Telecommuting Lagging Solution
Demand background
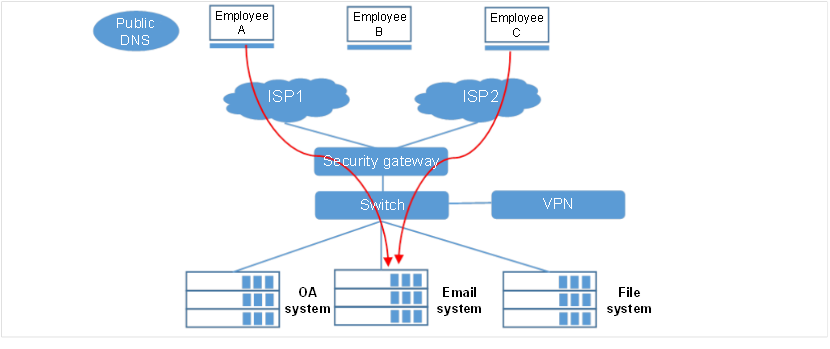
The epidemic in the early 2020 has spurred demands for the telecommuting scenario and made managers know the importance of information construction. The normal operation of a company relies significantly on access to OA, email, files and other systems, and employees mostly access such service systems remotely during the epidemic. However, at the early stage of information system construction, many companies did not expect massive remote access, which caused lagging of telecommuting and affected work efficiency.
Causes of service issues
![]() Random responds of public DNS with clients accessing randomly between two or more links, which resulted in low access rate.
Random responds of public DNS with clients accessing randomly between two or more links, which resulted in low access rate.
![]() The disorderly access of clients tends to cause congestion on a single link, resulting in service jams or interruptions.
The disorderly access of clients tends to cause congestion on a single link, resulting in service jams or interruptions.
![]() Failure in perception after links are faulty causes service interruption.
Failure in perception after links are faulty causes service interruption.
H3C telecommuting lagging solution
Intelligent DNS technology can provide internal server intelligent resolution service for external users, which can solve the problem of link selection for accessing internal servers from extranet. In networks without load balancing devices, external users can only select a single link or randomly select links when accessing internal servers, and the unoptimized random link selection cannot guarantee the access experience for external users.
Through the built-in intelligent DNS module, H3C load balancing devices can cooperate with the customers' resolution server to guide the domain resolution of the internal server. When an external user accesses the internal server through the domain name, the load balancing device will select a better link through the static list or dynamic judgment algorithm, and then resolve the domain name into the IP address of the corresponding link.
Benefits
Without being perceived by the clients, better access links are selected by dynamic detection based on intelligent DNS technology, which effectively solves the problem of service access lagging.
It solves the problem of congestion on a single link due to uneven service access distribution in the case of multiple links.
It proactively senses link health and smoothly switches faulty links to ensure uninterrupted service access.


