails on one DR member device.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if identical static ARP entries are configured on the DR member devices in a DR system.
202112060445
· Symptom: The storm-constrain control block command does not take effect.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the storm-constrain control block command is executed on an interface to configure the interface to suspend sending unknown unicast, known unicast, multicast, or broadcast packets when the packets exceed the upper threshold.
202111091341
· Symptom: When a MIB browser tool is used to read the entPhysicalVendorType node value of an absent power supply, the value is all-Fs, which should fail to be read.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if a MIB browser tool is used to read the entPhysicalVendorType node value of an absent power supply.
202203141354
· Symptom: After the device is rebooted, the detection interval configured for the BFD echo session does not take effect, and is displayed as the default value.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed on a DRNI network:
a. Configure a static BFD echo session with a detection interval different from that configured for the BFD echo session on an interface. The session can be negotiated as up.
b. Save the configuration, and then reboot the device.
202204130096
· Symptom: When the DR aggregate interface and IPL aggregate interface are deleted from a device, traffic cannot be forwarded at Layer 2 between physical interfaces in the original DR aggregate interface and IPL aggregate interface.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the following operations are performed:
c. On an EVPN+DRNI network, configure ACs on a DR aggregate interface.
d. Delete the DR aggregate interface and IPL aggregate interface in sequence on a DR member device.
202205091702
· Symptom: On an EVPN DRNI network, packets are dropped unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if packets are received on an AC, the packets are VXLAN-encapsulated, and the packets carry the PVID VLAN tag of the interface hosting the AC.
202205060729
· Symptom: You cannot configure both sFlow and the INT transit node on a device.
· Condition: None.
202205091696
· Symptom: The reply to an HTTP request on a device carries the server:HTTPD field, which is used to identify the server information. The vulnerability scanners consider that the server field might disclose the server information and result in attacks.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if the device receives HTTP requests.
202205091688
· Symptom: The memory leaks for the routed module.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you configure a gRPC sensor path to collect route information, and then make routes on the device flap.
202205091701
· Symptom: When ARP/ND traffic exists on an EVPN+DRNI network, if you repeatedly shut down and bring up the IPL aggregate interface of a DR member device, the device will reboot unexpectedly.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you repeatedly shut down and bring up the IPL aggregate interface of a DR member device when ARP/ND traffic exists on an EVPN+DRNI network.
202204251521
· Symptom: EVPN VXLAN does not load share traffic as expected.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the cost type is set to wide and fast reroute is enabled for IS-IS on the underlay network and one of the ECMP links for a VXLAN tunnel flaps.
202205110059
· Symptom: On an EVPN network, the number of L3 entries in the software is different from that in the hardware.
· Condition: This symptom occurs if you add and delete L3VNIs on a VSI interface.
202206160012
· Symptom: A multichassis aggregate interface is configured on an IRF fabric. When the selected ports on IRF member device 1 leave the aggregation group, the endpoints attached to those ports cannot communicate with the endpoints attached to the aggregation member ports on IRF member device 2.
· Condition: This symptom might occur if the following conditions exist:
¡ A multichassis aggregate interface is configured on an IRF fabric. The aggregation member ports on IRF member device 1 are selected, and the aggregation member ports on IRF member device 2 are unselected.
¡ The aggregation member pots on IRF member device 1 have the same port IDs as those on IRF member device 2. To view the port IDs, use the debug port mapping command.
¡ The aggregation member ports on IRF member device 1 leave the aggregation group.
Resolved problems in E6702
First release.
Troubleshooting resources
To obtain troubleshooting resources for the product:
1. Access Technical Documents at http://www.h3c.com/en/Technical_Documents.
2. Select the device category and model.
3. Select the Maintain or Maintenance menu.
Related documentation
Documentation set
· H3C S6825 Switch Series Installation Guide
· H3C S6825-54HF Switch Installation Quick Start
· H3C LSPM1FANSA & LSPM1FANSB Fan Trays User Guide
· H3C PSR450 Power Module Series User Manual
· H3C S6805 & S6825 & S6850 & S9850 Switch Series Configuration Guide-Release 671x
· H3C S6805 & S6825 & S6850 & S9850 Switch Series Command References-Release 671x
Obtaining documentation
To obtain the related documents from the H3C website at http://www.h3c.com.hk/:
1. Click http://www.h3c.com.hk/Technical_Documents.
2. Choose the desired product category and model.
Technical support
service@h3c.com
Table 5 S6825 series hardware features
Item | S6825-54HF |
Dimensions (H × W × D) | 440×400×44 |
Weight | ≤10kg |
Console ports | 1 |
Management Ethernet ports | 2 |
Mini USB(Console) | 1 |
USB ports | 1 |
SFP28 ports | 48 |
QSFP28 ports | 6 |
Fan trays | 5 · LSPM1FANSA · LSPM1FANSB |
Power modules | · PSR450-12A · PSR450-12A1 · PSR450-12D · PSR450-12AHD |
Input voltage | PSR450-12A/PSR450-12A1: AC input Rated voltage range: 100 to 240 VAC @ 50/60 Hz Max voltage range: 90 to 290 VAC @ 47 to 63 Hz High-voltage DC input Rated voltage range: 240 VDC Max voltage range: 180 to 320 VDC PSR450-12AHD: AC input Rated voltage range: 100 to 240 VAC @ 50/60 Hz Max voltage range: 90 to 290 VAC @ 47 to 63 Hz High-voltage DC input Rated voltage range e: 240 to 380 VDC Max voltage range: 180 to 400 VDC PSR450-12D: Rated voltage range: –48 to –60 VDC Max voltage range: –36 to –72 VDC |
Maximum power consumption | PSR450-12A/PSR450-12A1: Single AC input: 223 W Dual AC inputs: 228 W PSR450-12AHD: Single DC input: 213 W Dual DC inputs: 219 W PSR450-12D: Single DC input: 224 W Dual DC inputs: 227 W |
Operating temperature | 0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) |
Operating humidity | 5% to 95%, noncondensing |
Table 6 Software features of the S6825 series
Feature | S6825-54HF |
Full duplex Wire speed L2 switching capacity | 3.6Tbps |
Whole system Wire speed L2 switching Packet forwarding rate | 1001.7Mpps |
Forwarding mode | Store-forward and cut-through |
IRF | · Ring topology · Daisy-chain topology · LACP MAD · ARP MAD · ND MAD · BFD MAD · ISSU |
Link aggregation | · Static link aggregation · Dynamic link aggregation · When stacked, supports up to 1024 aggregation groups, each supporting up to 32 ports · NLB |
Data center features | · PFC · ETS · DCBX · FCoE · VXLAN · OpenFlow · RDMA · gRPC · INT |
Flow control | · IEEE 802.3x flow control and back pressure |
Jumbo Frame | · Supports maximum frame size of 9416 |
MAC address table | · 288K MAC addresses · 8K static MAC addresses · Blackhole MAC addresses · MAC address learning limit on a port · Static multicast MAC address |
VLAN | · Port-based VLANs (4094 VLANs) · Super VLAN |
QinQ | · Supported |
VLAN Mapping | · 1:1 VLAN Mapping · N:1 VLAN Mapping · 1:2 VLAN Mapping · 2:2 VLAN Mapping · 2:1 VLAN Mapping |
ARP | · Up to 272K entries · 1K static entries · Gratuitous ARP · Standard proxy ARP and local proxy ARP · ARP source suppression · ARP black hole · ARP detection (based on DHCP snooping entries/802.1x security entries/static IP-to-MAC bindings) · Multiport ARP entry |
ND | · Up to 136K entries · 1K static entries · ND proxy |
VLAN virtual interface | 2K |
Layer 3 Ethernet interface | Supported |
DHCP | · DHCP client · DHCP snooping · DHCP relay agent · DHCP server · DHCPv6 client · DHCPv6 snooping · DHCPv6 relay agent · DHCPv6 server |
UDP helper | · Supported |
DNS | · Dynamic domain name resolution · Dynamic domain name resolution client · IPv4/IPv6 addresses |
IPv4 routing | · 4K static routes · RIP(Routing Information Protocol) v1/2; up to 4K IPv4 routes · OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) v1/v2; up to 324K IPv4 routes · IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate system); up to 128K IPv4 routes · BGP (Border Gateway Protocol); up to 128K IPv4 routes · Up to 4K ECMP routes; each ECMP route supports up to 128 next hops · Routing policy · VRRP · PBR |
IPv6 routing | · 2K static routes · RIPng: Supports up to 2K IPv6 routes · OSPF v3: Supports up to 162K IPv6 routes · IPv6 IS-IS: Supports up to 162K IPv6 routes · BGP4+: Supports up to 162K IPv6 routes · Up to 4K ECMP routes; each ECMP route supports up to 128 next hops · Routing policy · VRRP · PBR |
uRPF | · Strict uRPF check · Loose uRPF check |
MCE | Supported |
BFD | · RIP/RIPng · OSPF/OSPFv3 · IS-IS/IPv6 IS-IS · BGP/BGP4+ · Static route/IPv6 static route |
Tunnel | · IPv4 over IPv4 tunnel · IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel · IPv6 over IPv4 manual tunnel · IPv6 over IPv4 6to4 tunnel · IPv6 over IPv4 ISATAP tunnel · IPv6 over IPv6 tunnel · GRE tunnel |
Multicast | · IGMP snooping · MLD snooping · IPv4 and IPv6 multicast VLAN · IPv4 and IPv6 PIM snooping · IGMP and MLD · PIM-DM, PIM-SM, PIM-SSM, BIDIR-PIM · IPv6 PIM-DM, IPv6 PIM-SM, IPv6 PIM-SSM, IPv6 BIDIR-PIM · MSDP · Multicast VPN · MBGP and IPv6 MBGP · MLD snooping proxying |
MPLS | · MPLS L3VPN · MPLS L2VPN · VPLS |
Broadcast/multicast/unknown unicast storm suppression | · ratio · PPS · kbps |
MSTP | · STP/RSTP/MSTP protocol · STP Root Guard · BPDU Guard |
RRPP | Supported |
Smart link | Supported |
Monitor link | Supported |
QoS/ACL | · Restriction of the rates at which a port sends and receives packets, with a granularity of 8 kbps. · Packet redirect · Committed access rate (CAR), with a granularity of traffic limit 8 kbps. · Eight output queues for each port · Flexible queue scheduling algorithms based on port and queue, including strict priority (SP), Weighted Deficit Round Robin (WDRR), Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ), SP + WDRR, and SP + WFQ. · Remarking of 802.1p and DSCP priorities · Packet filtering at L2 (Layer 2) through L4 (Layer 4); flow classification based on source MAC address, destination MAC address, source IP (IPv4/IPv6) address, destination IP (IPv4/IPv6) address, port, protocol, and VLAN. · Time range · Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) · Queue shaping · User profile · COPP · Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) |
Mirroring | · Flow mirroring · Port mirroring · Multiple mirror observing port |
Remote mirroring | · Port remote mirroring (RSPAN) |
Security | · Hierarchical management and password protection of users · AAA authentication · RADIUS · HWTACACS · SSH 2.0 · PKI · SSL · HTTPs · Attack detection and prevention · IP Source Guard · Keychain |
Traffic Management | · sFlow |
Loading and upgrading | · Loading and upgrading through FTP · Loading and upgrading through the trivial file transfer protocol (TFTP) · Loading and upgrading through XModem protocol |
Management and Maintenance | · Telemetry · Configuration at the command line interface · Remote configuration through Telnet · Configuration through Console port · Simple network management protocol (SNMP) · System log · Hierarchical alarms · NTP · Power supply alarm function · Fan and temperature alarms · Debugging information output · Ping and Tracert · DLDP · File download and upload through USB port |
Appendix B Fixed security vulnerabilities
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6715P01
CVE-2023-33953
gRPC contains a vulnerability that allows hpack table accounting errors could lead to unwanted disconnects between clients and servers in exceptional cases/ Three vectors were found that allow the following DOS attacks: - Unbounded memory buffering in the HPACK parser - Unbounded CPU consumption in the HPACK parser The unbounded CPU consumption is down to a copy that occurred per-input-block in the parser, and because that could be unbounded due to the memory copy bug we end up with an O(n^2) parsing loop, with n selected by the client. The unbounded memory buffering bugs: - The header size limit check was behind the string reading code, so we needed to first buffer up to a 4 gigabyte string before rejecting it as longer than 8 or 16kb. - HPACK varints have an encoding quirk whereby an infinite number of 0’s can be added at the start of an integer. gRPC’s hpack parser needed to read all of them before concluding a parse. - gRPC’s metadata overflow check was performed per frame, so that the following sequence of frames could cause infinite buffering: HEADERS: containing a: 1 CONTINUATION: containing a: 2 CONTINUATION: containing a: 3 etc…
CVE-2023-32732
gRPC contains a vulnerability whereby a client can cause a termination of connection between a HTTP2 proxy and a gRPC server: a base64 encoding error for `-bin` suffixed headers will result in a disconnection by the gRPC server, but is typically allowed by HTTP2 proxies. We recommend upgrading beyond the commit in https://github.com/grpc/grpc/pull/32309 https://www.google.com/url
CVE-2024-0727
Issue summary: Processing a maliciously formatted PKCS12 file may lead OpenSSL to crash leading to a potential Denial of Service attack Impact summary: Applications loading files in the PKCS12 format from untrusted sources might terminate abruptly. A file in PKCS12 format can contain certificates and keys and may come from an untrusted source. The PKCS12 specification allows certain fields to be NULL, but OpenSSL does not correctly check for this case. This can lead to a NULL pointer dereference that results in OpenSSL crashing. If an application processes PKCS12 files from an untrusted source using the OpenSSL APIs then that application will be vulnerable to this issue. OpenSSL APIs that are vulnerable to this are: PKCS12_parse(), PKCS12_unpack_p7data(), PKCS12_unpack_p7encdata(), PKCS12_unpack_authsafes() and PKCS12_newpass(). We have also fixed a similar issue in SMIME_write_PKCS7(). However since this function is related to writing data we do not consider it security significant. The FIPS modules in 3.2, 3.1 and 3.0 are not affected by this issue.
CVE-2023-5678
Issue summary: Generating excessively long X9.42 DH keys or checking excessively long X9.42 DH keys or parameters may be very slow. Impact summary: Applications that use the functions DH_generate_key() to generate an X9.42 DH key may experience long delays. Likewise, applications that use DH_check_pub_key(), DH_check_pub_key_ex() or EVP_PKEY_public_check() to check an X9.42 DH key or X9.42 DH parameters may experience long delays. Where the key or parameters that are being checked have been obtained from an untrusted source this may lead to a Denial of Service. While DH_check() performs all the necessary checks (as of CVE-2023-3817), DH_check_pub_key() doesn't make any of these checks, and is therefore vulnerable for excessively large P and Q parameters. Likewise, while DH_generate_key() performs a check for an excessively large P, it doesn't check for an excessively large Q. An application that calls DH_generate_key() or DH_check_pub_key() and supplies a key or parameters obtained from an untrusted source could be vulnerable to a Denial of Service attack. DH_generate_key() and DH_check_pub_key() are also called by a number of other OpenSSL functions. An application calling any of those other functions may similarly be affected. The other functions affected by this are DH_check_pub_key_ex(), EVP_PKEY_public_check(), and EVP_PKEY_generate(). Also vulnerable are the OpenSSL pkey command line application when using the "-pubcheck" option, as well as the OpenSSL genpkey command line application. The OpenSSL SSL/TLS implementation is not affected by this issue. The OpenSSL 3.0 and 3.1 FIPS providers are not affected by this issue.
CVE-2023-40217
An issue was discovered in Python before 3.8.18, 3.9.x before 3.9.18, 3.10.x before 3.10.13, and 3.11.x before 3.11.5. It primarily affects servers (such as HTTP servers) that use TLS client authentication. If a TLS server-side socket is created, receives data into the socket buffer, and then is closed quickly, there is a brief window where the SSLSocket instance will detect the socket as "not connected" and won't initiate a handshake, but buffered data will still be readable from the socket buffer. This data will not be authenticated if the server-side TLS peer is expecting client certificate authentication, and is indistinguishable from valid TLS stream data. Data is limited in size to the amount that will fit in the buffer. (The TLS connection cannot directly be used for data exfiltration because the vulnerable code path requires that the connection be closed on initialization of the SSLSocket.)
Fixed security vulnerabilities in R6715
CVE-2023-2650
Issue summary: Processing some specially crafted ASN.1 object identifiers or data containing them may be very slow. Impact summary: Applications that use OBJ_obj2txt() directly, or use any of the OpenSSL subsystems OCSP, PKCS7/SMIME, CMS, CMP/CRMF or TS with no message size limit may experience notable to very long delays when processing those messages, which may lead to a Denial of Service. An OBJECT IDENTIFIER is composed of a series of numbers - sub-identifiers - most of which have no size limit. OBJ_obj2txt() may be used to translate an ASN.1 OBJECT IDENTIFIER given in DER encoding form (using the OpenSSL type ASN1_OBJECT) to its canonical numeric text form, which are the sub-identifiers of the OBJECT IDENTIFIER in decimal form, separated by periods. When one of the sub-identifiers in the OBJECT IDENTIFIER is very large (these are sizes that are seen as absurdly large, taking up tens or hundreds of KiBs), the translation to a decimal number in text may take a very long time. The time complexity is O(n^2) with 'n' being the size of the sub-identifiers in bytes (*). With OpenSSL 3.0, support to fetch cryptographic algorithms using names / identifiers in string form was introduced. This includes using OBJECT IDENTIFIERs in canonical numeric text form as identifiers for fetching algorithms. Such OBJECT IDENTIFIERs may be received through the ASN.1 structure AlgorithmIdentifier, which is commonly used in multiple protocols to specify what cryptographic algorithm should be used to sign or verify, encrypt or decrypt, or digest passed data. Applications that call OBJ_obj2txt() directly with untrusted data are affected, with any version of OpenSSL. If the use is for the mere purpose of display, the severity is considered low. In OpenSSL 3.0 and newer, this affects the subsystems OCSP, PKCS7/SMIME, CMS, CMP/CRMF or TS. It also impacts anything that processes X.509 certificates, including simple things like verifying its signature. The impact on TLS is relatively low, because all versions of OpenSSL have a 100KiB limit on the peer's certificate chain. Additionally, this only impacts clients, or servers that have explicitly enabled client authentication. In OpenSSL 1.1.1 and 1.0.2, this only affects displaying diverse objects, such as X.509 certificates. This is assumed to not happen in such a way that it would cause a Denial of Service, so these versions are considered not affected by this issue in such a way that it would be cause for concern, and the severity is therefore considered low.
CVE-2023-0465
Applications that use a non-default option when verifying certificates may be vulnerable to an attack from a malicious CA to circumvent certain checks. Invalid certificate policies in leaf certificates are silently ignored by OpenSSL and other certificate policy checks are skipped for that certificate. A malicious CA could use this to deliberately assert invalid certificate policies in order to circumvent policy checking on the certificate altogether. Policy processing is disabled by default but can be enabled by passing the `-policy' argument to the command line utilities or by calling the `X509_VERIFY_PARAM_set1_policies()' function.
CVE-2023-0464
A security vulnerability has been identified in all supported versions of OpenSSL related to the verification of X.509 certificate chains that include policy constraints. Attackers may be able to exploit this vulnerability by creating a malicious certificate chain that triggers exponential use of computational resources, leading to a denial-of-service (DoS) attack on affected systems. Policy processing is disabled by default but can be enabled by passing the `-policy' argument to the command line utilities or by calling the `X509_VERIFY_PARAM_set1_policies()' function.
CVE-2023-0286
There is a type confusion vulnerability relating to X.400 address processing inside an X.509 GeneralName. X.400 addresses were parsed as an ASN1_STRING but the public structure definition for GENERAL_NAME incorrectly specified the type of the x400Address field as ASN1_TYPE. This field is subsequently interpreted by the OpenSSL function GENERAL_NAME_cmp as an ASN1_TYPE rather than an ASN1_STRING. When CRL checking is enabled (i.e. the application sets the X509_V_FLAG_CRL_CHECK flag), this vulnerability may allow an attacker to pass arbitrary pointers to a memcmp call, enabling them to read memory contents or enact a denial of service. In most cases, the attack requires the attacker to provide both the certificate chain and CRL, neither of which need to have a valid signature. If the attacker only controls one of these inputs, the other input must already contain an X.400 address as a CRL distribution point, which is uncommon. As such, this vulnerability is most likely to only affect applications which have implemented their own functionality for retrieving CRLs over a network.
CVE-2023-0215
The public API function BIO_new_NDEF is a helper function used for streaming ASN.1 data via a BIO. It is primarily used internally to OpenSSL to support the SMIME, CMS and PKCS7 streaming capabilities, but may also be called directly by end user applications. The function receives a BIO from the caller, prepends a new BIO_f_asn1 filter BIO onto the front of it to form a BIO chain, and then returns the new head of the BIO chain to the caller. Under certain conditions, for example if a CMS recipient public key is invalid, the new filter BIO is freed and the function returns a NULL result indicating a failure. However, in this case, the BIO chain is not properly cleaned up and the BIO passed by the caller still retains internal pointers to the previously freed filter BIO. If the caller then goes on to call BIO_pop() on the BIO then a use-after-free will occur. This will most likely result in a crash. This scenario occurs directly in the internal function B64_write_ASN1() which may cause BIO_new_NDEF() to be called and will subsequently call BIO_pop() on the BIO. This internal function is in turn called by the public API functions PEM_write_bio_ASN1_stream, PEM_write_bio_CMS_stream, PEM_write_bio_PKCS7_stream, SMIME_write_ASN1, SMIME_write_CMS and SMIME_write_PKCS7. Other public API functions that may be impacted by this include i2d_ASN1_bio_stream, BIO_new_CMS, BIO_new_PKCS7, i2d_CMS_bio_stream and i2d_PKCS7_bio_stream. The OpenSSL cms and smime command line applications are similarly affected.
CVE-2022-32221
When doing HTTP(S) transfers, libcurl might erroneously use the read callback (`CURLOPT_READFUNCTION`) to ask for data to send, even when the `CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS` option has been set, if the same handle previously was used to issue a `PUT` request which used that callback. This flaw may surprise the application and cause it to misbehave and either send off the wrong data or use memory after free or similar in the subsequent `POST` request. The problem exists in the logic for a reused handle when it is changed from a PUT to a POST.
CVE-2023-24329
An issue in the urllib.parse component of Python before 3.11.4 allows attackers to bypass blocklisting methods by supplying a URL that starts with blank characters.
CVE-2023-3817
Issue summary: Checking excessively long DH keys or parameters may be very slow. Impact summary: Applications that use the functions DH_check(), DH_check_ex() or EVP_PKEY_param_check() to check a DH key or DH parameters may experience long delays. Where the key or parameters that are being checked have been obtained from an untrusted source this may lead to a Denial of Service. The function DH_check() performs various checks on DH parameters. After fixing CVE-2023-3446 it was discovered that a large q parameter value can also trigger an overly long computation during some of these checks. A correct q value, if present, cannot be larger than the modulus p parameter, thus it is unnecessary to perform these checks if q is larger than p. An application that calls DH_check() and supplies a key or parameters obtained from an untrusted source could be vulnerable to a Denial of Service attack. The function DH_check() is itself called by a number of other OpenSSL functions. An application calling any of those other functions may similarly be affected. The other functions affected by this are DH_check_ex() and EVP_PKEY_param_check(). Also vulnerable are the OpenSSL dhparam and pkeyparam command line applications when using the "-check" option. The OpenSSL SSL/TLS implementation is not affected by this issue. The OpenSSL 3.0 and 3.1 FIPS providers are not affected by this issue.
CVE-2023-3446
Issue summary: Checking excessively long DH keys or parameters may be very slow. Impact summary: Applications that use the functions DH_check(), DH_check_ex() or EVP_PKEY_param_check() to check a DH key or DH parameters may experience long delays. Where the key or parameters that are being checked have been obtained from an untrusted source this may lead to a Denial of Service. The function DH_check() performs various checks on DH parameters. One of those checks confirms that the modulus ('p' parameter) is not too large. Trying to use a very large modulus is slow and OpenSSL will not normally use a modulus which is over 10,000 bits in length. However the DH_check() function checks numerous aspects of the key or parameters that have been supplied. Some of those checks use the supplied modulus value even if it has already been found to be too large. An application that calls DH_check() and supplies a key or parameters obtained from an untrusted source could be vulernable to a Denial of Service attack. The function DH_check() is itself called by a number of other OpenSSL functions. An application calling any of those other functions may similarly be affected. The other functions affected by this are DH_check_ex() and EVP_PKEY_param_check(). Also vulnerable are the OpenSSL dhparam and pkeyparam command line applications when using the '-check' option. The OpenSSL SSL/TLS implementation is not affected by this issue. The OpenSSL 3.0 and 3.1 FIPS providers are not affected by this issue.
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6712
CVE-2017-1000100
When doing a TFTP transfer and curl/libcurl is given a URL that contains a very long file name (longer than about 515 bytes), the file name is truncated to fit within the buffer boundaries, but the buffer size is still wrongly updated to use the untruncated length. This too large value is then used in the sendto() call, making curl attempt to send more data than what is actually put into the buffer. The endto() function will then read beyond the end of the heap based buffer. A malicious HTTP(S) server could redirect a vulnerable libcurl-using client to a crafted TFTP URL (if the client hasn't restricted which protocols it allows redirects to) and trick it to send private memory contents to a remote server over UDP. Limit curl's redirect protocols with --proto-redir and libcurl's with CURLOPT_REDIR_PROTOCOLS.
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6711
CVE-2015-7979
NTP before 4.2.8p6 and 4.3.x before 4.3.90 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (client-server association tear down) by sending broadcast packets with invalid authentication to a broadcast client.
CVE-2022-1292
The c_rehash script does not properly sanitise shell metacharacters to prevent command injection. This script is distributed by some operating systems in a manner where it is automatically executed. On such operating systems, an attacker could execute arbitrary commands with the privileges of the script. Use of the c_rehash script is considered obsolete and should be replaced by the OpenSSL rehash command line tool. Fixed in OpenSSL 3.0.3 (Affected 3.0.0,3.0.1,3.0.2). Fixed in OpenSSL 1.1.1o (Affected 1.1.1-1.1.1n). Fixed in OpenSSL 1.0.2ze (Affected 1.0.2-1.0.2zd).
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6707
CVE-2020-7469
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r367402, 11.4-STABLE before r368202, 12.2-RELEASE before p1, 12.1-RELEASE before p11 and 11.4-RELEASE before p5 the handler for a routing option caches a pointer into the packet buffer holding the ICMPv6 message. However, when processing subsequent options the packet buffer may be freed, rendering the cached pointer invalid. The network stack may later dereference the pointer, potentially triggering a use-after-free.
CVE-2021-22924
libcurl keeps previously used connections in a connection pool for subsequenttransfers to reuse, if one of them matches the setup.Due to errors in the logic, the config matching function did not take 'issuercert' into account and it compared the involved paths *case insensitively*,which could lead to libcurl reusing wrong connections.File paths are, or can be, case sensitive on many systems but not all, and caneven vary depending on used file systems.The comparison also didn't include the 'issuer cert' which a transfer can setto qualify how to verify the server certificate.
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6706
CVE-2022-0778
The BN_mod_sqrt() function, which computes a modular square root, contains a bug that can cause it to loop forever for non-prime moduli. Internally this function is used when parsing certificates that contain elliptic curve public keys in compressed form or explicit elliptic curve parameters with a base point encoded in compressed form. It is possible to trigger the infinite loop by crafting a certificate that has invalid explicit curve parameters. Since certificate parsing happens prior to verification of the certificate signature, any process that parses an externally supplied certificate may thus be subject to a denial of service attack. The infinite loop can also be reached when parsing crafted private keys as they can contain explicit elliptic curve parameters. Thus vulnerable situations include: - TLS clients consuming server certificates - TLS servers consuming client certificates - Hosting providers taking certificates or private keys from customers - Certificate authorities parsing certification requests from subscribers - Anything else which parses ASN.1 elliptic curve parameters Also any other applications that use the BN_mod_sqrt() where the attacker can control the parameter values are vulnerable to this DoS issue. In the OpenSSL 1.0.2 version the public key is not parsed during initial parsing of the certificate which makes it slightly harder to trigger the infinite loop. However any operation which requires the public key from the certificate will trigger the infinite loop. In particular the attacker can use a self-signed certificate to trigger the loop during verification of the certificate signature. This issue affects OpenSSL versions 1.0.2, 1.1.1 and 3.0. It was addressed in the releases of 1.1.1n and 3.0.2 on the 15th March 2022. Fixed in OpenSSL 3.0.2 (Affected 3.0.0,3.0.1). Fixed in OpenSSL 1.1.1n (Affected 1.1.1-1.1.1m). Fixed in OpenSSL 1.0.2zd (Affected 1.0.2-1.0.2zc).
Fixed security vulnerabilities in E6702
CVE-2013-2566
The RC4 algorithm, as used in the TLS protocol and SSL protocol, has many single-byte biases, which makes it easier for remote attackers to conduct plaintext-recovery attacks via statistical analysis of ciphertext in a large number of sessions that use the same plaintext.
CVE-2015-2808.
The RC4 algorithm, as used in the TLS protocol and SSL protocol, does not properly combine state data with key data during the initialization phase, which makes it easier for remote attackers to conduct plaintext-recovery attacks against the initial bytes of a stream by sniffing network traffic that occasionally relies on keys affected by the Invariance Weakness, and then using a brute-force approach involving LSB values, aka the "Bar Mitzvah" issue.
CVE-2015-0204
The ssl3_get_key_exchange function in s3_clnt.c in OpenSSL before 0.9.8zd, 1.0.0 before 1.0.0p, and 1.0.1 before 1.0.1k allows remote SSL servers to conduct RSA-to-EXPORT_RSA downgrade attacks and facilitate brute-force decryption by offering a weak ephemeral RSA key in a noncompliant role, related to the "FREAK" issue. NOTE: the scope of this CVE is only client code based on OpenSSL, not EXPORT_RSA issues associated with servers or other TLS implementations
CVE-2020-10188
utility.c in telnetd in netkit telnet through 0.17 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via short writes or urgent data, because of a buffer overflow involving the netclear and nextitem functions.
The following information describes how to upgrade software while the router is operating normally or when the router cannot correctly start up.
Software required for starting up the switch includes:
Boot ROM image—A .bin file that comprises a basic section and an extended section. The basic section is the minimum code that bootstraps the system. The extended section enables hardware initialization and provides system management menus. You can use these menus to load software and the startup configuration file or manage files when the switch cannot correctly start up.
Software images—Includes boot images and system images.
Boot image—A .bin file that contains the operating system kernel. It provides process management, memory management, file system management, and the emergency shell.
System image—A .bin file that contains the main application code required for device operation. This includes device management, interface management, configuration management, and routing management.
The software images that have been loaded are called "current software images." The software images specified to load at next startup are called "startup software images."
These images might be released separately or as a whole in one .ipe package file. If an .ipe file is used, the system automatically decompresses the file, loads the .bin boot and system images in the file and sets them as startup software images. Typically, the Boot ROM and software images for this switch series are released in an .ipe file named main.ipe.
In addition to these images, H3C irregularly releases patch packages for you to fix bugs without rebooting the switch. A patch package does not add new features or functions.
Upon power-on, the Boot ROM image runs to initialize hardware and then the software images run to start up the entire system, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 System startup process
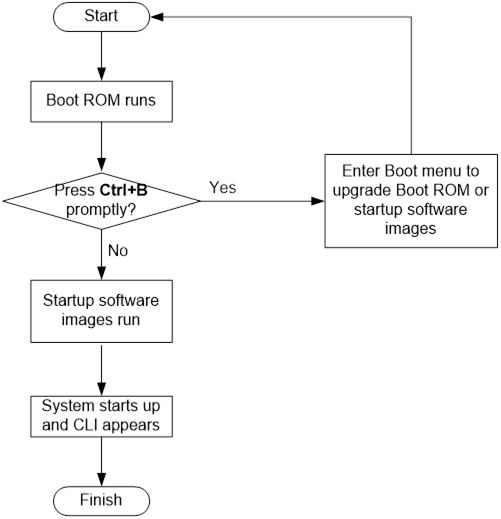
You can upgrade system software by using one of the following methods:
Upgrading method | Software types | Remarks |
Upgrading from the CLI | Software images | You must reboot the switch to complete the upgrade. This method can interrupt ongoing network services. |
Patch packages | The upgrade does not interrupt ongoing services. Make sure the patch packages match the current software images. A patch package can fix bugs only for its matching software image version. | |
Upgrading from the Boot menu | Boot ROM image Software images | Use this method when the switch cannot correctly start up.
Upgrading an IRF fabric from the CLI rather than the Boot menu. The Boot menu approach requires that you upgrade the member switches one by one and has larger impact on services than the CLI approach. |
The output in this document is for illustration only and might vary with software releases. For example, this document uses boot.bin and system.bin to represent boot and system image names, whereas the actual software image name format is chassis_software platform version_image type_release, for example, s6825-cmw710-boot-r6715p01.bin and s6825-cmw710-system-r6715p01.bin.
This section uses a two-member IRF fabric as an example to describe how to upgrade software from the CLI. If you have more than two subordinate switches, repeat the steps for the subordinate switch to upgrade their software. If you are upgrading a standalone switch, ignore the steps for upgrading the subordinate switch.
| IMPORTANT: Before you perform an IRF master/subordinate switchover, verify that the device is in stable state. |
1. Verify that the system state, redundancy state, and state of each slot are stable.
<Sysname> display system stable state
System state :Stable
Redundancy state :Stable
Slot CPU Role State
1 0 Active Stable
2 0 Standby Stable
2. If the device is unstable, use the following commands to troubleshoot the issue:
¡ Use the display device command to verify that the device is operating correctly.
¡ Use the display ha service-group command to verify that bulk backup has been finished for all modules.
¡ Use the display system internal process state command in probe view to verify that services are running correctly.
3. If a slot persists in unstable state or there are other unrecoverable issues, contact the technical support.
Preparing for the upgrade
Before you upgrade software, complete the following tasks:
1. Log in to the IRF fabric through Telnet or the console port (details not shown).
2. Perform the display irf command in any view to identify the number of IRF members, each member switch’s role and IRF member ID.
<Sysname> display irf
MemberID Role Priority CPU-Mac Description
*+1 Master 5 0023-8927-afdc ---
2 Standby 1 0023-8927-af43 ---
--------------------------------------------------
* indicates the device is the master.
+ indicates the device through which the user logs in.
The Bridge MAC of the IRF is: 0023-8927-afdb
Auto upgrade : no
Mac persistent : 12 min
Domain ID : 0
3. Perform the dir command in user view to identify the free storage space of each member switch.
4. Identify the free Flash space of the master switch.
<Sysname> dir
Directory of flash:
0 -rw- 41424 Aug 23 2013 00:33:57 startup.mdb
1 -rw- 3792 Aug 23 2013 00:33:56 startup.cfg
2 -rw- 53555200 Aug 23 2013 16:04:08 system.bin
3 drw- - Aug 23 2013 00:03:07 seclog
4 drw- - Aug 23 2013 00:03:07 diagfile
5 drw- - Aug 23 2013 00:03:07 logfile
6 -rw- 9959424 Aug 23 2013 16:04:08 boot.bin
7 -rw- 9012224 Aug 21 2013 09:54:27 backup.bin
1048576 KB total (977704 KB free)
5. Identify the free Flash space of each subordinate switch, for example, switch 2.
<Sysname> dir slot2#flash:/
Directory of slot2#flash:/
0 -rw- 41424 Aug 23 2013 00:33:57 startup.mdb
1 -rw- 3792 Aug 23 2013 00:33:56 startup.cfg
2 -rw- 93871104 Aug 23 2013 16:00:08 system.bin
3 drw- - Aug 23 2013 00:03:07 seclog
4 drw- - Aug 23 2013 00:03:07 diagfile
5 drw- - Aug 23 2013 00:03:07 logfile
6 -rw- 13611008 Aug 23 2013 15:59:00 boot.bin
7 -rw- 9012224 Aug 21 2013 09:54:27 backup.bin
1048576 KB total (934767 KB free)
6. Compare the free Flash space of each member switch with the size of the software file to load. If the space is sufficient, start the upgrade process. If not, go to the next step.
7. Delete obsolete files in Flash to free space:
| CAUTION: · To avoid data loss, do not delete the current configuration file. For information about the current configuration file, perform the display startup command. Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends that you preferentially delete obsolete software images. To avoid inadvertent delete of the current software images, perform the display boot-loader command in any view to identify them. · The delete /unreserved file command deletes a file permanently and the action cannot be undone. · The delete file command moves a file to the recycle bin and the file still occupies storage space. To permanently delete the file from the recycle bin, first perform the undelete command to restore the file and then perform the delete /unreserved file command. |
8. Delete obsolete files from the Flash memory of the master switch.
<Sysname> delete /unreserved flash:/backup.bin
The file cannot be restored. Delete flash:/backup.bin?[Y/N]:y
Deleting the file permanently will take a long time. Please wait...
Deleting file flash:/backup.bin...Done.
9. Delete obsolete files from the Flash memory of the subordinate switch.
<Sysname> delete /unreserved slot2#flash:/backup.bin
The file cannot be restored. Delete slot2#flash:/backup.bin?[Y/N]:y
Deleting the file permanently will take a long time. Please wait...
Deleting file slot2#flash:/backup.bin...Done.
Downloading software to the master switch
Before you start upgrading software images or patch packages, make sure you have downloaded the upgrading software files to the root directory in Flash memory. This section describes downloading an .ipe software file as an example.
The following are ways to download, upload, or copy files to the master switch:
FTP download from a server
FTP upload from a client
TFTP download from a server
Copying files from a USB flash drive
Prerequisites
If FTP or TFTP is used, the IRF fabric and the PC working as the FTP/TFTP server or FTP client can reach each other.
Prepare the FTP server or TFTP server program yourself for the PC. The switch series does not come with these software programs.
FTP download from a server
You can use the switch as an FTP client to download files from an FTP server.
To download a file from an FTP server, for example, the server at 10.10.110.1:
1. Run an FTP server program on the server, configure an FTP username and password, specify the working directory and copy the file, for example, newest.ipe, to the directory.
2. Perform the ftp command in user view on the IRF fabric to access the FTP server.
<Sysname> ftp 10.10.110.1
Trying 10.10.110.1...
Press CTRL+K to abort
Connected to 10.10.110.1
220 FTP service ready.
User(10.10.110.1:(none)):username
331 Password required for username.
Password:
230 User logged in
3. Enable the binary transfer mode.
ftp> binary
200 Type set to I.
4. Perform the get command in FTP client view to download the file from the FTP server.
ftp> get newest.ipe
227 Entering Passive Mode (10,10,110,1,17,97).
125 BINARY mode data connection already open, transfer starting for /newest.ipe
226 Transfer complete.
63521792 bytes received in 35 seconds (896. 0 kbyte/s)
ftp> bye
221 Server closing.
FTP upload from a client
You can use the IRF fabric as an FTP server and upload files from a client to the IRF fabric.
To FTP upload a file from a client:
1. On the IRF fabric:
2. Enable FTP server.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ftp server enable
3. Add a local FTP user account, set its password and access service type, and assign it to the user role network-admin for uploading file to the working directory of the server.
[Sysname] local-user abc
[Sysname-luser-manage-abc] password simple pwd
[Sysname-luser-manage-abc] service-type ftp
[Sysname-luser-manage-abc] authorization-attribute user-role network-admin
[Sysname-luser-manage-abc] quit
[Sysname] quit
4. On the PC:
5. FTP to the IRF fabric (the FTP server).
c:\> ftp 1.1.1.1
Connected to 1.1.1.1.
220 FTP service ready.
User(1.1.1.1:(none)):abc
331 Password required for abc.
Password:
230 User logged in.
6. Enable the binary file transfer mode.
ftp> binary
200 TYPE is now 8-bit binary.
7. Upload the file (for example, newest.ipe) to the root directory in the Flash memory of the master switch.
ftp> put newest.ipe
200 PORT command successful
150 Connecting to port 10002
226 File successfully transferred
ftp: 63521792 bytes sent in 64.58 secs (497.60 Kbytes/sec).
TFTP download from a server
To download a file from a TFTP server, for example, the server at 10.10.110.1:
1. Run a TFTP server program on the server, specify the working directory, and copy the file, for example, newest.ipe, to the directory.
2. On the IRF fabric, perform the tftp command in user view to download the file to the root directory in the Flash memory of the master switch.
<Sysname> tftp 10.10.110.1 get newest.ipe
Press CTRL+C to abort.
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 60.5M 0 60.5M 0 0 143k 0 --:--:-- 0:03:38 --:--:-- 142k
Copying files from a USB flash drive
Every switch provides a USB port for you to copy files from a USB flash drive.
To copy a file from a USB flash drive to the Flash memory of the master switch:
1. Plug the USB flash drive in the USB port of the switch.
2. Copy the file (for example, newest.ipe) to the Flash memory of the switch.
<Sysname> cd usba:
<Sysname> copy usba:/newest.ipe newest.ipe
Copy usba:/newest.ipe to flash:/newest.ipe?[Y/N]:y
Start to copy usba:/newest.ipe to flash:/newest.ipe... Done.
Upgrading the software images
To upgrade the software images:
1. Specify the upgrading image file (newest.ipe in this example) used at the next startup for the master switch, and assign the M attribute to the boot and system images in the file.
<Sysname> boot-loader file flash:/newest.ipe slot 1 main
Verifying the file flash:/newest.ipe on slot 1....Done..
Images in IPE:
boot.bin
system.bin
Decompressing file boot.bin to flash:/boot.bin................Done.
Decompressing file system.bin to flash:/system.bin.............................Done.
Decompression completed.
You are recommended to delete the .ipe file after you set startup software images for all slots.
Do you want to delete flash:/newest.ipe now? [Y/N]:n
Verifying the file flash:/boot.bin on slot 1...Done.
Verifying the file flash:/system.bin on slot 1...Done.
The images that have passed all examinations will be used as the backup startup software images at the next reboot on slot 1
2. Specify the upgrading image file used at next startup for the subordinate switch, and assign the M attribute to the boot and system images in the file. (As a result, the subordinate switch automatically copies the file to the root directory in its Flash memory.)
<Sysname> boot-loader file flash:/newest.ipe slot 2 main
Verifying the file flash:/newest.ipe on slot 2....Done..
Images in IPE:
boot.bin
system.bin
Decompressing file boot.bin to flash:/boot.bin................Done.
Decompressing file system.bin to flash:/system.bin.............................Done.
Decompression completed.
You are recommended to delete the .ipe file after you set startup software images for all slots.
Do you want to delete flash:/newest.ipe now? [Y/N]:n
Verifying the file flash:/boot.bin on slot 2...Done.
Verifying the file flash:/system.bin on slot 2...Done.
The images that have passed all examinations will be used as the backup startup software images at the next reboot on slot 2
3. (Optional) If the IRF fabric size has a lot of members, enable the software auto-update function.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] irf auto-update enable
[Sysname] quit
Software auto-update is typically used for synchronizing the software images of the master switch to new member switches when you expand the IRF fabric. This function enables a subordinate switch to compare its main startup software image version with that of the IRF master. If the versions are different, the subordinate switch automatically downloads the current software images from the master, sets the downloaded images as the main software images at the next reboot, and automatically reboots with the new images to re-join the IRF fabric. In this upgrade process, the function avoids the failure of assign all the subordinate switch the same main software image file as the master switch causing an upgrade failure.
4. Save the current configuration in any view to prevent data loss.
<Sysname> save
The current configuration will be written to the device. Are you sure? [Y/N]:y
Please input the file name(*.cfg)[flash:/startup.cfg]
(To leave the existing filename unchanged, press the enter key):
flash:/startup.cfg exists, overwrite? [Y/N]:y
Validating file. Please wait.................
Saved the current configuration to mainboard device successfully.
Slot 2:
Save next configuration file successfully.
5. Reboot the IRF fabric to complete the upgrade.
<Sysname> reboot
Start to check configuration with next startup configuration file, please wait.
........DONE!
This command will reboot the device. Continue? [Y/N]:y
Now rebooting, please wait...
The system automatically loads the .bin boot and system images in the .ipe file and sets them as the startup software images.
6. Perform the display version command in any view to verify that the current main software images have been updated (details not shown).
| NOTE: The system automatically checks the compatibility of the Boot ROM image and the boot and system images during the reboot. If you are prompted that the Boot ROM image in the upgrading image file is different than the current Boot ROM image, upgrade both the basic and extended sections of the Boot ROM image for compatibility. If you choose to not upgrade the Boot ROM image, the system will ask for an upgrade at the next reboot performed by powering on the switch or rebooting from the CLI (promptly or as scheduled). If you fail to make any choice in the required time, the system upgrades the entire Boot ROM image. |
Installing a patch package
To install a patch package, for example, system-patch.bin:
1. Activate the patch package on the master switch and the subordinate switch.
<Sysname> install activate patch flash:/system-patch.bin slot 1
<Sysname> install activate patch flash:/system-patch.bin slot 2
2. Verify that the patch package has been activated.
<Sysname> display install active
Active packages on slot 1:
flash:/boot.bin
flash:/system.bin
flash:/system-patch.bin
Active packages on slot 2:
flash:/boot.bin
flash:/system.bin
flash:/system-patch.bin
3. Commit the installation so the patch package continues to take effect after a reboot.
<Sysname> install commit
4. Verify that the patch package installation has been committed.
<Sysname> display install committed
Committed packages on slot 1:
flash:/boot.bin
flash:/system.bin
flash:/system-patch.bin
Committed packages on slot 2:
flash:/boot.bin
flash:/system.bin
flash:/system-patch.bin
For more information about installing patch packages, see HP FlexFabric 5945 Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Upgrading from the Boot menu
You can upgrade the Boot ROM image and software images but not patch packages from the Boot menu.
In this approach, you must access the Boot menu of each member switch to upgrade their software one by one. If you are upgrading software images for an IRF fabric, using the CLI is a better choice.
The following sections describe the methods of upgrading software images:
Using TFTP to upgrade software images through the management Ethernet port
Using FTP to upgrade software through the management Ethernet port
Using XMODEM to upgrade software through the console port
The following sections describe the methods of upgrading Boot ROM images:
Using TFTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the management Ethernet port
Using FTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the management Ethernet port
Using XMODEM to upgrade Boot ROM through the console port
| TIP: Upgrading through an Ethernet port is faster than through the console port. |
Prerequisites
Make sure that the prerequisites are met before you start upgrading software from the Boot menu.
Upgrading environment
Use a console cable to connect the console terminal, for example, a PC, to the console port on the switch. Run a terminal emulator program on the console terminal and set the following terminal settings:
Bits per second—9,600
Data bits—8
Parity—None
Stop bits—1
Flow control—None
Emulation—VT100
TFTP/FTP download
To use TFTP or FTP:
Run a TFTP or FTP server program on the file server or the console terminal.
Copy the upgrade file to the file server.
Correctly set the working directory on the TFTP or FTP server.
Make sure that the file server and the switch can reach each other.
Storage space
Make sure that sufficient space is available for the upgrading software file. If no sufficient space is available, delete obsolete files as described in "Managing files from the Boot menu."
Upgrading time
Make sure that the upgrade has minimal impact on the network services. During the upgrade, the switch cannot provide any services.
Using TFTP to upgrade software images through the management Ethernet port
1. Enter 1 in the Boot menu to access the file transfer protocol submenu.
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 1 to set the TFTP parameters.
Load File Name :update.ipe
Server IP Address :192.168.0.3
Local IP Address :192.168.0.2
Subnet Mask :255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Address :0.0.0.0
Table 7 TFTP parameter description
Item | Description |
Load File Name | Name of the file to download (for example, update.ipe). |
Server IP Address | IP address of the TFTP server (for example, 192.168.0.3). |
Local IP Address | IP address of the switch (for example, 192.168.0.2). |
Subnet Mask | Subnet mask of the switch (for example, 255.255.255.0). |
Gateway IP Address | IP address of the gateway (in this example, no gateway is required because the server and the switch are on the same subnet). |
| NOTE: To use the default setting for a field, press Enter without entering any value. If the switch and the server are on different subnets, you must specify a gateway address for the switch. |
3. Enter all required parameters, and enter Y to confirm the settings. The following prompt appears:
Are you sure to download file to flash? Yes or No (Y/N):Y
4. Enter Y to start downloading the image file. To return to the Boot menu, enter N.
Loading.........................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................Done!
5. Enter the M (main), B (backup), or N (none) attribute for the images. In this example, assign the main attribute to the images.
Please input the file attribute (Main/Backup/None) M
Image file boot.bin is self-decompressing...
Free space: 534980608 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
................................................................................
...................................................................Done!
Image file system.bin is self-decompressing...
Free space: 525981696 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
.......................................................................Done!
| NOTE: The switch always attempts to boot first with the main images, and if the attempt fails, for example, because the main images are not available, the switch tries to boot with the backup images. An image with the none attribute is just stored in Flash memory for backup and you must change its attribute to make it usable at reboot. If an image with the same attribute as the image you are loading is already in Flash memory, the attribute of the old image changes to none after the new image becomes valid. |
6. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new software images.
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
9. Set default boot storage medium
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-9):0
Using FTP to upgrade software through the management Ethernet port
1. Enter 1 in the Boot menu to access the file transfer protocol submenu.
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 2 to set the FTP parameters.
Load File Name :update.ipe
Server IP Address :192.168.0.3
Local IP Address :192.168.0.2
Subnet Mask :255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Address :0.0.0.0
FTP User Name :switch
FTP User Password :***
Table 8 FTP parameter description
Item | Description |
Load File Name | Name of the file to download (for example, update.ipe). |
Server IP Address | IP address of the FTP server (for example, 192.168.0.3). |
Local IP Address | IP address of the switch (for example, 192.168.0.2). |
Subnet Mask | Subnet mask of the switch (for example, 255.255.255.0). |
Gateway IP Address | IP address of the gateway (in this example, no gateway is required because the server and the switch are on the same subnet). |
FTP User Name | Username for accessing the FTP server, which must be the same as configured on the FTP server. |
FTP User Password | Password for accessing the FTP server, which must be the same as configured on the FTP server. |
| NOTE: To use the default setting for a field, press Enter without entering any value. If the switch and the server are on different subnets, you must specify a gateway address for the switch. |
3. Enter all required parameters, and enter Y to confirm the settings. The following prompt appears:
Are you sure to download file to flash? Yes or No (Y/N):Y
4. Enter Y to start downloading the image file. To return to the Boot menu, enter N.
Loading.........................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................Done!
5. Enter the M (main), B (backup), or N (none) attribute for the images. In this example, assign the main attribute to the images.
Please input the file attribute (Main/Backup/None) M
Image file boot.bin is self-decompressing...
Free space: 534980608 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
................................................................................
...................................................................Done!
Image file system.bin is self-decompressing...
Free space: 525981696 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
................................................................................
.......................................................................Done!
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
9. Set default boot storage medium
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-9):0
| NOTE: The switch always attempts to boot first with the main images, and if the attempt fails, for example, because the main images not available, the switch tries to boot with the backup images. An image with the none attribute is just stored in Flash memory for backup and you must change its attribute to make it usable at reboot. If an image with the same attribute as the image you are loading is already in Flash memory, the attribute of the old image changes to none after the new image becomes valid. |
6. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new software images.
Using XMODEM to upgrade software through the console port
XMODEM download through the console port is slower than TFTP or FTP download through the management Ethernet port. To save time, use the management Ethernet port as long as possible.
1. Enter 1 in the Boot menu to access the file transfer protocol submenu.
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 3 to set the XMODEM download baud rate.
Please select your download baudrate:
1.* 9600
2. 19200
3. 38400
4. 57600
5. 115200
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-5):5
3. Select an appropriate download rate, for example, enter 5 to select 115200 bps.
Download baudrate is 115200 bps
Please change the terminal's baudrate to 115200 bps and select XMODEM protocol
Press enter key when ready
5. Select Call > Disconnect in the HyperTerminal window to disconnect the terminal from the switch.
Figure 2 Disconnecting the terminal from the switch
6. Select File > Properties, and in the Properties dialog box, click Configure.
Figure 3 Properties dialog box
7. Select 115200 from the Bits per second list and click OK.
Figure 4 Modifying the baud rate
8. Select Call > Call to reestablish the connection.
Figure 5 Reestablishing the connection
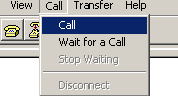
9. Press Enter. The following prompt appears:
Are you sure to download file to flash? Yes or No (Y/N):Y
10. Enter Y to start downloading the file. (To return to the Boot menu, enter N.)
Now please start transfer file with XMODEM protocol
If you want to exit, Press <Ctrl+X>
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
11. Select Transfer > Send File in the HyperTerminal window.
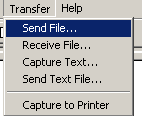
12. In the dialog box that appears, click Browse to select the source file, and select Xmodem from the Protocol list.
Figure 7 File transmission dialog box
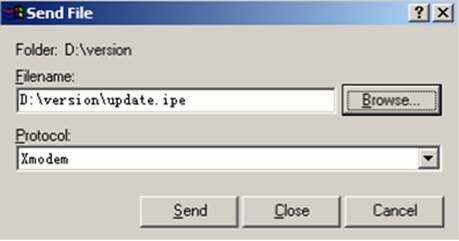
13. Click Send. The following dialog box appears:
Figure 8 File transfer progress
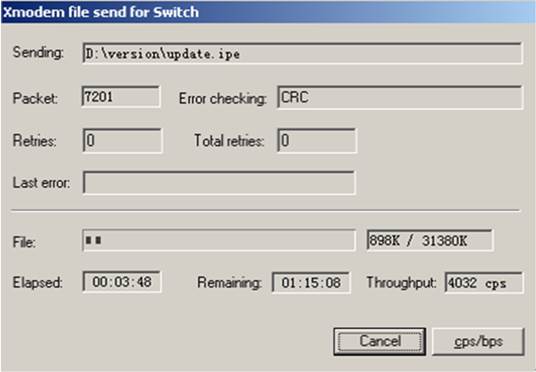
14. Enter the M (main), B (backup), or N (none) attribute for the images. In this example, assign the main attribute to the images.
Please input the file attribute (Main/Backup/None) m
The boot.bin image is self-decompressing...
At the Load File name prompt, enter a name for the Boot image to be saved to Flash memory.
Load File name : default_file boot-update.bin
Free space: 470519808 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
.............Done!
The system-update.bin image is self-decompressing...
At the Load File name prompt, enter a name for the system image to be saved to Flash memory.
Load File name : default_file system-update.bin
Free space: 461522944 bytes
Writing flash...................................................................
.............Done!
Your baudrate should be set to 9600 bps again!
Press enter key when ready
| NOTE: The switch always attempts to boot first with the main images, and if the attempt fails, for example, because the main images not available, the switch tries to boot with the backup images. An image with the none attribute is just stored in Flash memory for backup and you must change its attribute to make it usable at reboot. If an image with the same attribute as the image you are loading is already in Flash memory, the attribute of the old image changes to none after the new image becomes valid. |
15. If the baud rate of the HyperTerminal is not 9600 bps, restore it to 9600 bps. If the baud rate is 9600 bps, skip this step.
To access the switch through the console port after a reboot, you must perform this step, because the console port rate reverts to 9600 bps at a reboot.
16. Press Enter to access the Boot menu.
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
9. Set default boot storage medium
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-9):0
17. Enter 0 to reboot the system with the new software images.
Using TFTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the management Ethernet port
1. Enter 6 in the Boot menu to access the Boot ROM update menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 1 in the Boot ROM update menu to upgrade the full Boot ROM.
The file transfer protocol submenu appears:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
3. Enter 1 to set the TFTP parameters.
Load File Name :update.btm
Server IP Address :192.168.0.3
Local IP Address :192.168.0.2
Subnet Mask :255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Address :0.0.0.0
Table 9 TFTP parameter description
Item | Description |
Load File Name | Name of the file to download (for example, update.btm). |
Server IP Address | IP address of the TFTP server (for example, 192.168.0.3). |
Local IP Address | IP address of the switch (for example, 192.168.0.2). |
Subnet Mask | Subnet mask of the switch (for example, 255.255.255.0). |
Gateway IP Address | IP address of the gateway (in this example, no gateway is required because the server and the switch are on the same subnet). |
| NOTE: To use the default setting for a field, press Enter without entering any value. If the switch and the server are on different subnets, you must specify a gateway address for the switch. |
4. Enter all required parameters and press Enter to start downloading the file.
Loading.................................................Done!
5. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the basic Boot ROM section.
Will you Update Basic BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating Basic BootRom...........Done.
6. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the extended Boot ROM section.
Updating extended BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating extended BootRom.........Done.
7. Enter 0 in the Boot ROM update menu to return to the Boot menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
8. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new Boot ROM image.
Using FTP to upgrade Boot ROM through the management Ethernet port
1. Enter 6 in the Boot menu to access the Boot ROM update menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 1 in the Boot ROM update menu to upgrade the full Boot ROM.
The file transfer protocol submenu appears:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
3. Enter 2 to set the FTP parameters.
Load File Name :update.btm
Server IP Address :192.168.0.3
Local IP Address :192.168.0.2
Subnet Mask :255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Address :0.0.0.0
FTP User Name :switch
FTP User Password :***
Table 10 FTP parameter description
Item | Description |
Load File Name | Name of the file to download (for example, update.btm). |
Server IP Address | IP address of the FTP server (for example, 192.168.0.3). |
Local IP Address | IP address of the switch (for example, 192.168.0.2). |
Subnet Mask | Subnet mask of the switch (for example, 255.255.255.0). |
Gateway IP Address | IP address of the gateway (in this example, no gateway is required because the server and the switch are on the same subnet). |
FTP User Name | Username for accessing the FTP server, which must be the same as configured on the FTP server. |
FTP User Password | Password for accessing the FTP server, which must be the same as configured on the FTP server. |
| NOTE: To use the default setting for a field, press Enter without entering any value. If the switch and the server are on different subnets, you must specify a gateway address for the switch. |
4. Enter all required parameters and press Enter to start downloading the file.
Loading.................................................Done!
5. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the basic Boot ROM section.
Will you Update Basic BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating Basic BootRom...........Done.
6. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the extended Boot ROM section.
Updating extended BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating extended BootRom.........Done.
7. Enter 0 in the Boot ROM update menu to return to the Boot menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
8. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new Boot ROM image.
Using XMODEM to upgrade Boot ROM through the console port
XMODEM download through the console port is slower than TFTP or FTP download through the management Ethernet port. To save time, use the management Ethernet port as long as possible.
1. Enter 6 in the Boot menu to access the Boot ROM update menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
2. Enter 1 in the Boot ROM update menu to upgrade the full Boot ROM.
The file transfer protocol submenu appears:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameters
2. Set FTP protocol parameters
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameters
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
3. Enter 3 to set the XMODEM download baud rate.
Please select your download baudrate:
1.* 9600
2. 19200
3. 38400
4. 57600
5. 115200
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-5):5
4. Select an appropriate download rate, for example, enter 5 to select 115200 bps.
Download baudrate is 115200 bps
Please change the terminal's baudrate to 115200 bps and select XMODEM protocol
Press enter key when ready
5. Set the serial port on the terminal to use the same baud rate and protocol as the console port. If you select 9600 bps as the download rate for the console port, skip this task.
6. Select Call > Disconnect in the HyperTerminal window to disconnect the terminal from the switch.
Figure 9 Disconnecting the terminal from the switch

7. Select File > Properties, and in the Properties dialog box, click Configure.
Figure 10 Properties dialog box
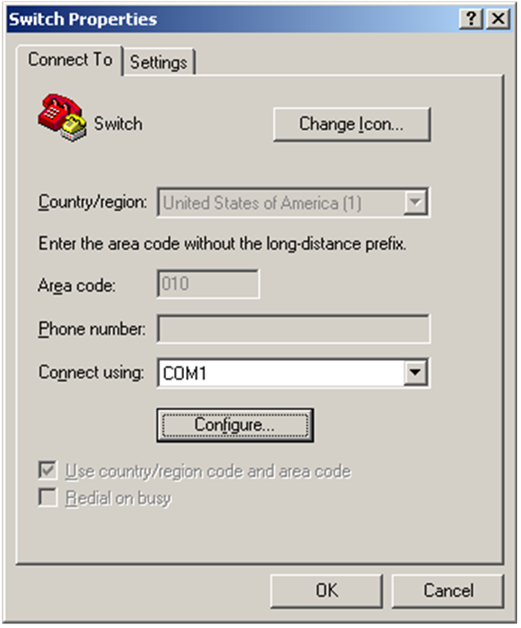
8. Select 115200 from the Bits per second list and click OK.
Figure 11 Modifying the baud rate

9. Select Call > Call to reestablish the connection.
Figure 12 Reestablishing the connection

10. Press Enter to start downloading the file.
Now please start transfer file with XMODEM protocol
If you want to exit, Press <Ctrl+X>
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
11. Select Transfer > Send File in the HyperTerminal window.
Figure 13 Transfer menu

12. In the dialog box that appears, click Browse to select the source file, and select Xmodem from the Protocol list.
Figure 14 File transmission dialog box
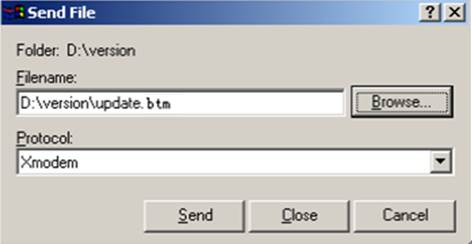
13. Click Send. The following dialog box appears:
Figure 15 File transfer progress
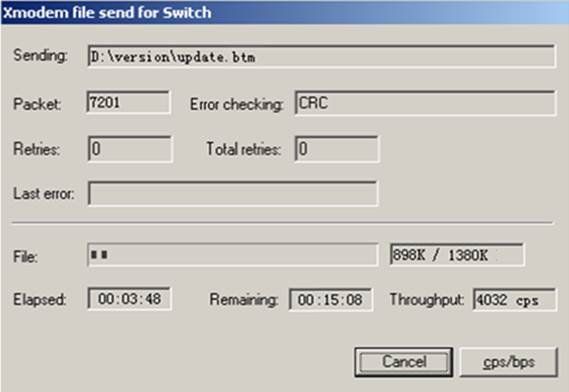
14. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the basic Boot ROM section.
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCCCCCC ...Done!
Will you Update Basic BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating Basic BootRom...........Done.
15. Enter Y at the prompt to upgrade the extended Boot ROM section.
Updating extended BootRom? (Y/N):Y
Updating extended BootRom.........Done.
16. If the baud rate of the HyperTerminal is not 9600 bps, restore it to 9600 bps at the prompt. If the baud rate is 9600 bps, skip this step.
Please change the terminal's baudrate to 9600 bps, press ENTER when ready.
To access the switch through the console port after a reboot, you must perform this step, because the console port rate reverts to 9600 bps at a reboot.
17. Press Enter to access the Boot ROM update menu.
18. Enter 0 in the Boot ROM update menu to return to the Boot menu.
1. Update full BootRom
2. Update extended BootRom
3. Update basic BootRom
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
19. Enter 0 in the Boot menu to reboot the switch with the new Boot ROM image.
Managing files from the Boot menu
From the Boot menu, you can display files in Flash memory to check for obsolete files, incorrect files, or space insufficiency, delete files to release storage space, or change the attributes of software images.
Displaying all files
Enter 3 in the Boot menu to display all files in Flash memory and identify the free space size.
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
9. Set default boot storage medium
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-9): 3
The following is a sample output:
Display all file(s) in flash:
File Number File Size(bytes) File Name
================================================================================
1 8177 flash:/testbackup.cfg
2(*) 53555200 flash:/system.bin
3(*) 9959424 flash:/boot.bin
4 3678 flash:/startup.cfg_backup
5 30033 flash:/default.mdb
6 42424 flash:/startup.mdb
7 18 flash:/.pathfile
8 232311 flash:/logfile/logfile.log
9 5981 flash:/startup.cfg_back
10(*) 6098 flash:/startup.cfg
11 20 flash:/.snmpboots
Free space: 1009906637 bytes
The current image is boot.bin
(*)-with main attribute
(b)-with backup attribute
(*b)-with both main and backup attribute
Deleting files
If storage space is insufficient, delete obsolete files to free up storage space.
To delete files:
1. Enter 4 in the Boot menu:
Deleting the file in flash:
File Number File Size(bytes) File Name
================================================================================
1 8177 flash:/testbackup.cfg
2(*) 53555200 flash:/system.bin
3(*) 9959424 flash:/boot.bin
4 3678 flash:/startup.cfg_backup
5 30033 flash:/default.mdb
6 42424 flash:/startup.mdb
7 18 flash:/.pathfile
8 232311 flash:/logfile/logfile.log
9 5981 flash:/startup.cfg_back
10(*) 6098 flash:/startup.cfg
11 20 flash:/.snmpboots
Free space: 1009906637 bytes
The current image is boot.bin
(*)-with main attribute
(b)-with backup attribute
(*b)-with both main and backup attribute
2. Enter the number of the file to delete. For example, enter 1 to select the file testbackup.cfg.
Please input the file number to change: 1
3. Enter Y at the confirmation prompt.
The file you selected is testbackup.cfg,Delete it? (Y/N):Y
Deleting....................................Done!
Changing the attribute of software images
Software image attributes include main (M), backup (B), and none (N). System software and boot software can each have multiple none-attribute images but only one main image and one backup image on the switch. You can assign both the M and B attributes to one image. If the M or B attribute you are assigning has been assigned to another image, the assignment removes the attribute from that image. If the removed attribute is the sole attribute of the image, its attribute changes to N.
For example, the system image system.bin has the M attribute and the system image system-update.bin has the B attribute. After you assign the M attribute to system-update.bin, the attribute of system-update.bin changes to M+B and the attribute of system.bin changes to N.
To change the attribute of a system or boot image:
1. Enter 2 in the Boot menu.
EXTENDED BOOT MENU
1. Download image to flash
2. Select image to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Restore to factory default configuration
6. Enter BootRom upgrade menu
7. Skip current system configuration
8. Set switch startup mode
9. Set default boot storage medium
0. Reboot
Ctrl+Z: Access EXTENDED ASSISTANT MENU
Ctrl+F: Format file system
Ctrl+P: Change authentication for console login
Ctrl+R: Download image to SDRAM and run
Enter your choice(0-9): 2
2. Enter 1 or 2 at the prompt to set the attribute of a software image. (The following output is based on the option 2. To set the attribute of a configuration file, enter 3.)
1. Set image file
2. Set bin file
3. Set configuration file
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3): 2
File Number File Size(bytes) File Name
================================================================================
1(*) 53555200 flash:/system.bin
2(*) 9959424 flash:/boot.bin
3 13105152 flash:/boot-update.bin
4 91273216 flash:/system-update.bin
Free space: 905848832 bytes
(*)-with main attribute
(b)-with backup attribute
(*b)-with both main and backup attribute
Note:Select .bin files. One but only one boot image and system image must be included.
3. Enter the number of the file you are working with. For example, enter 3 to select the boot image boot-update.bin and enter 4 to select the system image system-update.bin.
Enter file No.(Allows multiple selection):3
Enter another file No.(0-Finish choice):4
4. Enter 0 to finish the selection.
Enter another file No.(0-Finish choice):0
You have selected:
flash:/boot-update.bin
flash:/system-update.bin
5. Enter M or B to change its attribute to main or backup. If you change its attribute to M, the attribute of boot.bin changes to none.
Please input the file attribute (Main/Backup) M
This operation may take several minutes. Please wait....
Next time, boot-update.bin will become default boot file!
Next time, system-update.bin will become default boot file!
Set the file attribute success!
Handling software upgrade failures
If a software upgrade fails, the system runs the old software version.
To handle a software upgrade failure:
1. Verify that the software release is compatible with the switch model and the correct file is used.
2. Verify that the software release and the Boot ROM release are compatible. For software and Boot ROM compatibility, see the hardware and software compatibility matrix in the correct release notes.
3. Check the physical ports for a loose or incorrect connection.
4. If you are using the console port for file transfer, check the HyperTerminal settings (including the baud rate and data bits) for any wrong setting.
5. Check the file transfer settings:
If XMODEM is used, you must set the same baud rate for the terminal as for the console port.
If TFTP is used, you must enter the same server IP addresses, file name, and working directory as set on the TFTP server.
If FTP is used, you must enter the same FTP server IP address, source file name, working directory, and FTP username and password as set on the FTP server.
6. Check the FTP or TFTP server for any incorrect setting.
7. Check that the storage device has sufficient space for the upgrade file.
